Modeling loudspeakers based on cascading lumped parameter models with neural networks
a loudspeaker and neural network technology, applied in the field of loudspeaker systems, can solve the problems of unsuitable conventional design approaches, prohibitive time required to simulate different aspects of loudspeaker behavior using such techniques, and reduce the accuracy of a given lumped parameter model, so as to achieve efficient and accurate simulation of nonlinear aspects of loudspeaker systems, efficient and accurate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018]In the following description, numerous specific details are set forth to provide a more thorough understanding of the present invention. However, it will be apparent to one of skill in the art that the present invention may be practiced without one or more of these specific details.
Loudspeaker Characterization System
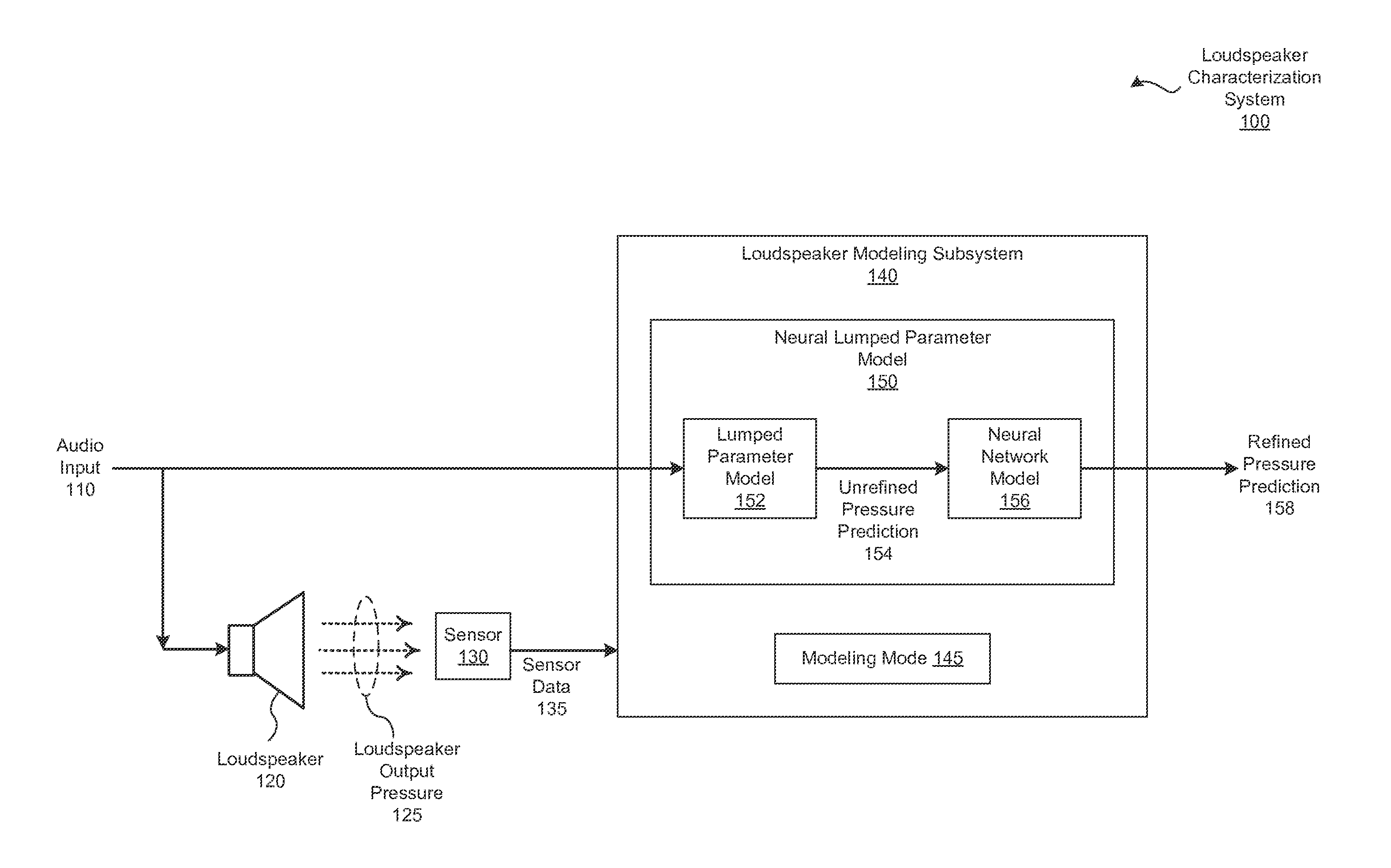
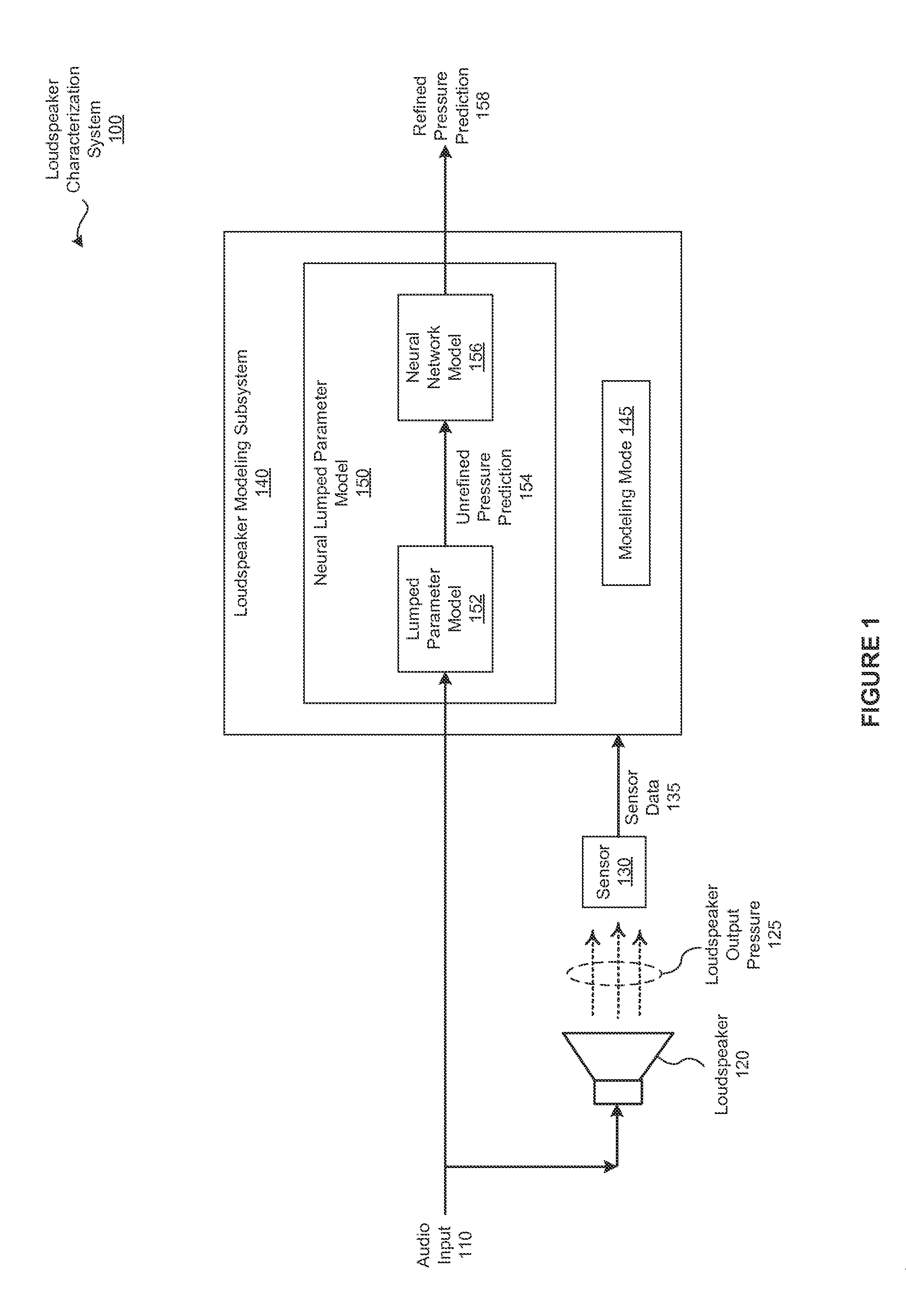
[0019]FIG. 1 illustrates a loudspeaker characterization system 100 configured to implement one or more aspects of the various embodiments. As shown, the loudspeaker characterization system 100 includes, without limitation, a loudspeaker 120, a sensor 130 and a loudspeaker modeling subsystem 140.
[0020]The loudspeaker 120 transforms an audio input 110 (i.e., an electrical audio signal) into a loudspeaker output pressure 125 to generate sound. The loudspeaker 120 may be implemented in any technically feasible fashion. For example, and without limitation, in some embodiments the loudspeaker 120 may be a “horn” loudspeaker. Alternatively, and without limitation, in some...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com