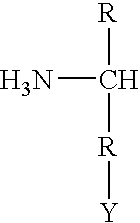
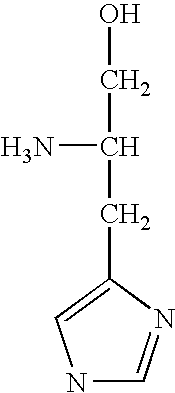
Cloning, overexpression and therapeutic use of bioactive histidine ammonia lyase
a technology of histidine ammonia and lyase, which is applied in the field of bioactive, amino aciddegrading enzymes, can solve the problems of not being purified, many of the therapeutically beneficial properties associated with this hal were unknown, and the usefulness of l-histidinol as a single agent is limited
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
working examples
Example 1
Isolation of the DNA Encoding HAL
[0120] The bacterium from the family Corynebacteriaceae that produces bioactive histidine ammonia lyase (HAL) was grown in 100 ml of Luria broth overnight at 30° C. The cells were harvested and resuspended in 10 ml of 50 mM Tris (pH 7.5) with 10 mM EDTA. Solid lysozyme was added to 0.2 mg / ml and the suspension was incubated at 4° C. for 30 minutes. Following this incubation, the suspension was frozen for several hours at −70° C. Upon thawing, SDS was added to 0.1% and proteinase K was added to 0.2 mg / ml and was incubated at 37° C. overnight. Next, RNAse was added to 0.1 mg / ml and the mixture incubated at 55° C. for 30 minutes. The resulting DNA was extracted five times with an equal volume of phenol / chloroform (1:1) and precipitated with 2 volumes of absolute ethanol. The DNA was spooled out on a glass Pasteur pipette, washed with ice cold 70% ethanol, and resuspended in a minimal amount of TE buffer.
[0121] Genomic DNA was restricted with...
example 2
Peptide Sequencing of HAL
[0132] HAL from a bacterium from the family Corynebacteriaceae that had been partially purified using ammonium sulfate and DEAE—Sephadex was resolved by SDS-PAGE. The separated material was electrophoretically transferred to Immobilon-P and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. The major band of 55 000 daltons was excised and subjected to N-terminal sequencing. This fraction was sent to Commonwealth Biotechnologies, Inc. (Richmond, Va.), cleaved with BrCN, HPLC purified, and fractions sequenced. The data are shown in FIG. 2.
example 3
Expression of Histidine Ammonia Lyase from a Bacterium from the Family Corynebacteriaceae Using a High-Efficiency Prokaryotic Expression System
[0133] The E. coli expression plasmid pHUT102, depicted in FIG. 4, is designed to express HAL DNA sequences from the strong phage T7 gene 10 promoter using T7 RNA Polymerase. This vector, pSN75, is a derivative of pET11b (Novagen) that has an additional transcriptional terminator inserted upstream of the T7 promoter. This provides the target cassette in as transcriptionally silent a context as possible.
[0134] Two mutagenic oligonucleotides, TM96 and TM97 (see Table 1), were synthesized based on histidine ammonia lyase sequence. The N-terminal oligo adds an NdeI site at the ATG start codon and the C-terminal oligo adds a BamHI site just beyond the C-terminus. These were used to thermal cycle amplify the HAL gene out of the genome of a bacterium from the family Corynebacteriaceae. The resulting fragment was restricted with NdeI and BamHI and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com