Versatile resource computer-based training system
a computer-based training system and virtual resource technology, applied in the field of computer-based training systems, can solve the problems of prohibitively expensive programming time, computer memory, and other scarce resources of conventional cbt systems, and achieve the effects of reducing the number of simultaneous actions of complex tasks such as call center operations or flight simulations, and reducing the number of simultaneous actions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
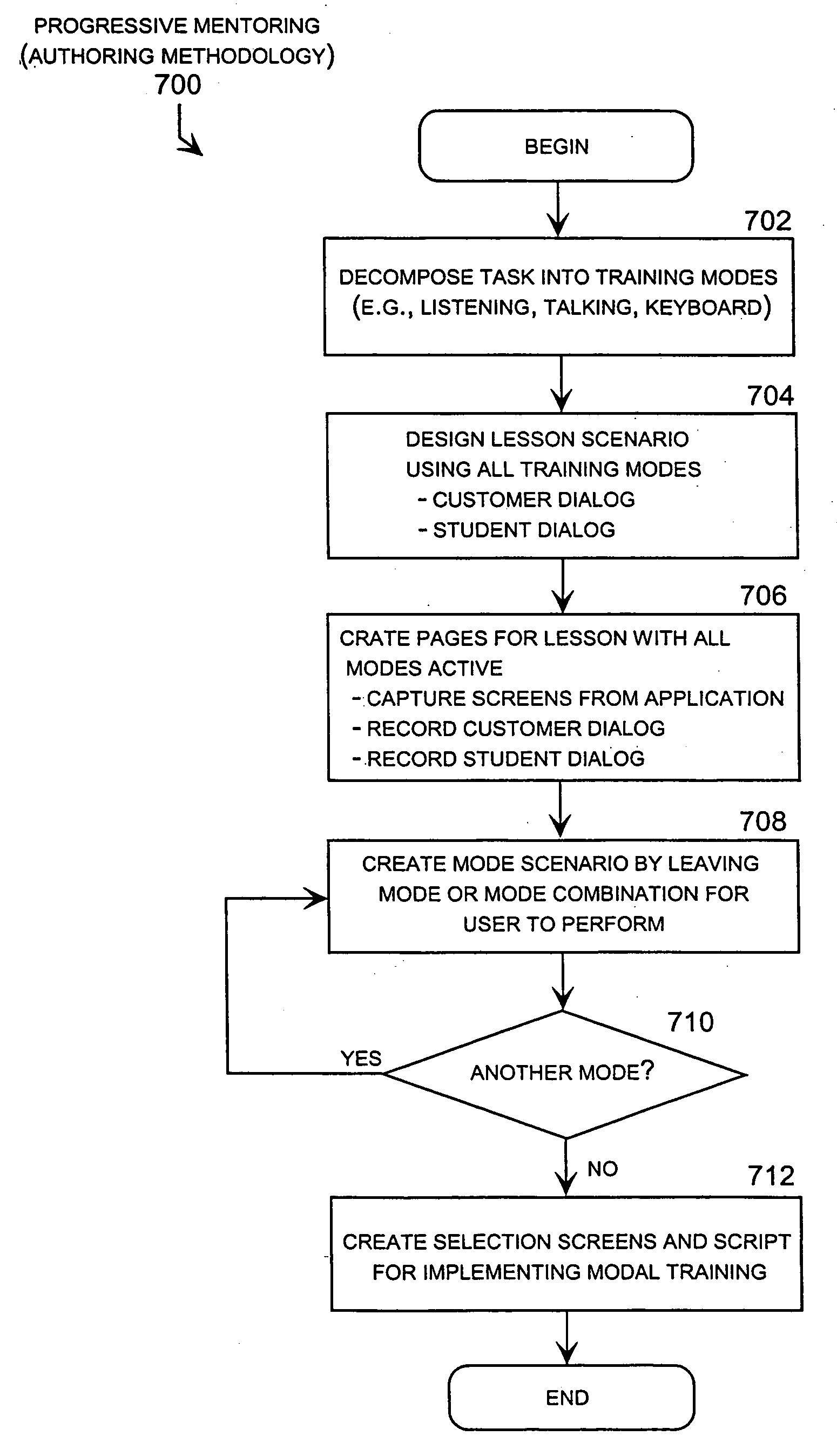
