Method for identifying double-layer disc and optical disc apparatus
A discrimination method and a technology of an optical disc device, which are applied to optical recording/reproduction/erasing methods, optical recording carriers, recording information on magnetic disks, etc., and can solve the problems of inability to distinguish types and complex discrimination processing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example 1
[0087] In the case of DVD+RW (two-layer phase-change samples), the first protective layer (ZnSSiO 2 , thickness 70nm), the first information recording layer (Ag 5 In 5 Ge 5 Sb 67 Te 18 , thickness 17nm), the second protective layer (ZnSSiO 2 , thickness 17nm), and a reflective layer (Ag, thickness 120nm) that is easy to dissipate heat was provided thereon to form a first information recording structure.
[0088] On the other hand, on a transparent substrate (polycarbonate) with guide grooves, a protective layer (ZnSSiO2, thickness 65nm), a recording layer (Ag 5 In 5 Ge 5 Sb 67 Te 18 , thickness 7nm), protective layer (ZnSSiO2, thickness 18nm), ZrCO layer (thickness 3nm), reflective layer Ag, thickness 10nm), translucent layer (ITO, In 2 o 3 and SnO, thickness 100nm) to form the second recording layer structure.
[0089] The first recording layer structure and the second recording layer structure were bonded together with a UV curable resin (SD318) having a thicknes...
specific example 2
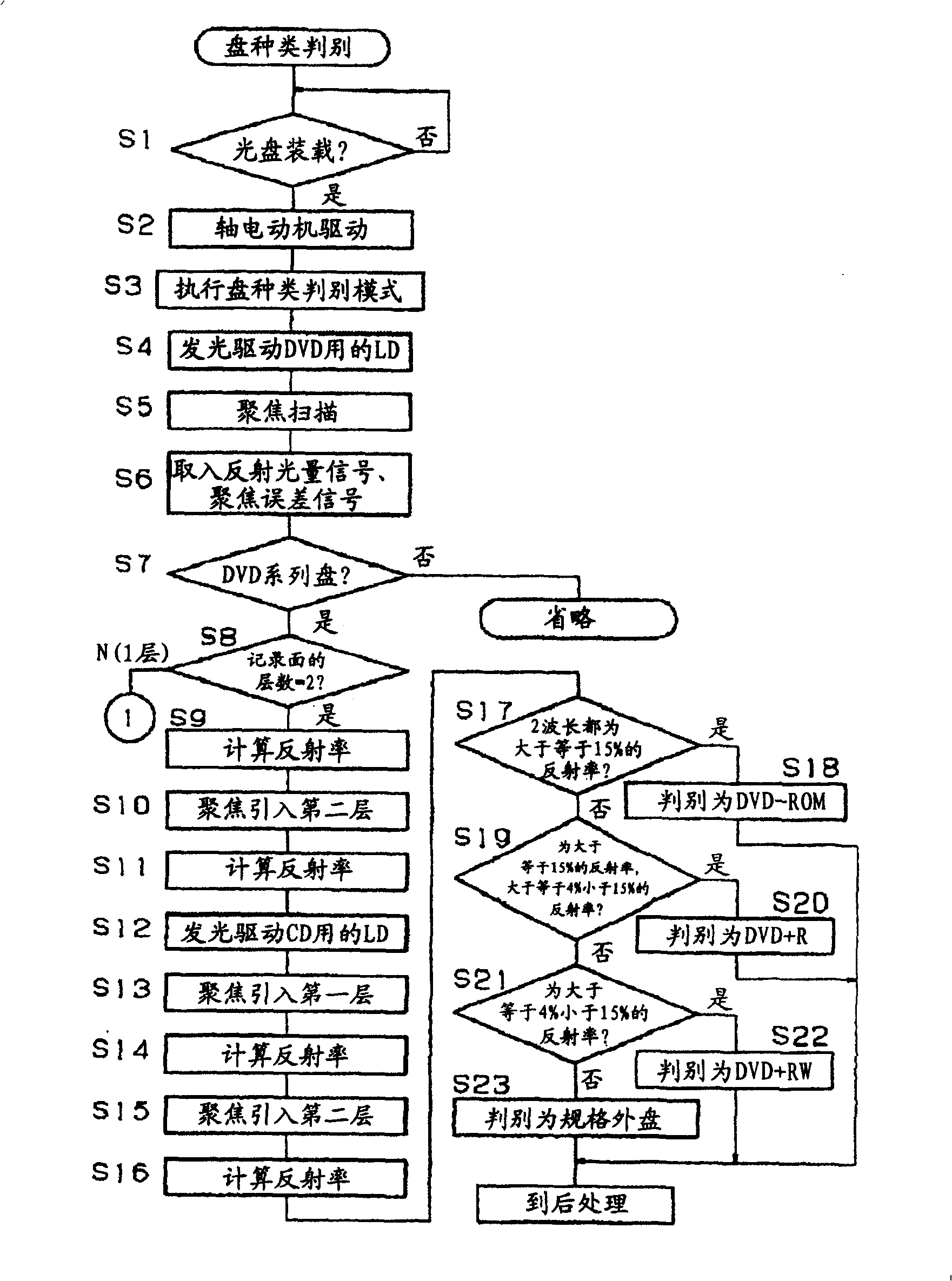
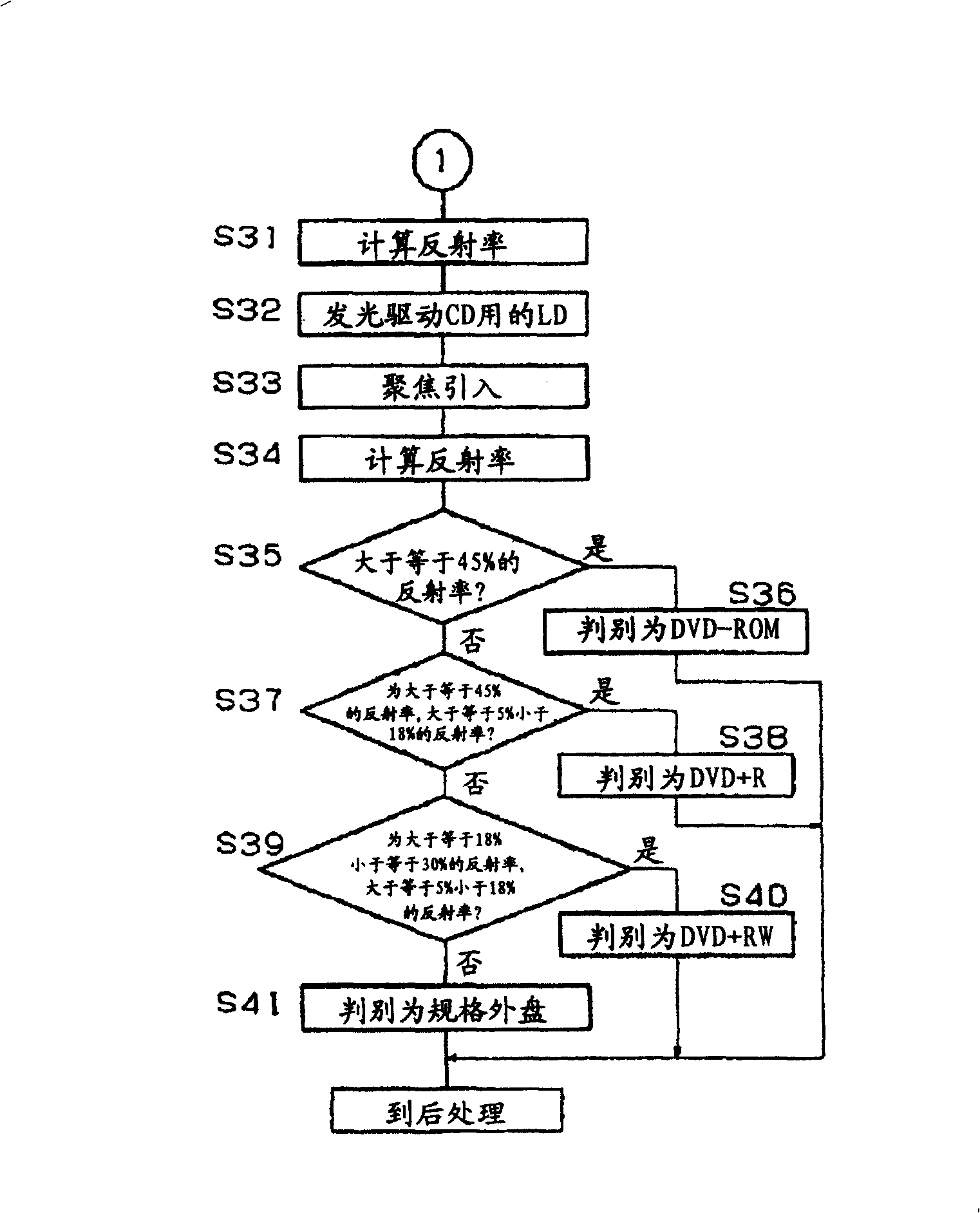
[0093] Screen printing (ultraviolet curing) lacquer (lacquer) on the light incident surface and reflective surface of the disc produced in Specific Example 1, the resin surface was added to the light incident surface and the result of loading it into the optical disc device 1 is based on the following The reflectance obtained from the RF signal when DVD wavelength = 660nm and CD wavelength = 780nm were focused was 1%, and it was judged not to be any of the ROM type, R type, and RW type. That is, according to figure 2 In the schematic flow shown, it can be determined that the disk is out of specification in step S23.
specific example 3
[0095] On the first substrate made of polycarbonate, the first pigment layer (cyanine) was formed by spin coating (spin coat), and the IZO (In 2 o 3 and ZnO mixture). On the other hand, after IZO was formed by sputtering as a second translucent layer on a second substrate made of polycarbonate, a second dye layer (cyanine) was formed by spin coating. Next, the first substrate on which the first pigment layer was formed and the second substrate on which the second pigment layer was formed were faced to each other so that the pigment layer was located inside, and they were bonded with UV curable resin (SD318) to obtain a two-layer disk. .
[0096] Furthermore, the thickness of each structural layer was controlled as follows and produced.
[0097] Two substrates: 0.6mm, 1st pigment layer: 60nm, 1st translucent layer: 80nm, resin intermediate layer: 55μm, 2nd pigment layer: 70nm, 2nd translucent layer: 100nm
[0098] Furthermore, the track pitch of the first substrate was set ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com