A torque analysis method, device, vehicle controller and vehicle
An analytical method and vehicle technology, applied in the field of vehicles, can solve the problem that the torque cannot effectively meet the actual needs of the driver
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
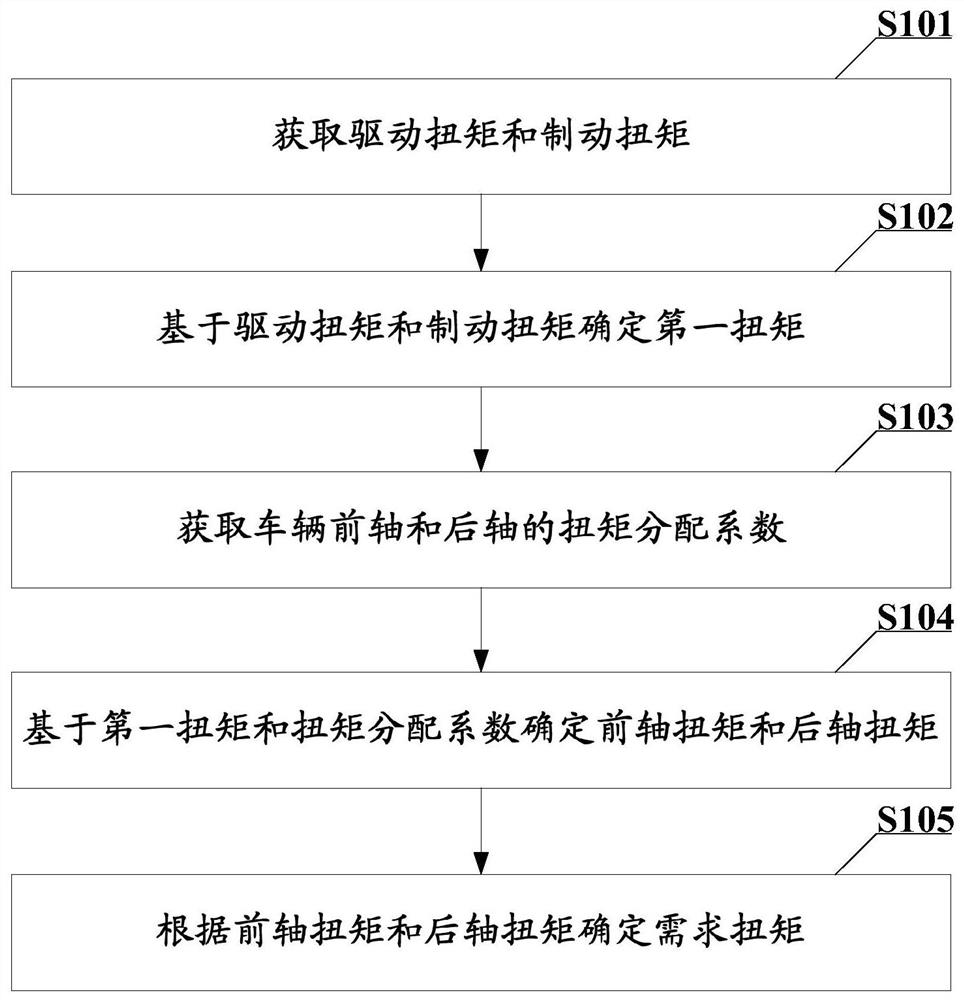
[0046] Please see figure 1 , figure 1 A schematic flow diagram of a torque analysis method provided in the embodiment of the present application, including:
[0047] S101: acquiring driving torque and braking torque;
[0048] It should be noted that, in the embodiment of the present application, the driving torque refers to the required output torque after the driver steps on the accelerator pedal; and the braking torque refers to the required output torque after the driver steps on the brake pedal.
[0049] In the embodiment of the present application, the driving torque can be obtained by looking up a table according to the current vehicle speed and the depth of the accelerator pedal. For example, the corresponding relationship between the vehicle speed, the depth of the accelerator pedal and the driving torque can be recorded in the table, and then the corresponding driving torque can be obtained according to the current vehicle speed and the depth of the accelerator peda...