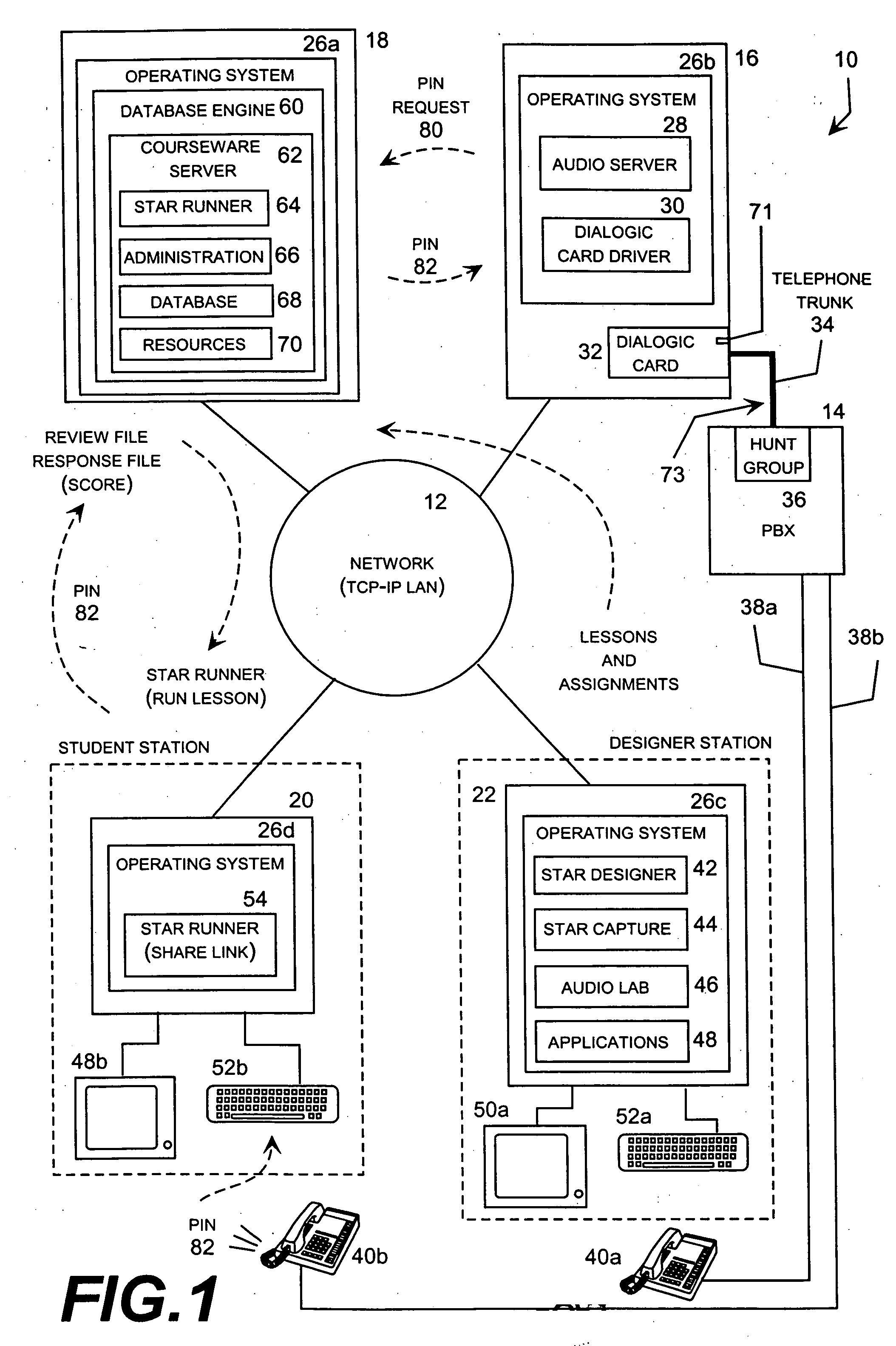
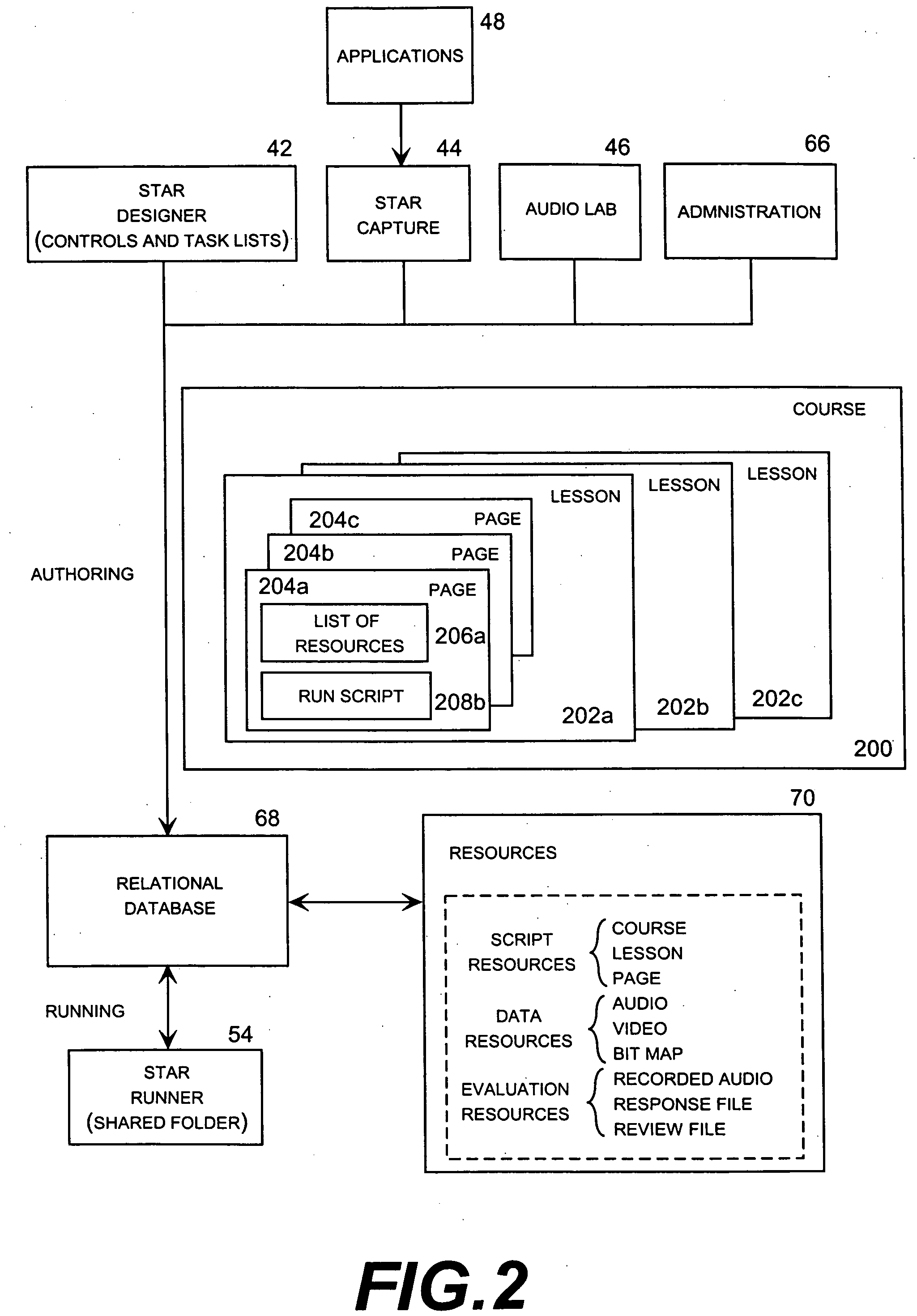
[0064] The present invention may be embodied in a network-based computer-based training (CBT) system configured to perform training simulations using versatile resources. For example, the CBT system presently sold under the name “StarTrainer” embodies many aspects of the invention as described in this specification. The resources used by StarTrainer are referred to as “versatile” resources because they are separately stored in memory and independently retrievable for display or play in association with multiple lessons. These versatile resources typically include lesson pages and separately stored data files that can be displayed or played in association with lessons or lesson pages, such as sound files, video files, and bit maps.
[0065] There are three main components of the StarTrainer CBT system: an audio server, which manages the voice portion of simulation; a courseware server, which manages the application portion of simulation; and authoring tools, which allow the creation of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com