Clinical Data Reconciliation as Part of a Report Generation Solution
a technology for generating reports and clinical data, applied in the field of clinical data reconciliation as part of a report generation solution, can solve the problems of many barriers to updating emrs, tedious process, time-consuming and error-prone,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
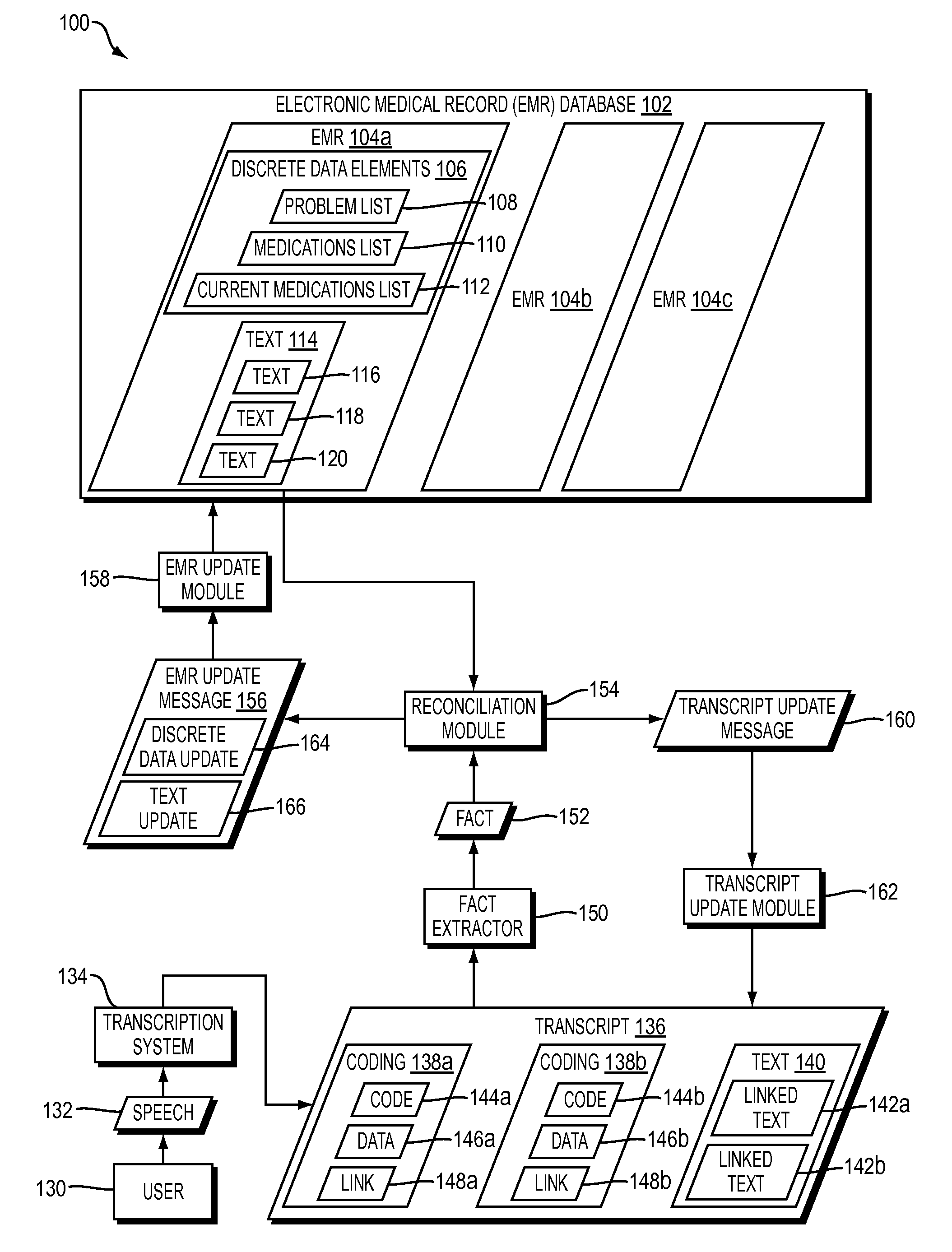
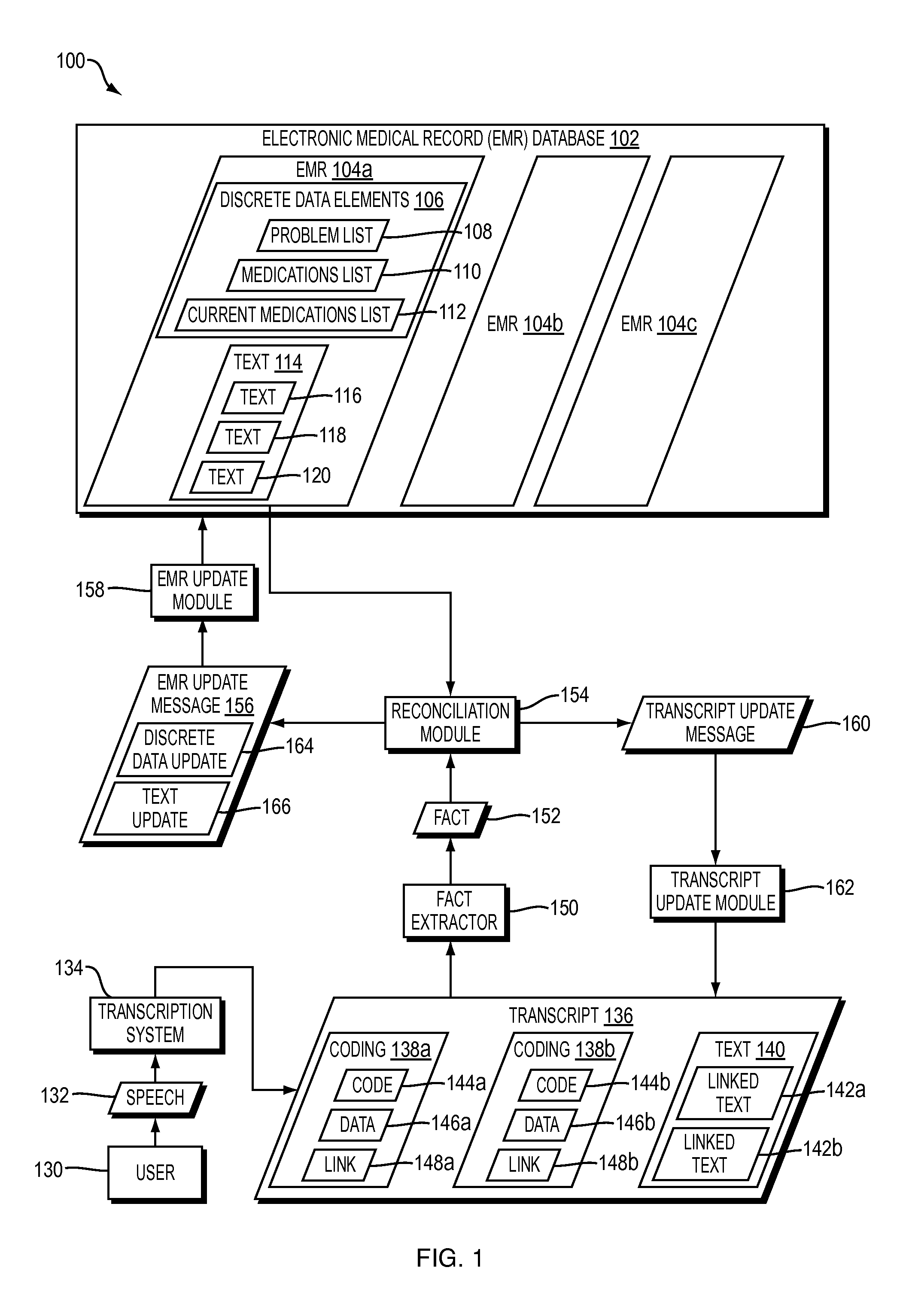
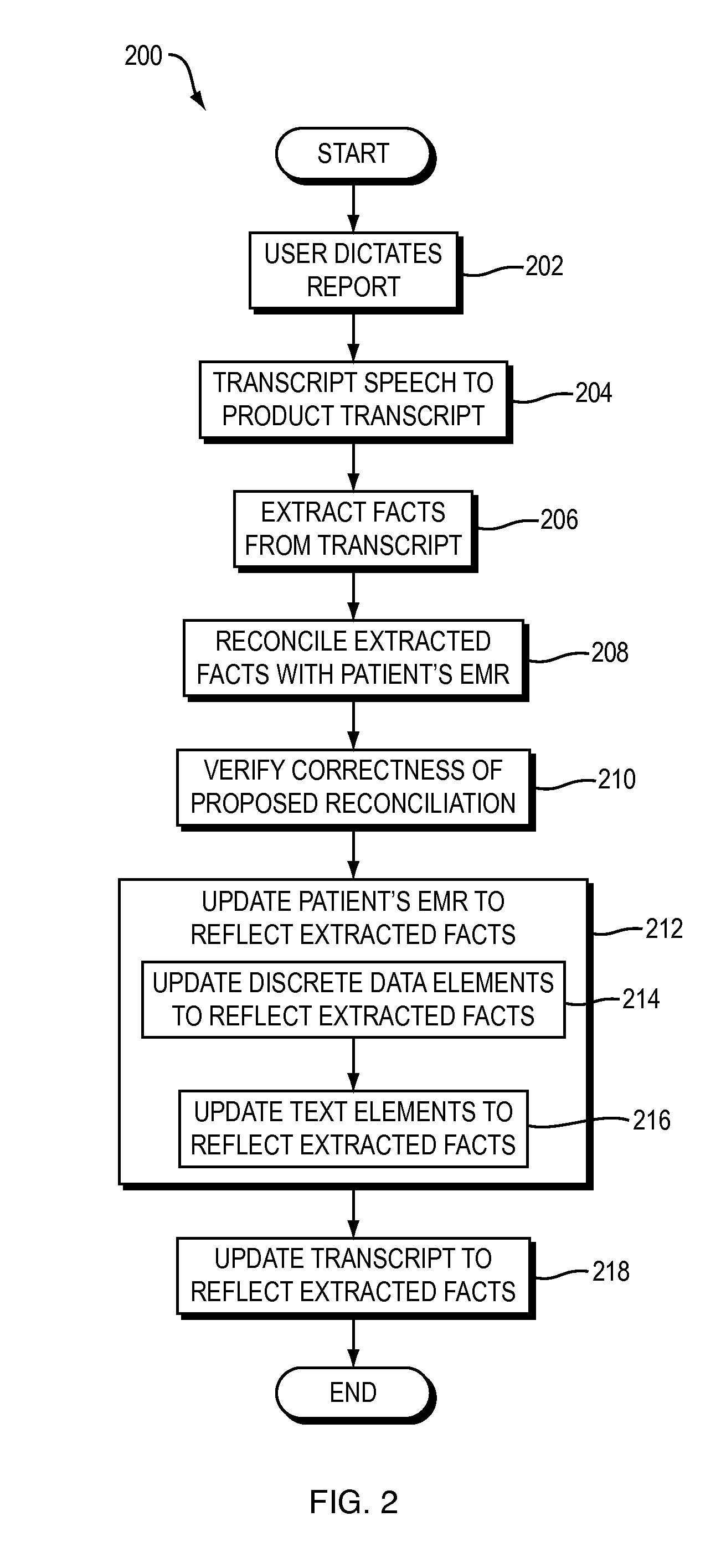
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to techniques for updating electronic medical records (EMRs) quickly, accurately, and with minimal human effort. For example, FIG. 1 shows a dataflow diagram of a system 100 for automatically updating an EMR based on the content of a transcript according to one embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 shows a flowchart of a method performed by the system 100 of FIG. 1 according to one embodiment of the present invention.
In the system 100 of FIG. 1, an EMR database 102 contains a plurality of EMRS 104a-c, each of which may correspond to a distinct patient. For ease of illustration, only the contents of EMR 104a are shown in FIG. 1. However, EMRs 104b and 104c may contain data having the same or similar format as that shown for EMR 104a.
More specifically, EMR 106 contains both discrete data elements 106 and text 114. The discrete data elements 106 may include, for example, a problem list 108, a medications list 110, and a current m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com