Embodiment 2
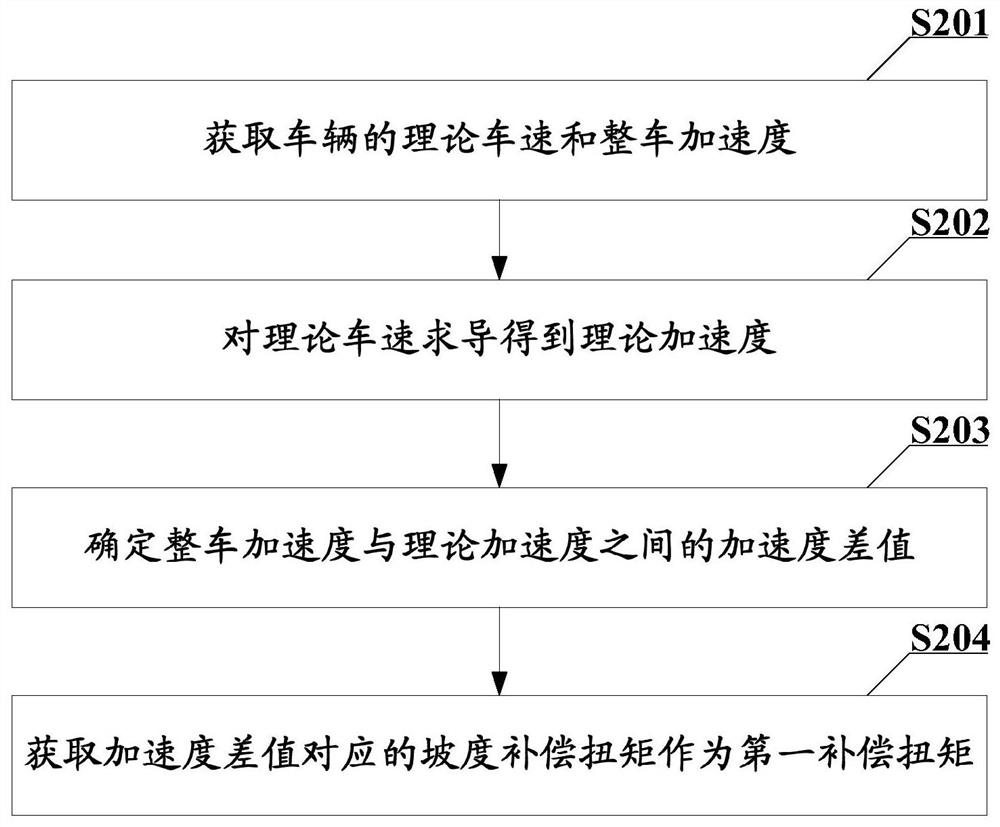
[0099] In this embodiment, on the basis of the first embodiment, two more specific torque analysis processes are taken as examples to further illustrate the present application.
example 1
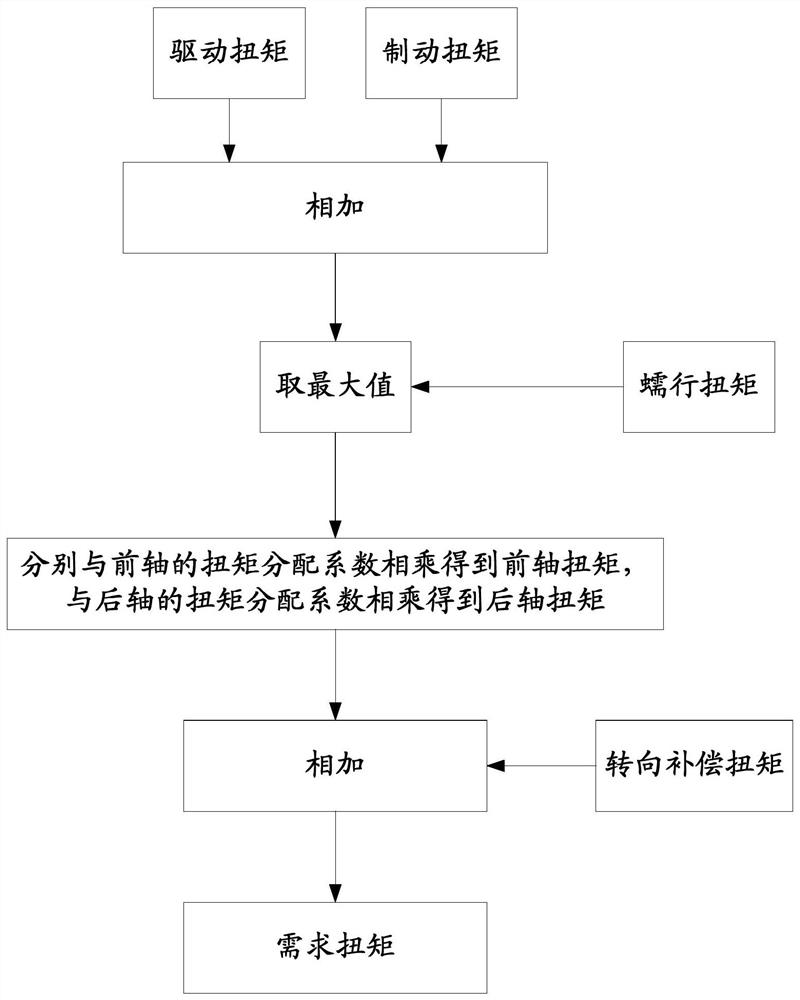
[0101] see image 3 As shown, the VCU will obtain the driving torque, braking torque, creep torque, torque distribution coefficient of the front axle and rear axle, and steering compensation torque. When analyzing, the VCU first adds the driving torque and the braking torque, then compares the summed torque with the creep torque, takes the maximum value and multiplies it with the torque distribution coefficient of the front axle respectively to obtain the front torque. Axle torque, multiplied by the torque distribution coefficient of the rear axle to obtain the rear axle torque; then add the front axle torque and steering compensation torque to obtain the demand torque of the front axle, and add the rear axle torque and steering compensation torque to obtain the demand of the rear axle torque.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com