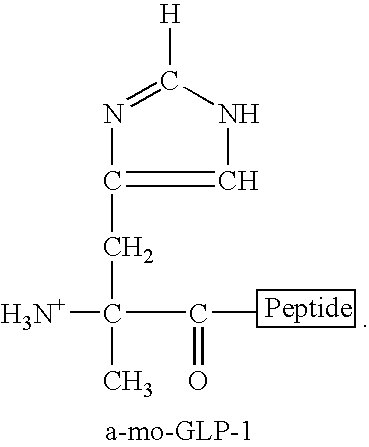
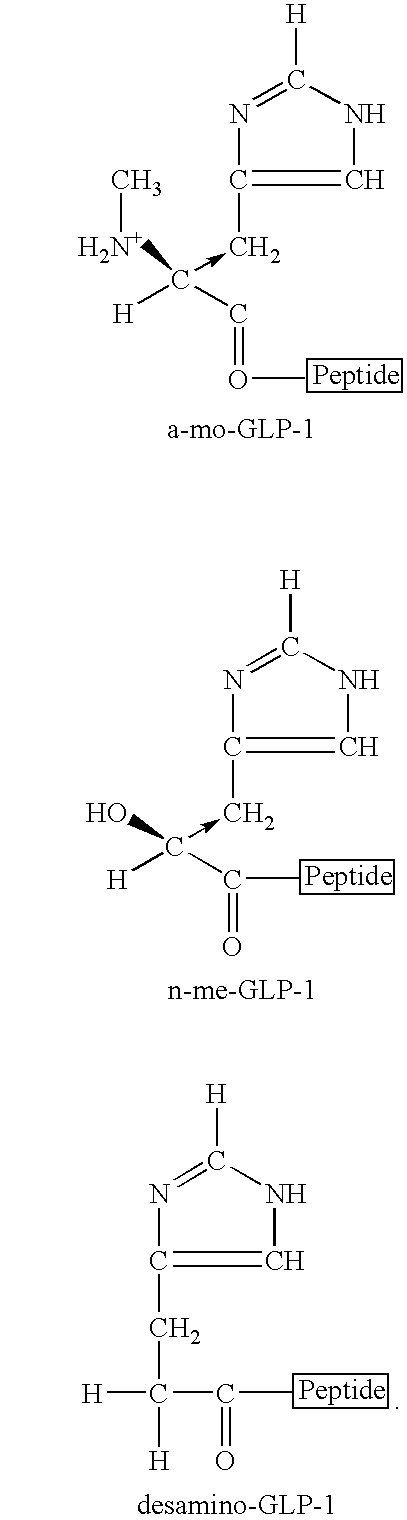
Compounds and methods for increasing neurogenesis
a neurogenesis and compound technology, applied in the field of compound and method for increasing neurogenesis, can solve the problems of limited fetal tissue grafting, small factors known to affect neurogenesis in vivo, and donor tissu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Reagents
[0148] Chemicals for dissociation of tissue included trypsin, hyaluronidase, and DNase (all purchased from SIGMA). Medium (DMEM 4.5 mg / ml glucose, and DMEM / F12), B27 supplement, and trypsin / EDTA were purchased from GIBCO. All plastic ware was purchased from ComingCostar. EGF for cell cultures was purchased from BD Biosciences, and the ATP-SL kit was purchased from BioThema.
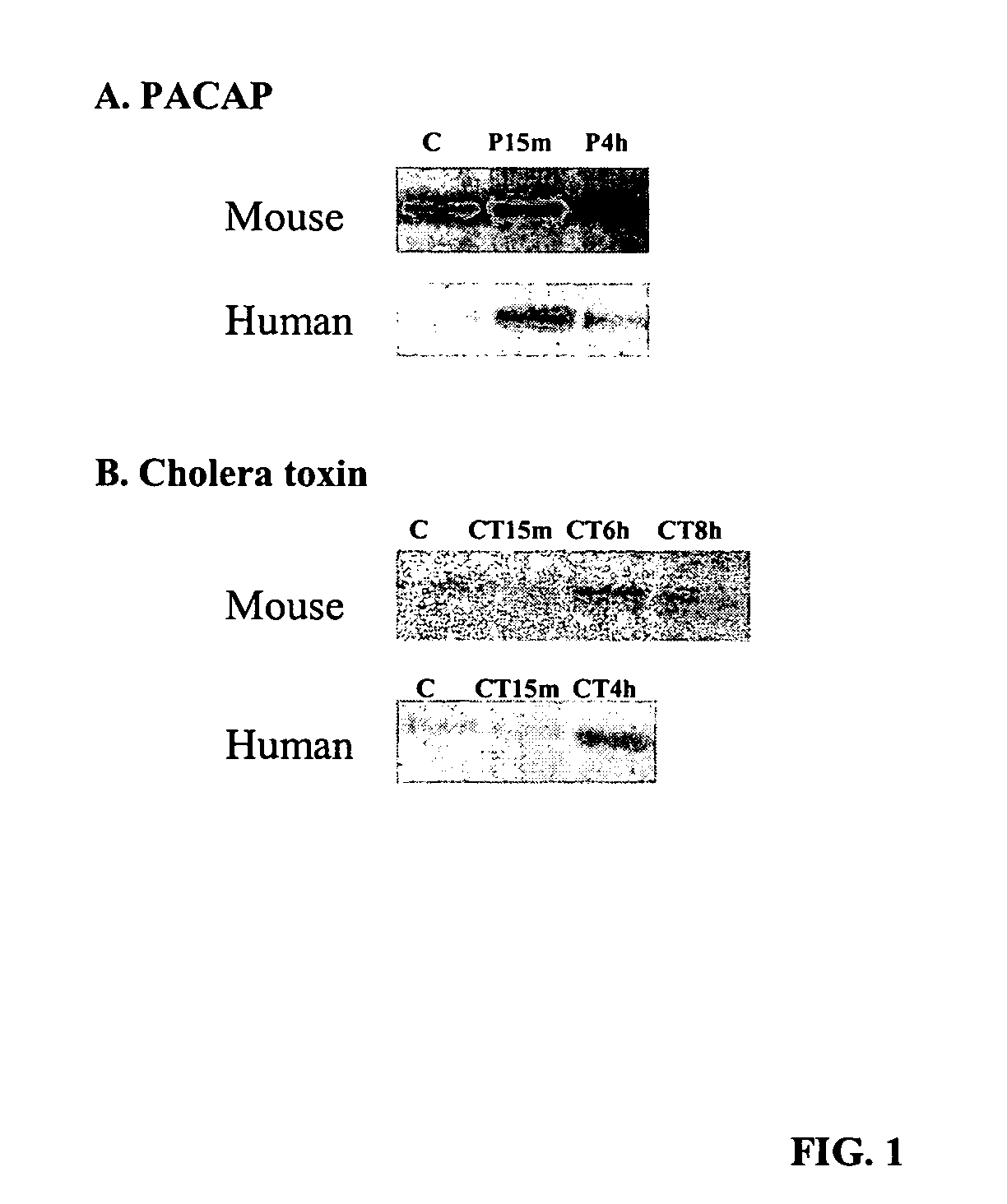
[0149] For the test substances, the library was purchased from Phoenix pharmaceuticals Inc., USA, variety Pack Peptide Library (#L-001). Compounds purchased from Sigma-Aldrich included forskolin (#F6886), rolipram (#R6520), n-6,2-o-dibutyryladenosine (#D0260), cholera toxin (#C8052), MECA (#A024), HE-NECA (#H8034), nor-Binaltorphimine (#N1771), and adrenocorticotropic hormone (#A0298).
example 2
Mouse Neurosphere Cultures
[0150] The anterior lateral wall of the lateral ventricle of 5-6 week old mice was enzymatically dissociated in 0.8 mg / ml hyaluronidase and 0.5 mg / ml trypsin in DMEM containing 4.5 mg / ml glucose and 80 units / ml DNase at 37° C. for 20 minutes. The cells were gently triturated and mixed with