Associated device discovery in IMS networks
a technology of ims network and associated devices, applied in the field of ims network associated device discovery, can solve the problems of high networking cost of administrative domains, difficult operation, high uneven availability of network coverage supporting multimedia services,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
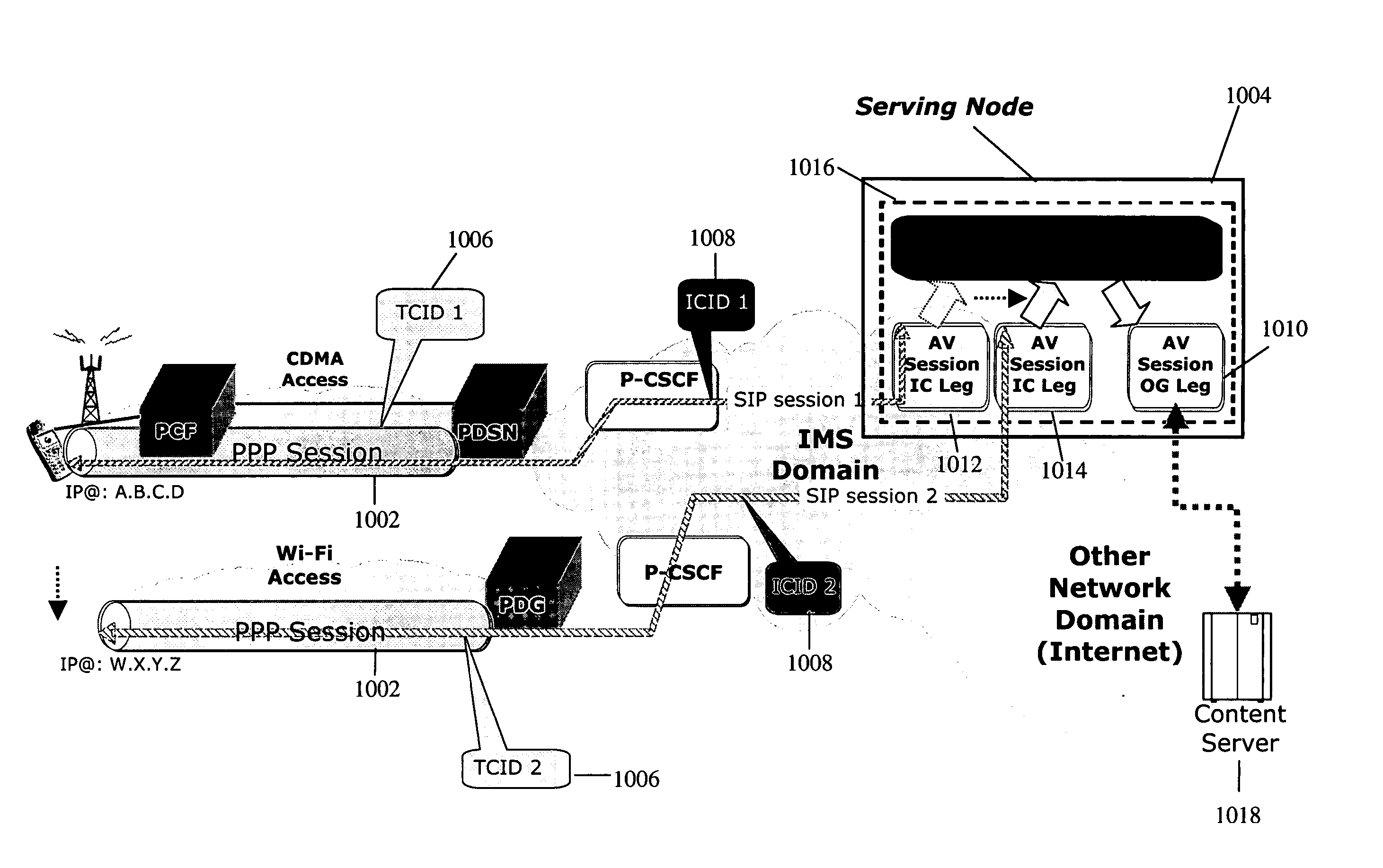
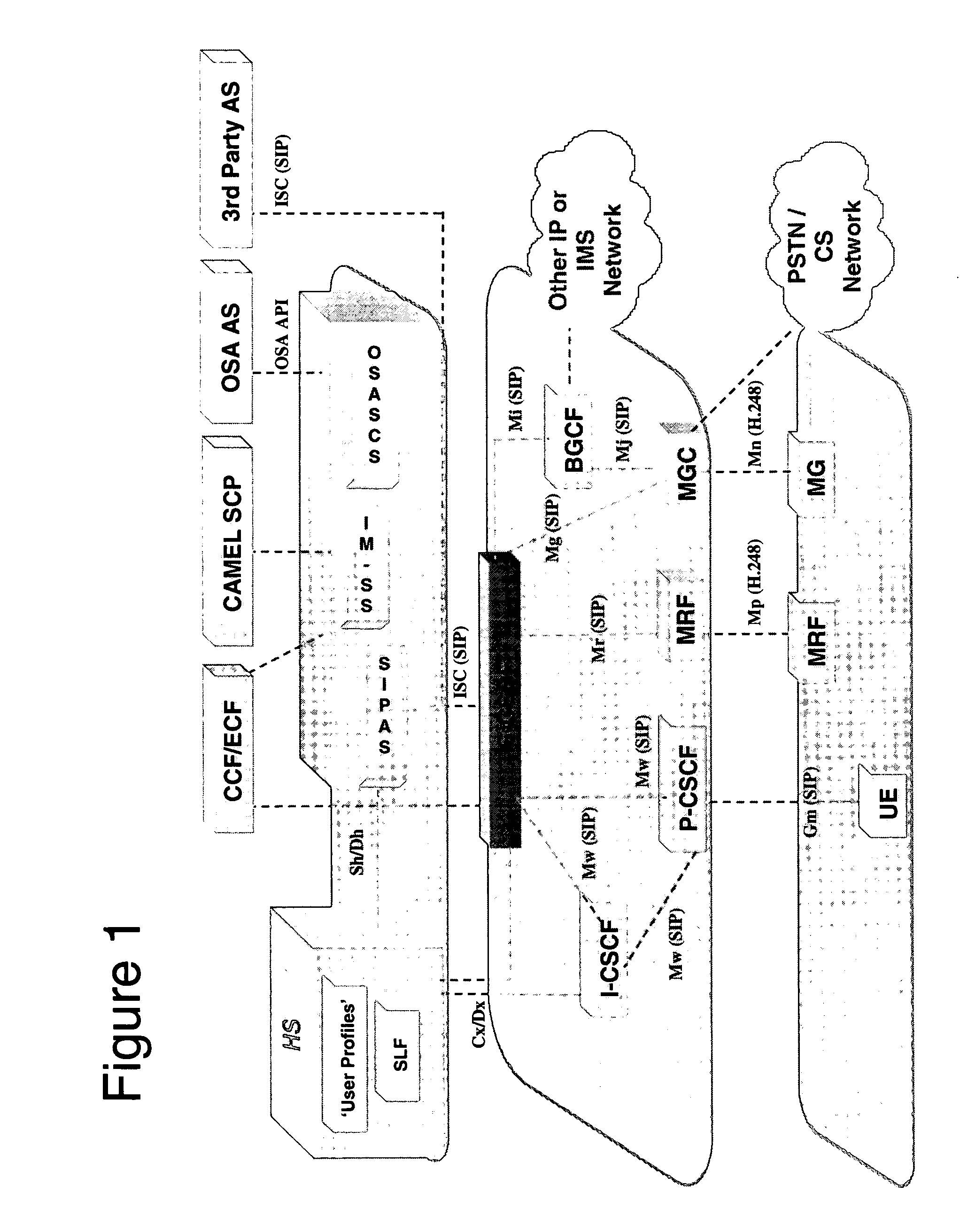
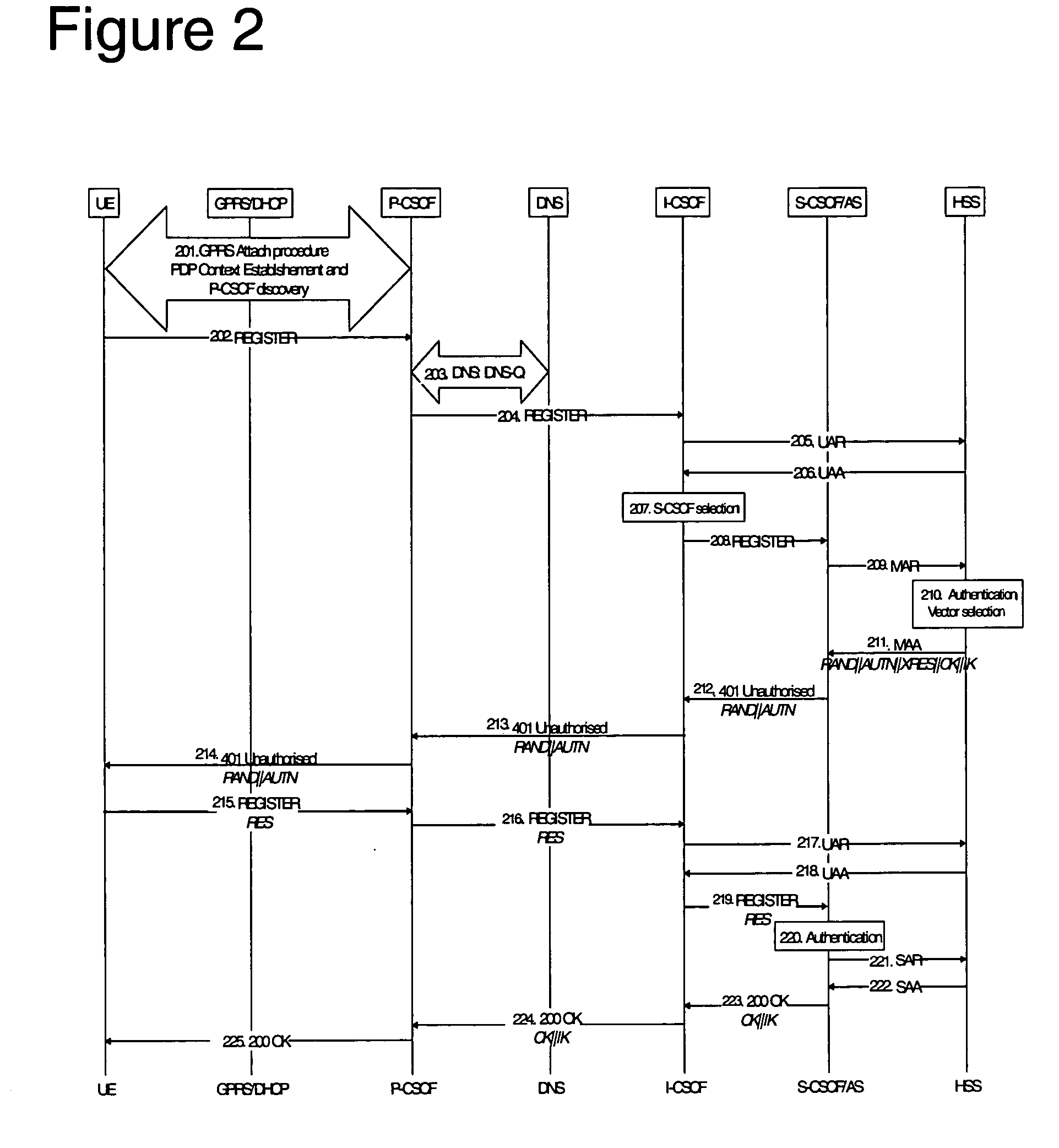
[0071] Preferred embodiments of the invention permit IMS user sessions to utilize devices that are discovered by the UE during the course of an IMS session. The embodiments provide for the discovery of available devices, and for choosing whether to add a discovered device to the IMS session. The choice can be made to depend on physical and / or technical factors, such as whether the IMS session involves the use of content that could benefit from the incorporation of the associated device into the IMS session. For example, if the user is receiving video, and a large-screen TV set is discovered, it would be beneficial for the user to view the video on the large screen of the discovered TV set rather than on the small screen of a handset. In addition, the decision to include the discovered device can be made to depend on a set of policies that involve business relationships (such as of the user to owner / operator of the available devices) and cost. The described embodiments allow the sign...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com