Monitoring physiological conditions
a physiological condition and monitoring technology, applied in the field of monitoring physiological conditions, can solve the problems of significant time passing during, system not using driver fatigue assessment systems to assess well-being or health, and system not anticipating problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
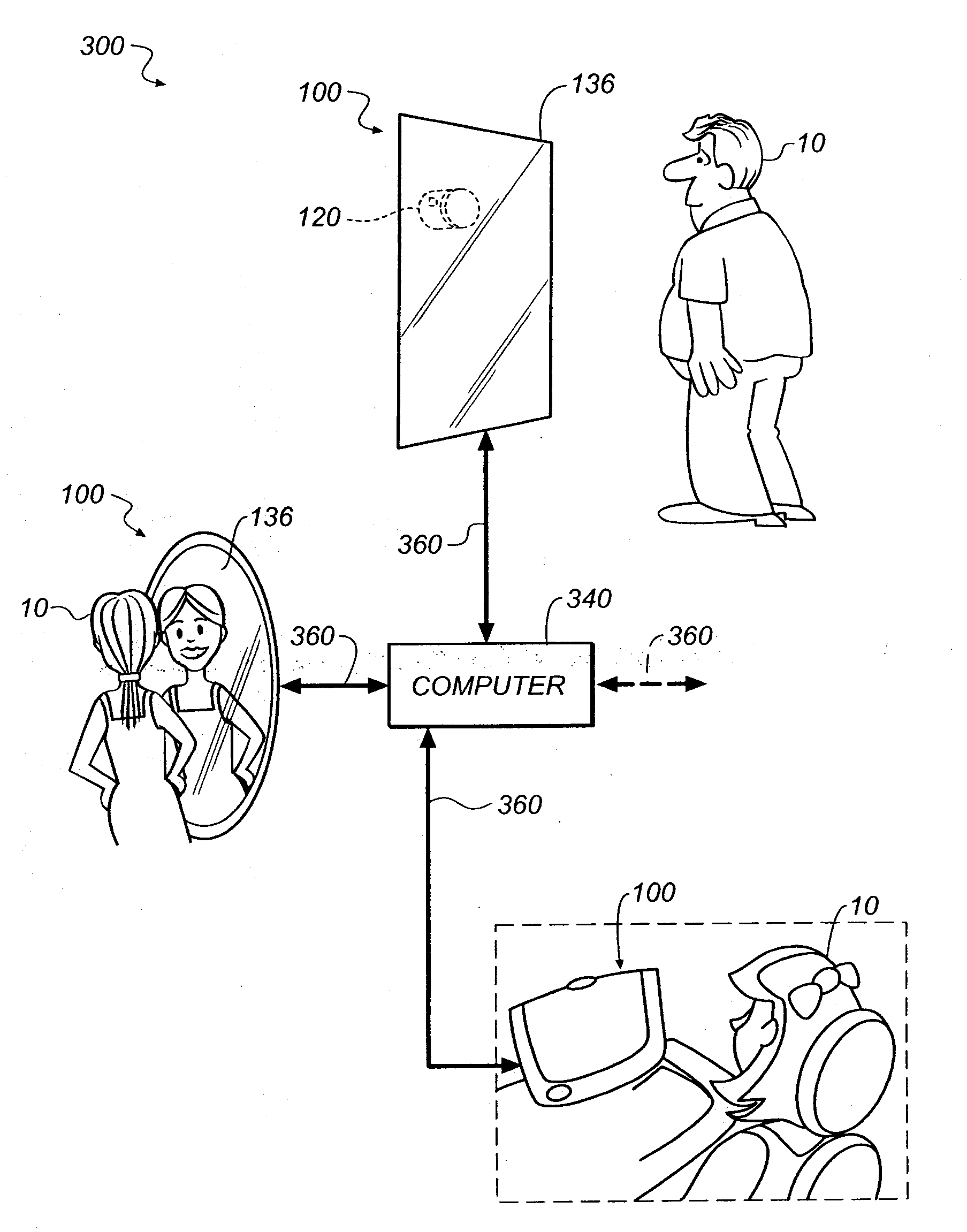
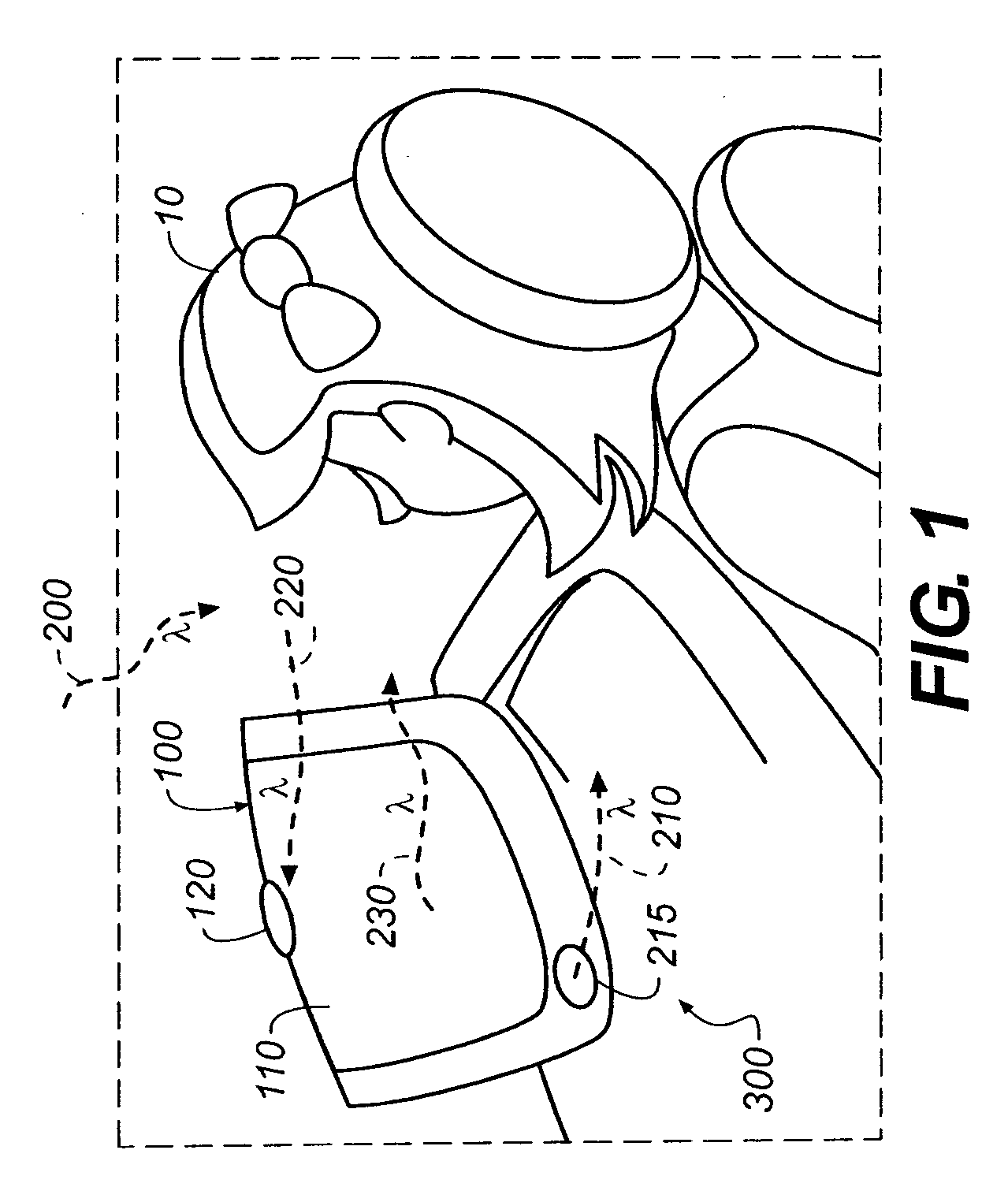
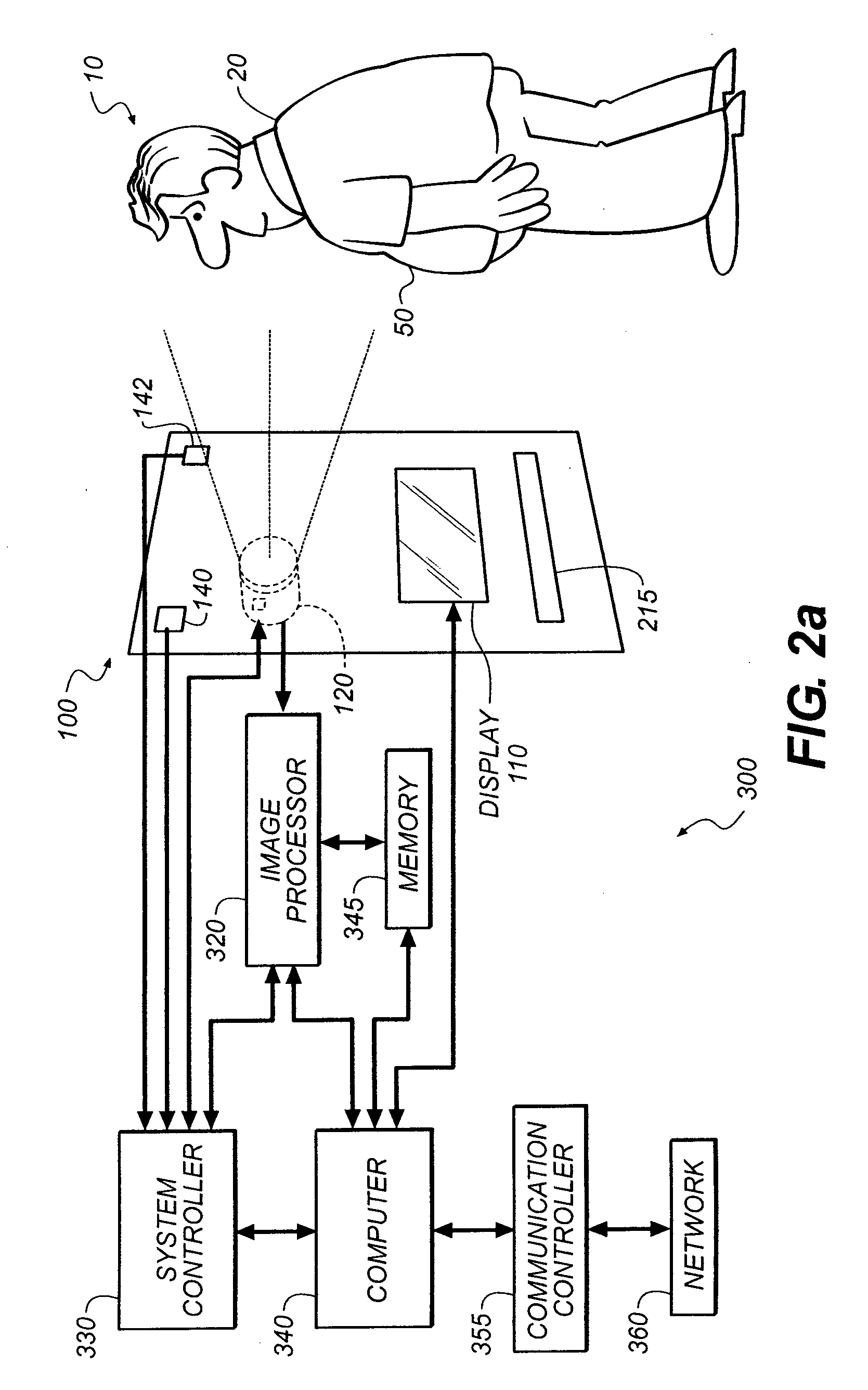
[0028]The apparatus and method of the present invention addresses the need for a system for monitoring physiological conditions, which includes technologies to acquire physiological data over time, analyze the data to provide wellness assessments, validate the data and test the assessments, and provide assessments to the users. The system can include an integrated display and image capture device. The key functional attributes of the system include the following:[0029]It provides day after day ongoing access in an unobtrusive way, targeted for the home environment.[0030]It is designed with consideration for family privacy issues.[0031]It is enabled by identification of individual users (user provided, face recognition, audio recognition, for example)[0032]It can be adapted to provide monitoring and assessments for new individuals or new conditions.[0033]It can use an integrated capture & display device, which can use more than just visible light.[0034]It is primarily used as an imag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com