High speed video action recognition and localization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
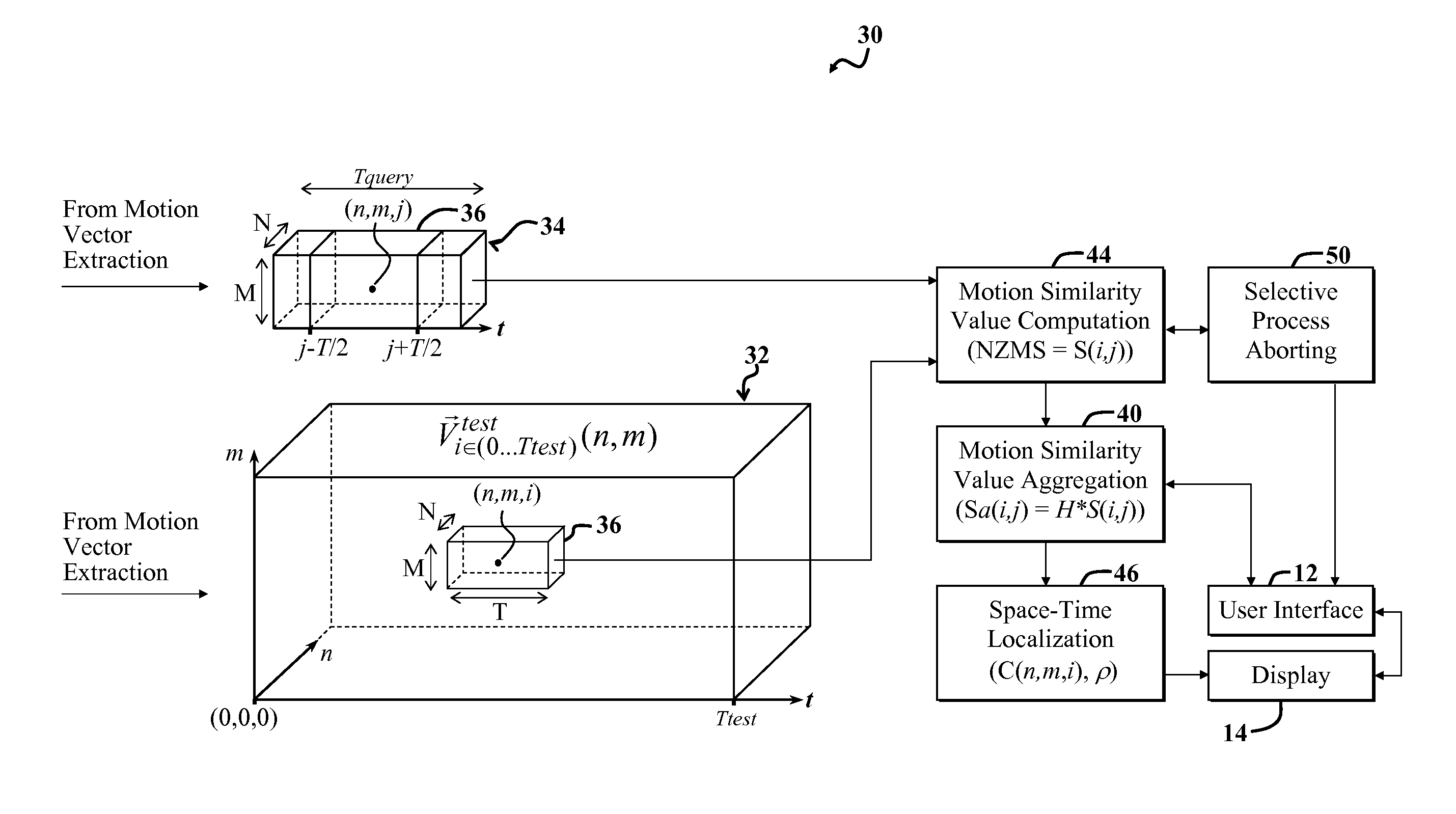
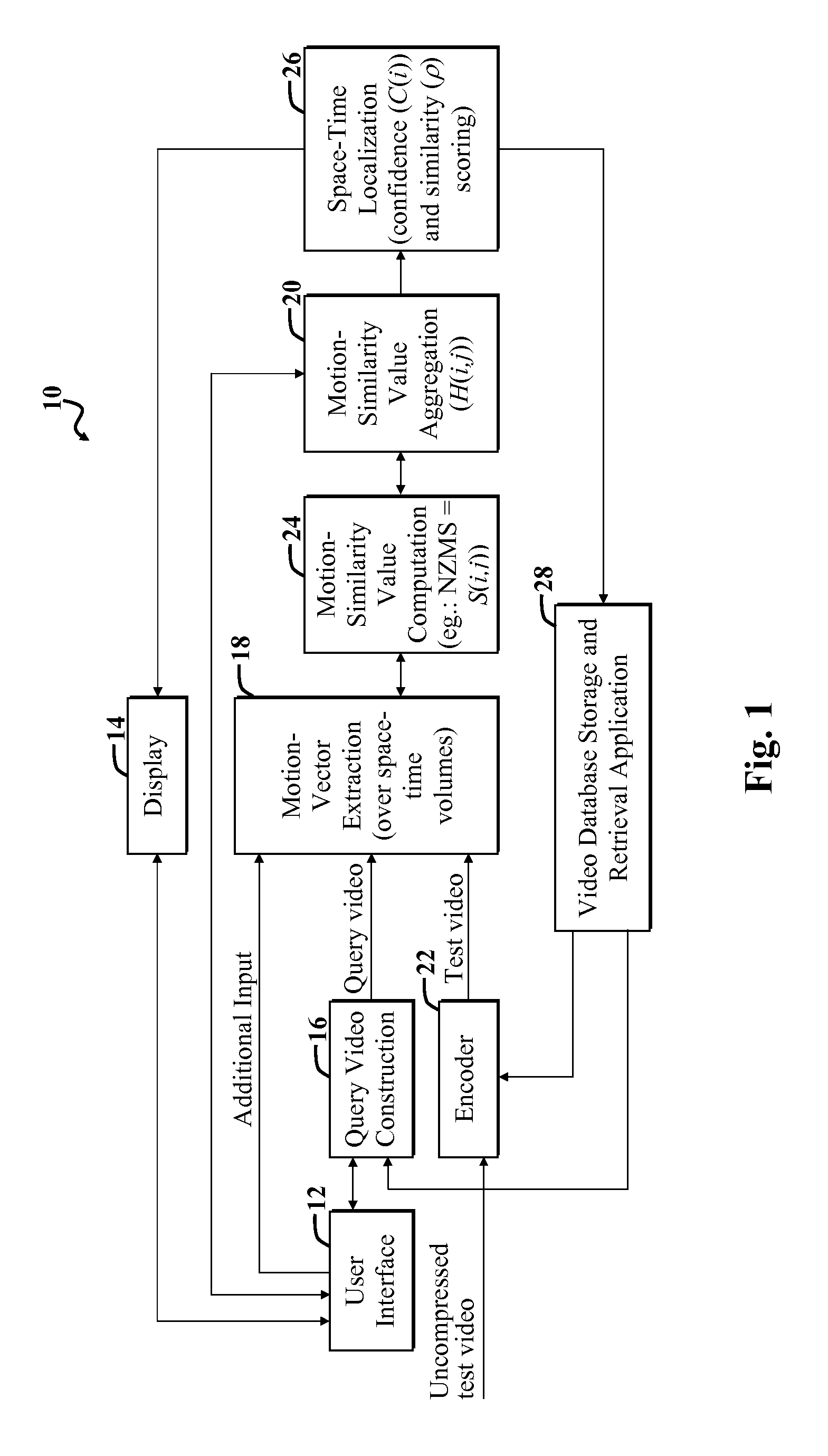
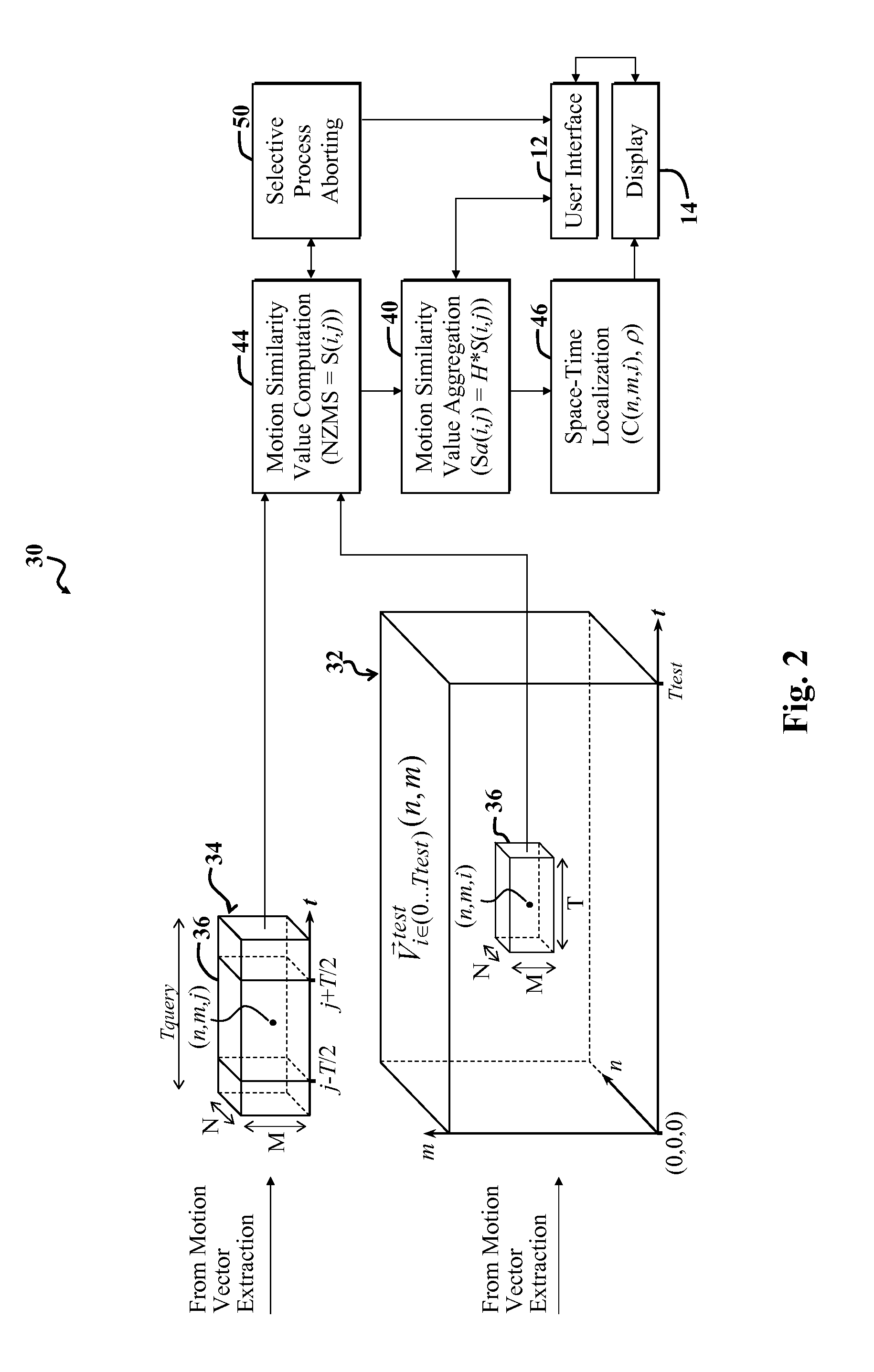
[0004]Certain embodiments of the invention provide an apparatus for detecting or locating an action in a test video. In a specific embodiment, the apparatus includes a first mechanism for employing motion vector or field information to identify a predetermined characteristic of an action and to provide a first signal in response thereto. A second mechanism includes instructions for determining where in a video sequence a certain motion exists or is likely to exist based on the first signal.
[0005]In a more specific embodiment, the predetermined characteristic includes the motion that is associated with the action. The first mechanism further includes a third mechanism for determining a motion similarity between a first group of pixels in a first frame in a test video and a second group of pixels in a second frame in a query video. The query video includes a representation of the action, and the test video represents the video sequence.
[0006]In this embodiment, the motion similarity i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com