Neurosphere medium (DMEM / F12, B27 supplement, 12.5 mM HEPES pH7.4), 100 units / ml penicillin and 100 μg / ml streptomycin. After passing through a 70 μm strainer, the cells were pelleted at 200×g for 4 minutes. The supernatant was subsequently removed and the cells were resuspended in Neurosphere medium supplemented with 3 nM EGF. Cells were plated out in culture dishes and incubated at 37° C. Neurospheres were ready to be split at approximately 7 days after plating.
[0151] To split neurosphere cultures, neurospheres were collected by centrifugation at 200×g for 4 minutes. The neurospheres were resuspended in 0.5 ml trypsin / EDTA in HBSS (1×), incubated at 37° C. for 2 minut...
example 3
ATP-Assay
[0152] To determine proliferation, neurospheres were split and seeded in Neurosphere medium as single cells in 96-well plates, at 10,000 cells / well. The following experiment was performed in sets of four parallel experiments (i.e., performed in quadruplicate) such that the cells may be used for different assays. Substances to be tested were added and cells were incubated at 37° C. for 4 days. Cells were lysed with 0.1% Triton-X100 in Tris-EDTA buffer. Intracellular ATP was measured using an ATP-SL kit according to the manufacturer's instructions (BioThema, Sweden). Intracellular ATP was shown to correlate with cell number. For each experiment, wells were visually examined for signs of neurogenesis and counted to confirm the results of the assay. Results were repeatable and statistically significant.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com