Method for automatic tracking 3D geological horizon
An automatic tracking and geological horizon technology, applied in seismic signal processing and other directions, can solve the problems of limited use range, difficult to widely use, and reduced tracking quality, and achieve the goal of improving tracking quality, improving work efficiency, and accurate spatial horizon tracking. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
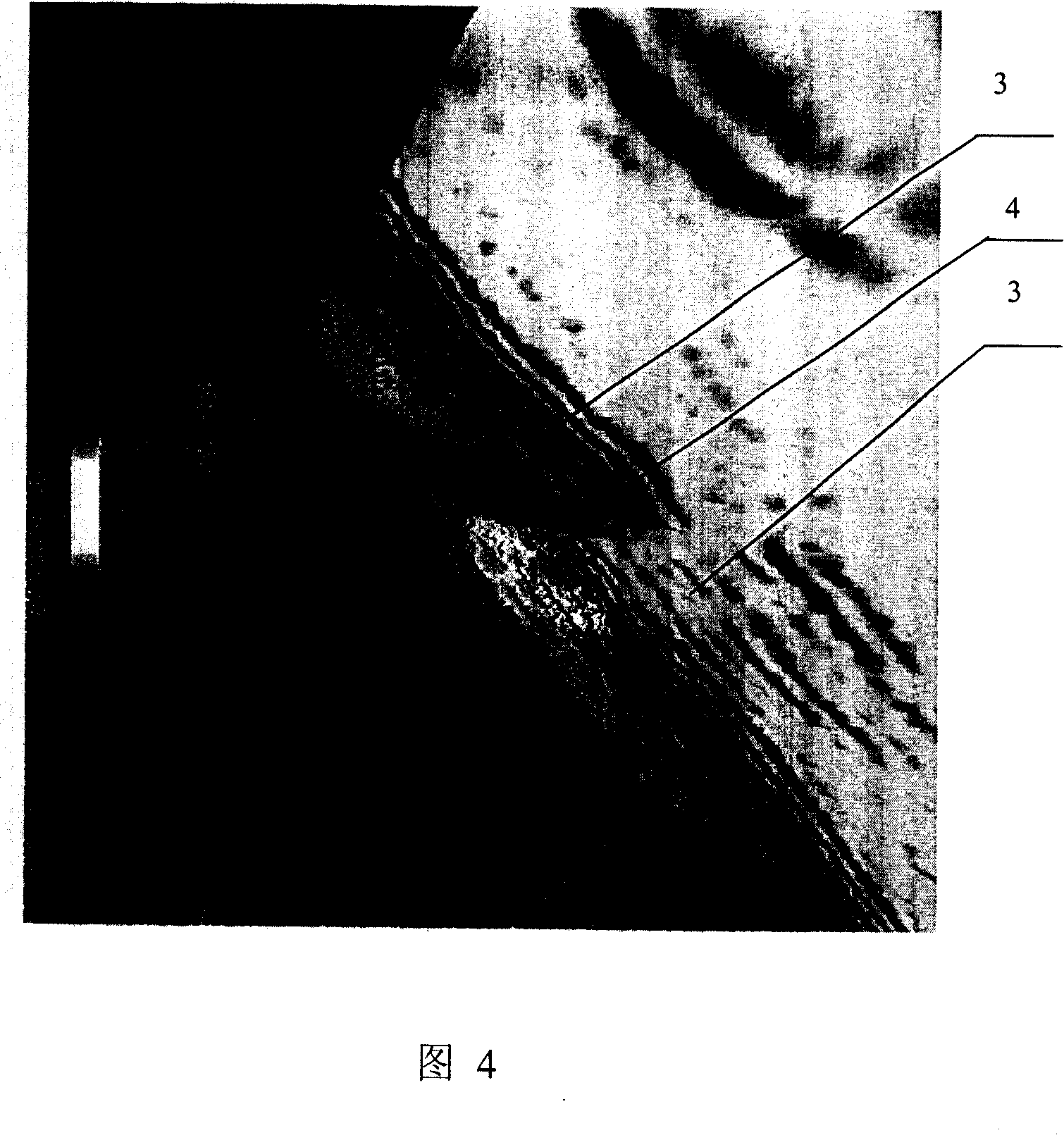
[0045] (1) In the collected seismic data, use the mouse to define 3 seed points in the 720th line section along the Line direction, as shown in Figure 7, three points 5, 6, and 7 are stored in the seed point queue. The order of storage is the same as the order of picking up seed points. The seed point queue is a linear queue, as shown in the figure below to illustrate the storage of seed points.
[0046] The first seed point picked
[0047] (2) Define the tracking range. The actual volume data used is Line direction: from 450 lines to 790 lines; CDP direction: from 350 to 500 channels; Time direction: from 1350ms to 1600ms. The defined tracking range can only be in Line, Within the scope of CDP. According to the actual data, choose to track all Lines and CDP ranges.
[0048] (3) Define the horizon automatic tracking parameters, where the picking position is the peak, the picking method is the correlation comparison algorithm and the amplitude comparison algorithm, ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] (1) Use the interpreted horizon data as seed points in the collected seismic data, and store them in the seed point queue.
[0057] (2) Define the tracking range.
[0058] (3) Define the horizon automatic tracking parameters, where the picking position is the trough, the picking method is the correlation comparison algorithm and the amplitude comparison algorithm, and the tracking method is the two-point calibration method.
[0059] (4) The user selects the name of the fault as a fault barrier, screens the fault data, removes faults without actual data, removes faults that cannot be constructed, and automatically fits each selected fault into a fault plane.
[0060] (5) Use the seed point whose serial number is 1 in the seed queue as the first current working seed point, and search for the target point in its adjacent lines and roads;
[0061] (6) The target points that have not been tracked and meet the horizon tracking conditions are compared with the seed points to ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] (1) Use the interpreted horizon data as seed points in the collected seismic data, and store them in the seed point queue.
[0066] (2) Define the tracking range.
[0067] (3) Define the horizon automatic tracking parameters, where the picking position is the zero-crossing point value, the picking method is the correlation comparison algorithm and the amplitude comparison algorithm, and the tracking method is the four-point calibration method.
[0068] (4) The user selects the name of the fault as a fault barrier, screens the fault data, removes faults without actual data, removes faults that cannot be constructed, and automatically fits each selected fault into a fault plane.
[0069] (5) Use the seed point whose serial number is 1 in the seed queue as the first current working seed point, and search for the target point in its adjacent lines and roads;
[0070] (6) The target points that have not been tracked and meet the horizon tracking conditions are compared with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com