Selectively aligning nanometer-scale components using AC fields
A selective, electric field technique used in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc. for materials and surface science
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
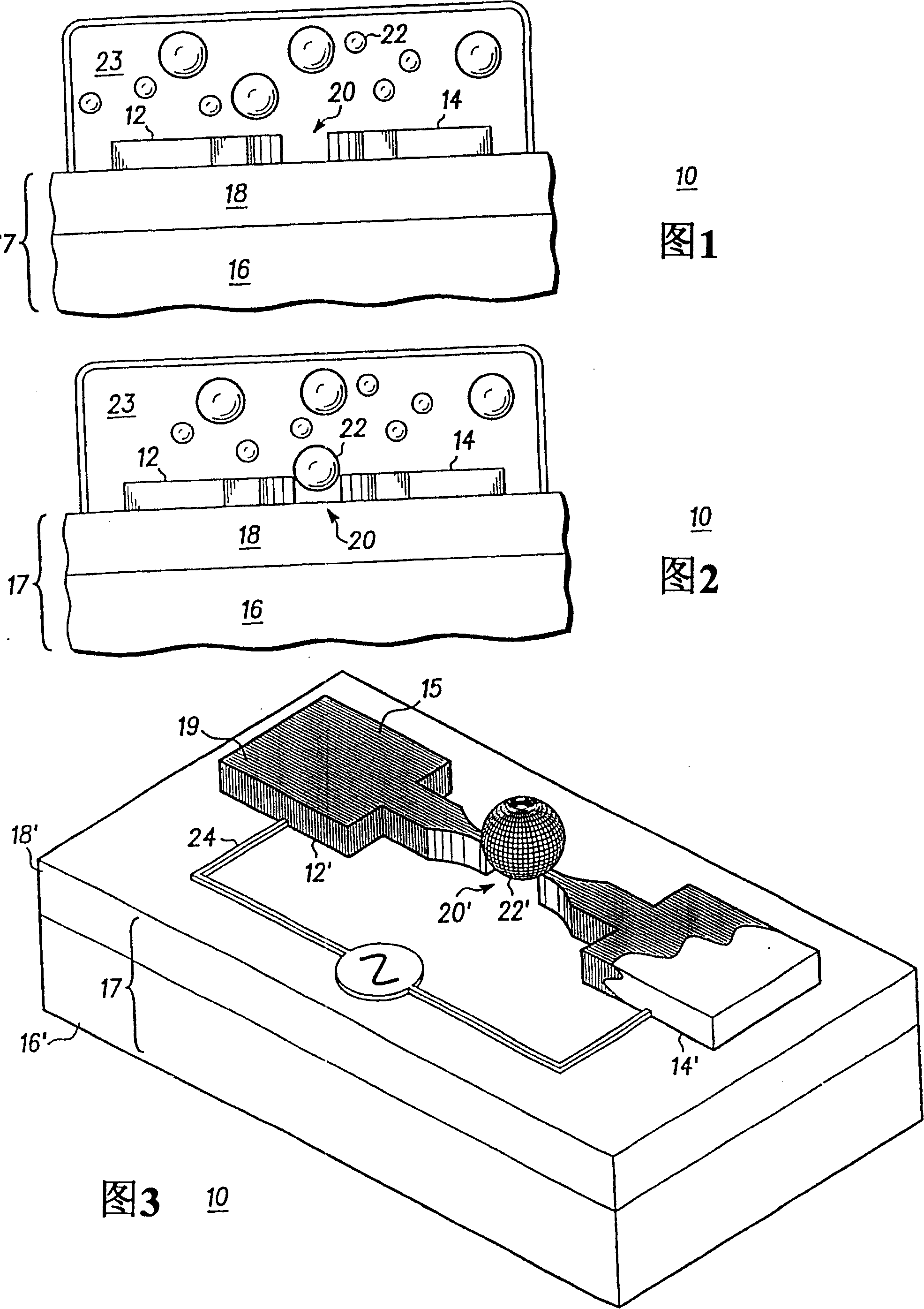
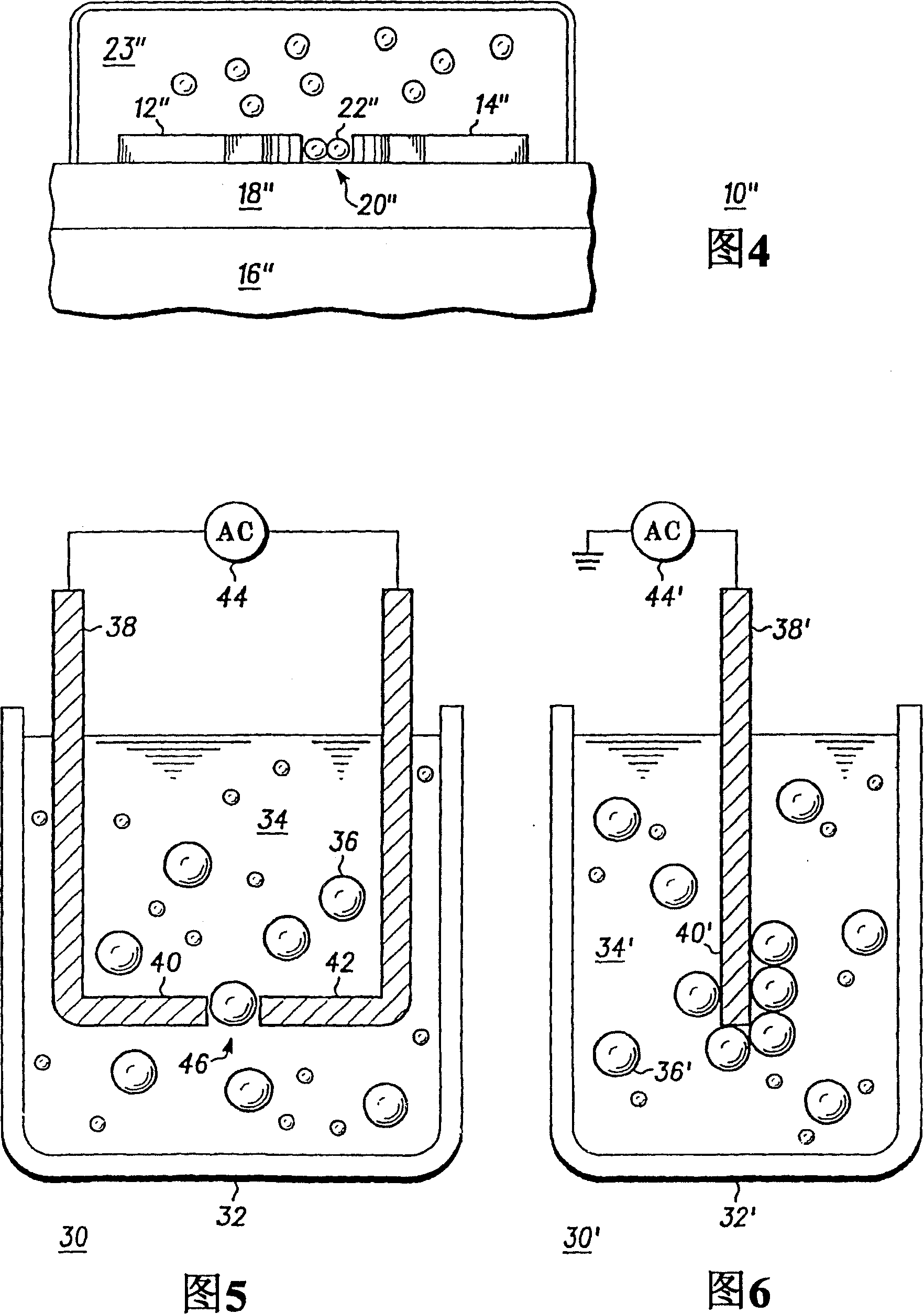
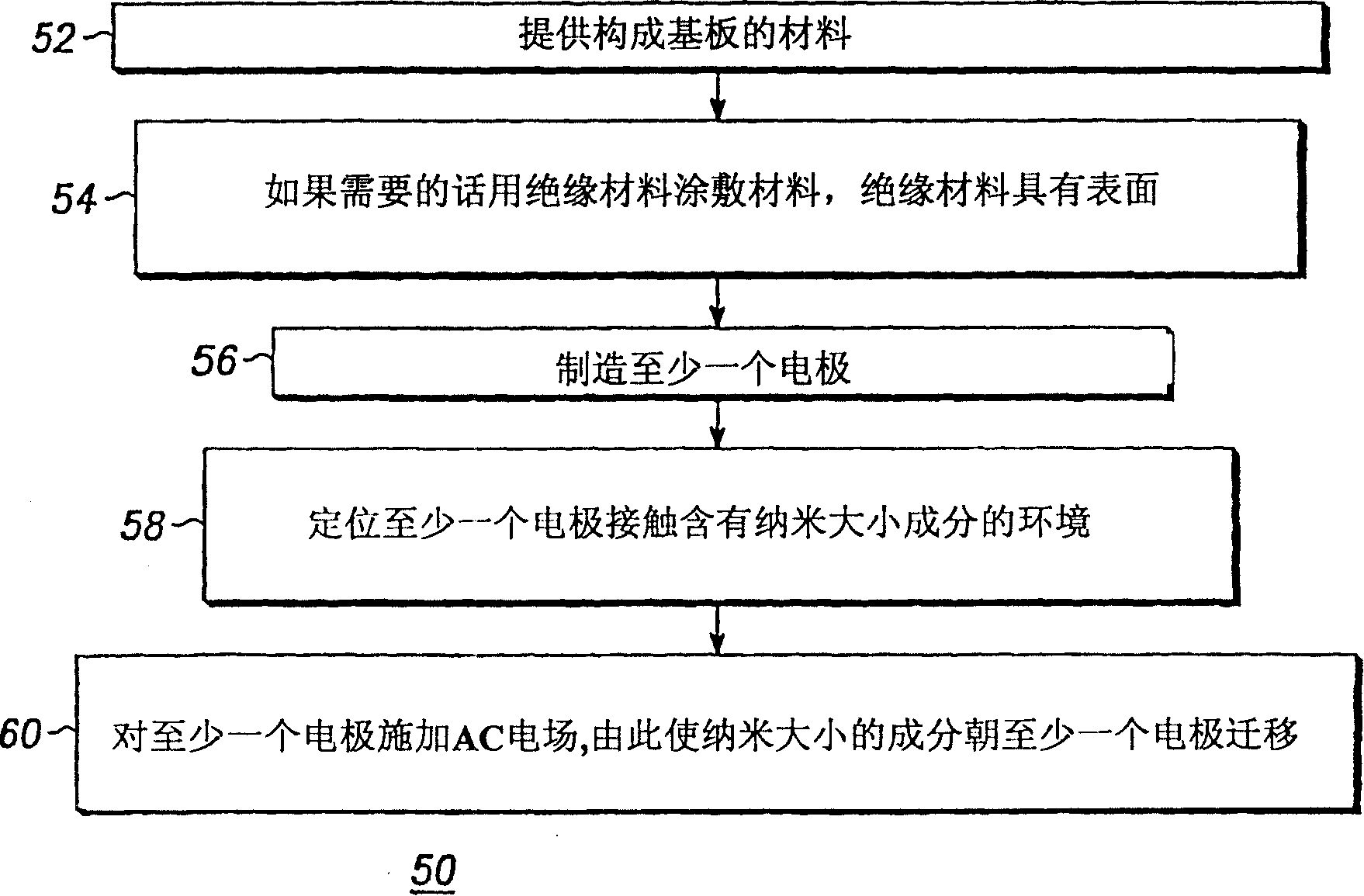
[0015] A molecular ensemble technique using alternating current (AC) electric fields is disclosed to facilitate selective alignment and migration measurements of electronic nanoscale components. For purposes of this disclosure, the term nano-sized components is intended to include nanoparticles, nanotubes, nanowires, nanorods, synthetic polymers, synthetic molecules, and biomolecules including DNA molecules, proteins, and the like. With proper selection of amplitude and frequency, the use of AC bias significantly enhances the desired nanocomposition ratio location of other contaminant species in solution, for example in solutions containing carbon nanotubes and organic or inorganic contaminants.
[0016] Referring now to FIGS. 1-2 , illustrated in simplified cross-sectional views are component structures for selective alignment of nanometer-sized components in accordance with the present invention and methods of using the structures to provide selective alignment. More specifi...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap