Resin-soluble veils for composite article fabrication and methods of manufacturing the same
a technology of resin-soluble veils and composite articles, which is applied in the direction of textiles and paper, metal-working apparatus, woven fabrics, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitable lri applications for addition of conventionally added tougheners, unsuitable viscosity levels necessary to achieve injection process, and inability to use toughening agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026]The following detailed description is of the best currently contemplated modes of carrying out the invention. The description is not to be taken in a limiting sense, but is made merely for the purpose of illustrating the general principles of the invention.
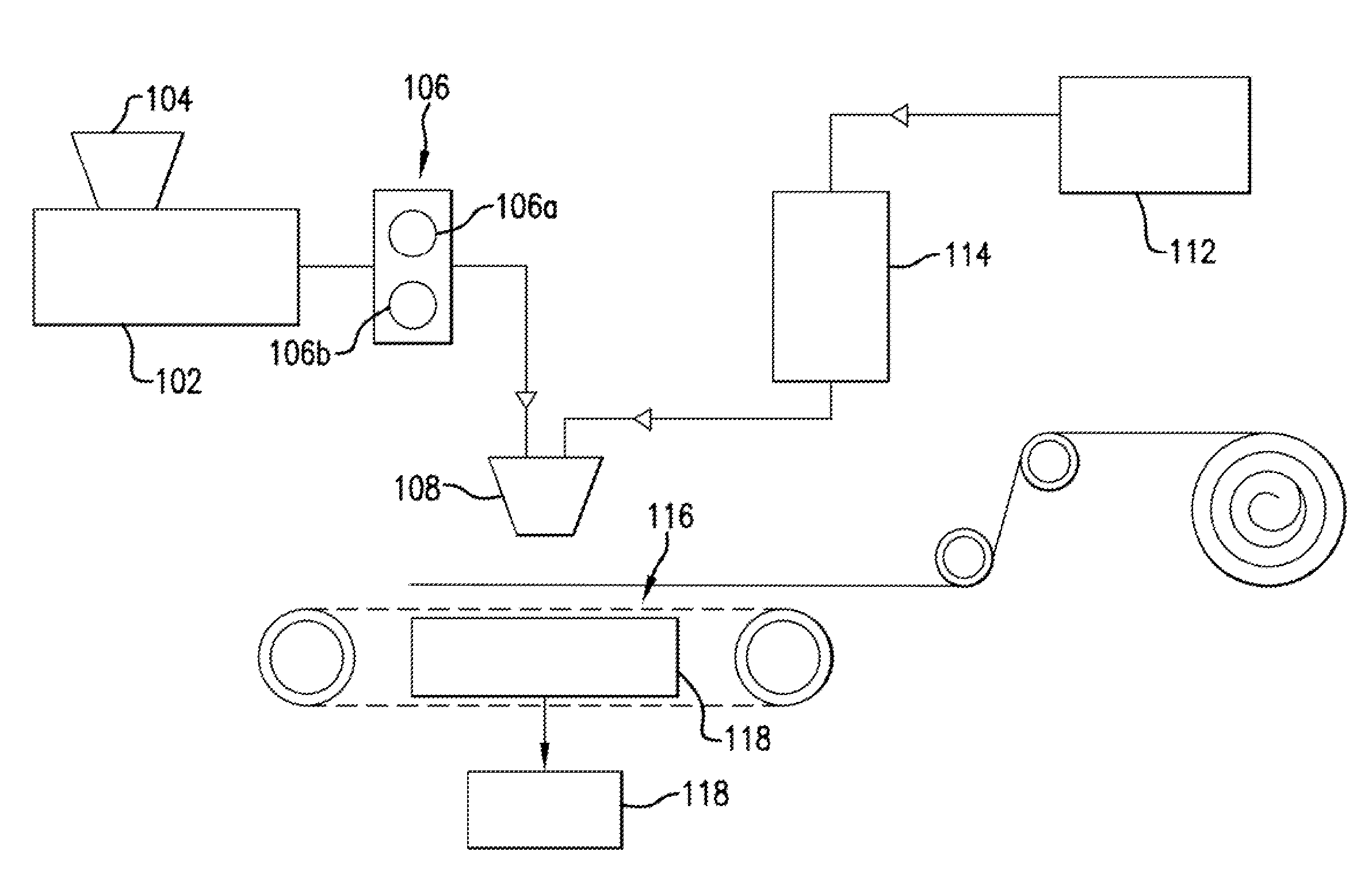
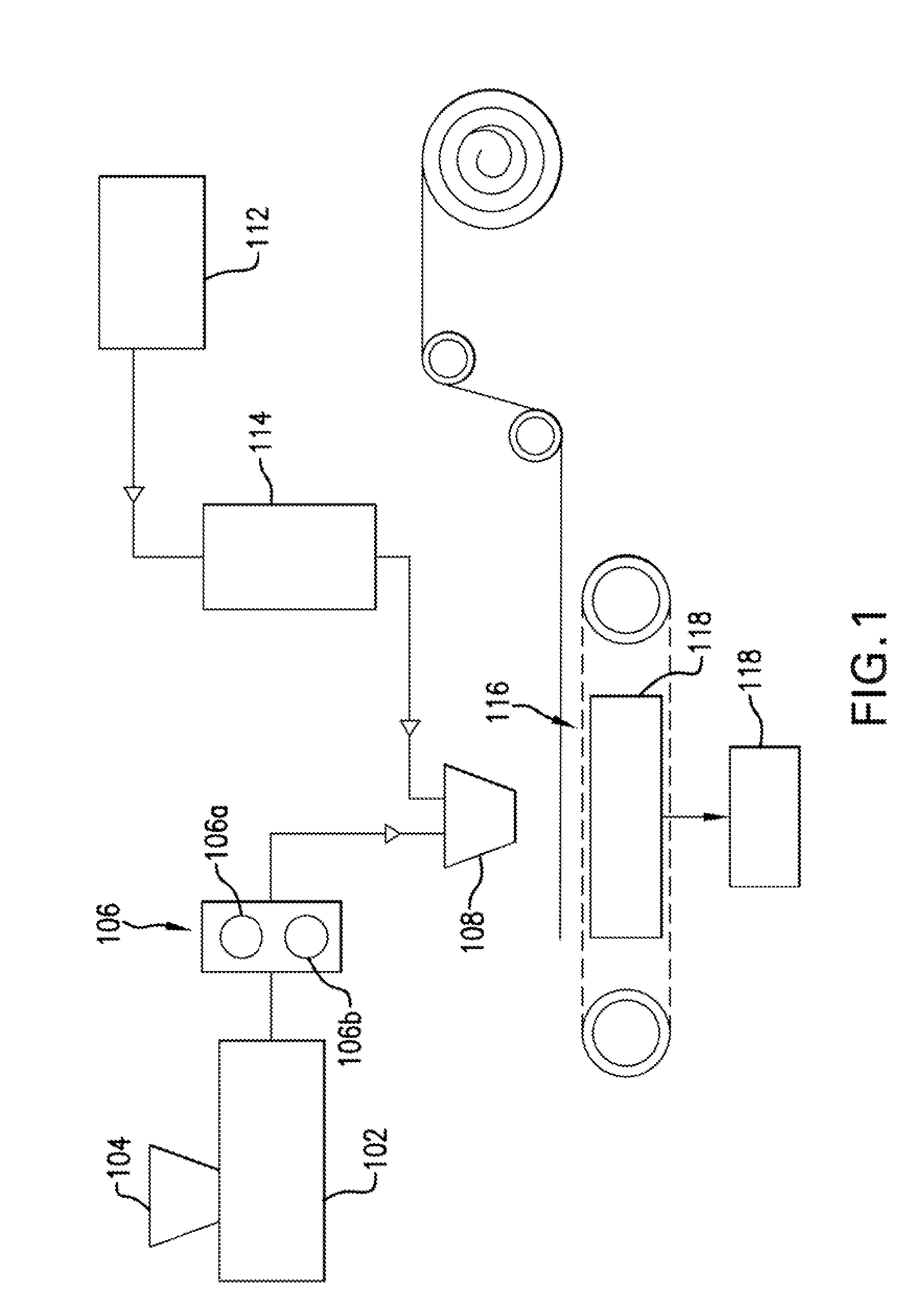
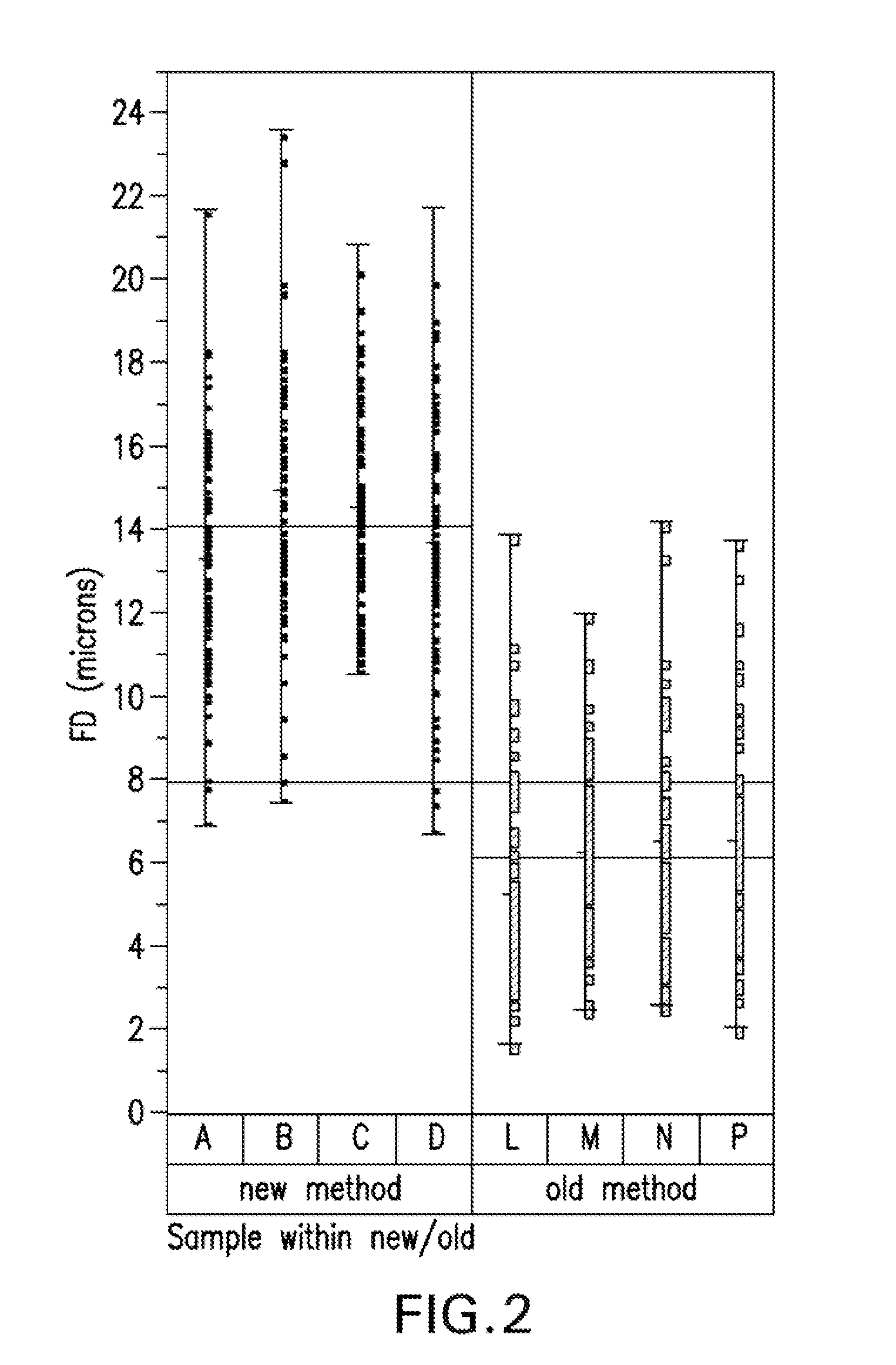
[0027]Embodiments of the invention are directed to non-woven engineered veils, which include non-woven, resin-soluble thermoplastic veils for use in liquid resin infusion processes, methods of manufacturing non-woven engineered veils for use in liquid resin infusion processes, and methods of manufacturing composite articles using non-woven engineered veils for use in liquid resin infusion applications. In addition to functioning as a toughening agent in composites when incorporated therein, the non-woven engineered veils according to embodiments of the invention have improved characteristics including, but not limited to, increased uniformity and decreased thickness relative to prior art veils. These characteristics translat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com