Method and device for two-way template motion vector fine-tuning for video encoding and decoding
A video encoding and decoding, motion vector technology, applied in the field of fine-tuning the motion of bidirectional prediction blocks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] The main concept of Embodiment 1 is that if the motion vector difference after fine-tuning is less than a threshold, the iteration will be terminated. An example of a specific algorithm can be as Figure 9 As shown, Target_context_value=L0_MV_difference+L1_MV_difference. For example, L0_MV_difference may be the difference between the original L0 MV and the fine-tuned MV. Likewise, the L1MV difference can be calculated. According to the following equation, L0_MV_difference and L1_MV_difference can be calculated:
[0082] L0_MV_difference = abs("original L0 MV x part" - "fine tuned L0 MV x part") + abs("original L0 MV y part" - "fine tuned L0 MV y part")
[0083] L1_MV_difference = abs("original L1 MV x part" - "fine tuned L1 MV x part") + abs("original L1 MV y part" - "fine tuned L1 MV y part")
[0084] In the above equation, abs() is the absolute value. The "x part" is the horizontal part of the MV. "y-section" is the vertical section of the MV.
Embodiment 2
[0086] The main concept of embodiment 2 is that if the pixel difference between the current reference block and the fine-tuning reference block is smaller than some threshold, the iteration will be ended. The specific algorithm can be as Figure 9 As shown, Target_context_value=L0_block_difference+L1_block_difference. For example, L0_block_difference can be calculated as the difference between the original L0 reference block and the L0 fine-tuning block. Similarly, L1_block_difference can be calculated. According to the following procedure, L0_block_difference and L1_block_difference can be calculated:
[0087] L0_block_difference = SAD between L0 reference block and L0 trimming block
[0088] L1_block_difference = SAD between L1 reference block and L1 fine-tuning block
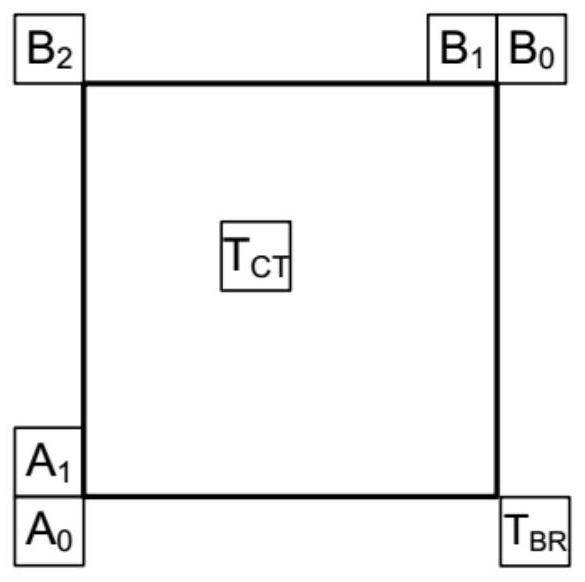
[0089] In the above equation, SAD corresponds to the sum of absolute differences, and the L0 reference block and the L0 fine-tuning block are defined as Figure 9 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0091] The main concept behind Example 3 is that if some combination of motion vector difference and pixel difference is less than a threshold, the iteration will be ended. An example of a specific algorithm for implementing this embodiment may be as Figure 9 As shown, Target_context_value=a*(L0_MV_difference+L1_MV_difference)+b*(L0_block_difference+L1_block_difference), where a and b are weighting factors.
[0092] Sub-PU-based two-way template MV fine-tuning
[0093] In order to improve encoding and decoding efficiency, the present invention discloses sub-PU-based two-way template MV fine-tuning. The main idea behind this method is to split the PU into sub-PUs and then perform bi-directional template MV fine-tuning in the sub-PU layer. An example of the specific operation of this method can be as Figure 10 , where only operations related to the L0 portion are shown. Similarly, operations related to the L1 part can be derived. Figure 10 The exemplary procedure in incl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com