Method and system for identifying epileptic waves in brain waves
A technology for epilepsy radio waves and identification methods, applied in the medical field, can solve the problems of easy error identification, complex identification methods, and inability to identify, and achieve the effect of efficient identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
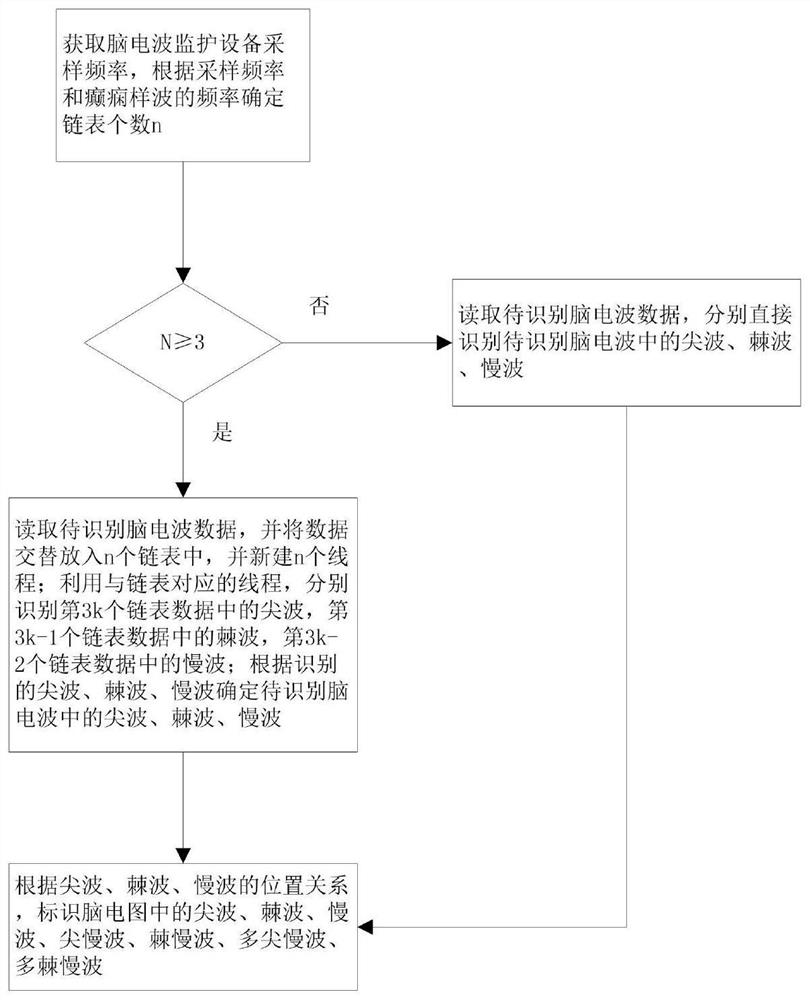
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a method for identifying epileptic electric waves in brain waves, the method comprising the following steps:
[0040] Step 1, obtain the sampling frequency of the brainwave monitoring equipment, and determine the number n of linked lists according to the sampling frequency and the frequency of the epileptiform wave; the epileptiform wave includes sharp wave-like waves, spike-like waves, and slow-wave-like waves; if n≥ 3, then go to step 2, otherwise go to step 3;
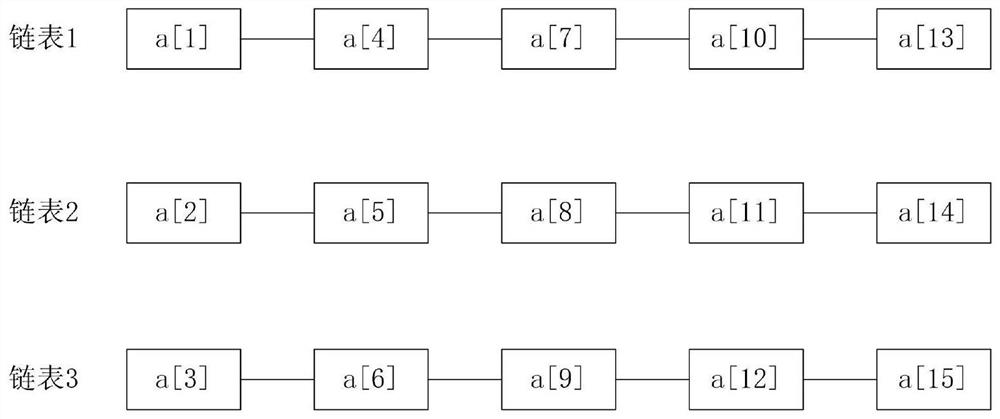
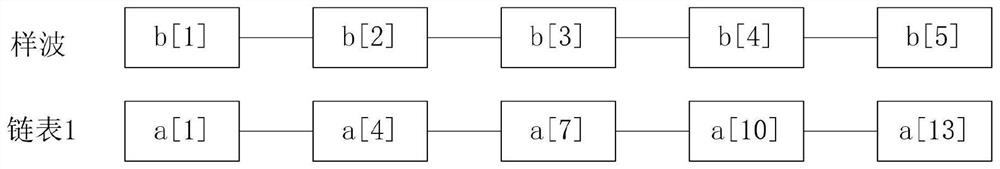
[0041] Step 2, read the brain wave data to be identified, put the data into n linked lists alternately, and create n threads, the threads correspond to the linked lists one by one; use the threads corresponding to the linked lists to identify the 3kth The sharp wave in the linked list data, the spike wave in the 3k-1 linked list data, the slow wave in the 3k-2 linked list data; determine the brain wave to be identified according to the identified shar...
specific Embodiment 2
[0060] The present invention also provides a system for identifying epileptic electric waves in brain waves, and the system includes the following modules:
[0061] The calculation module is used to obtain the sampling frequency of the brain wave monitoring equipment, and determine the number n of linked lists according to the sampling frequency and the frequency of the epileptiform wave; the epileptiform wave includes a sharp wave-like wave, a spike-like wave, and a slow-wave-like wave; if n≥3, execute the first identification module, otherwise execute the second identification module;
[0062] The first identification module is used to read the brain wave data to be identified, and put the data into n linked lists alternately, and create n threads, and the threads correspond to the linked lists one by one; using the threads corresponding to the linked lists, Respectively identify the sharp wave in the 3kth linked list data, the spike wave in the 3k-1 linked list data, and th...
specific Embodiment 3
[0071] The present invention also provides a computer-readable storage medium for storing computer program instructions, wherein the computer program instructions implement the method according to Embodiment 1 when executed by a processor.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap