Message forwarding control method and device and electronic equipment
A technology of message forwarding and control methods, which is applied in the field of network communication, and can solve problems such as inability to realize micro-segmentation, not supporting LPM table, and not supporting LPM table to be divided into SEBP and DEBP
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Embodiment 1 is applied to an IPv4 scenario. In this IPv4 scenario, the source IP address and the destination IP address of a packet are two different IPv4 addresses.
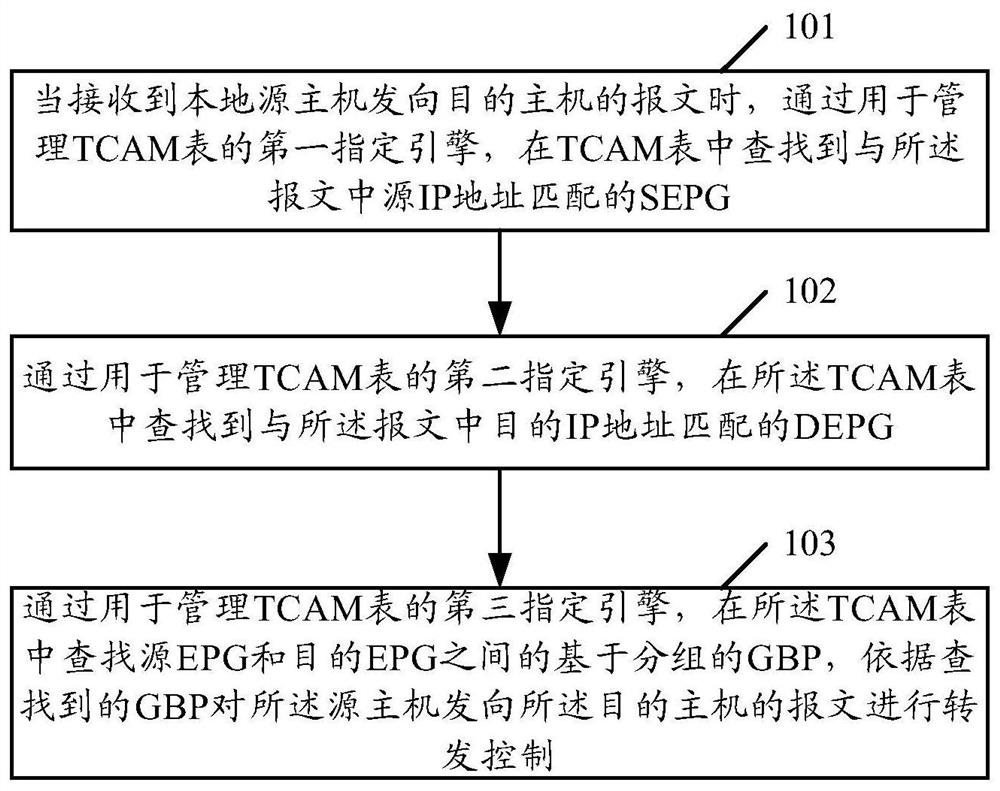
[0071] When a network device such as a VTEP receives a packet sent by a local host (recorded as the source host), such as figure 2 As shown, the TTI engine uses the source IP address of the packet as a keyword and searches the TCAM table for the EPG corresponding to the keyword according to the longest match principle, and determines the found EPG as the SEPG.
[0072] Afterwards, the IPCL engine uses the destination IP address of the message as a keyword and searches for the EPG corresponding to the keyword in the TCAM table according to the longest match principle, and determines the found EPG as the DEPG.
[0073] Afterwards, as an embodiment, the IPCL engine uses SEPG and DEPG as keywords to search for GBP whose matching condition is the keyword. Or, as another embodiment, the virtual private netwo...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Embodiment 2 is applied to an IPv6 scenario. In this IPv6 scenario, the source IP address and the destination IP address of the message are two different IPv6 addresses. The IPv6 address is 128 bits, which is 4 times higher than the 32-bit IPv4 address. However, the TTI engine only supports 30 bytes, which leads to the fact that the TTI engine cannot fully match the 128-bit IPv6 address when using the TTI engine to find the SEPG that matches the source IP address. Based on this, in this embodiment, the 128-bit source IP address (128-bit IPv6 address) can be converted into a 48-bit MAC address to save TTI resources.
[0078] Specifically, when a network device such as a VTEP receives a message sent by a local host (recorded as the source host), as in image 3 As shown, the TTI engine first determines that the IP address is the source MAC address of the source host of the source IP address in the packet. Optionally, in this embodiment, the TTI engine can find the MAC ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com