Ship target identification method based on feature migration
A target recognition and target technology, applied in the field of ship target recognition, can solve the problems of poor target recognition effect and achieve the effect of improving the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
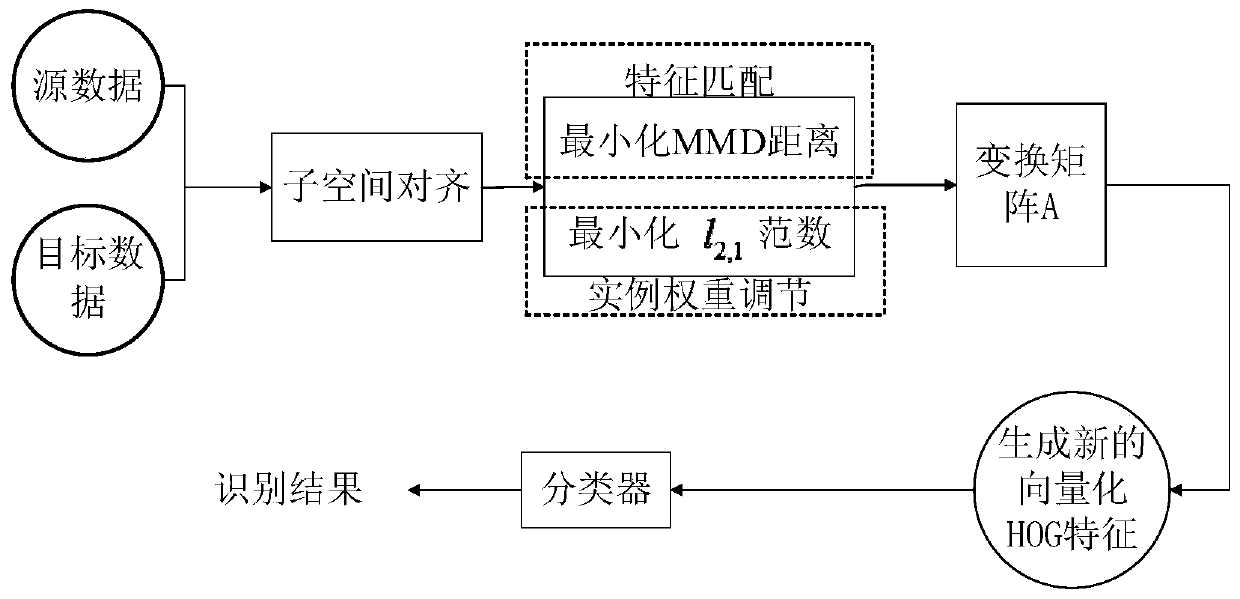
[0028] Specific implementation manner one: such as figure 1 Shown. The method for recognizing ship targets based on feature migration described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0029] Step 1. Select the high-resolution ship image as the training set image, and separately cut out the target slice of each image in the training set, and use the high-resolution ship image in the training set as the source domain to obtain the target slice of the source domain;
[0030] High-resolution ship image refers to the resolution within 0.5m;
[0031] Step 2: Calculate the HOG feature of the source domain target slice obtained in step 1, and vectorize the calculated HOG feature to obtain the vectorized HOG feature of the source domain (each slice has a corresponding vectorized HOG feature) ;
[0032] Step 3: For the low-resolution ship image to be recognized by the target, cut out the target slice of the image to be recognized, and use the low-resolution ship image to be recogniz...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that in the first step, the size of the target slice is set according to the size of the target in the high-resolution ship image.
[0046] For the recognition of ship targets, the training set images are from the Google Earth data source. The targets in the training set images are divided into aircraft carriers, destroyers and cruisers, and the target slices corresponding to each training set image have the same size.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0047] Specific embodiment three: this embodiment is different from specific embodiment two in that: the specific process of step four is:
[0048] Step 4: Generate subspace:
[0049] The vectorized HOG feature of the source domain and the vectorized HOG feature of the target domain are respectively subjected to standard normalization (mean value is 0, variance is 1), and the normalized vectorized HOG feature of the source domain and the normalization of the target domain are obtained. Vectorize the HOG feature after transformation;
[0050] After PCA (Principal Component Analysis) transformation is performed on the normalized vectorized HOG feature of the source domain, the feature vector corresponding to the first d large feature values is selected, and the selected feature vector is used as the base B of the subspace of the source domain S ;
[0051] In the same way, after PCA transformation is performed on the normalized vectorized HOG feature of the target domain, the feature v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com