Conjugates of biologically active proteins having a modified in vivo half-life
A bioactive, bioactive polypeptide technology, applied in the field of changing the half-life of bioactive proteins, can solve the problems of increasing drug complexity, changing the biological activity or safety of bioactive proteins, and increasing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Cloning of chimeric DNA molecules
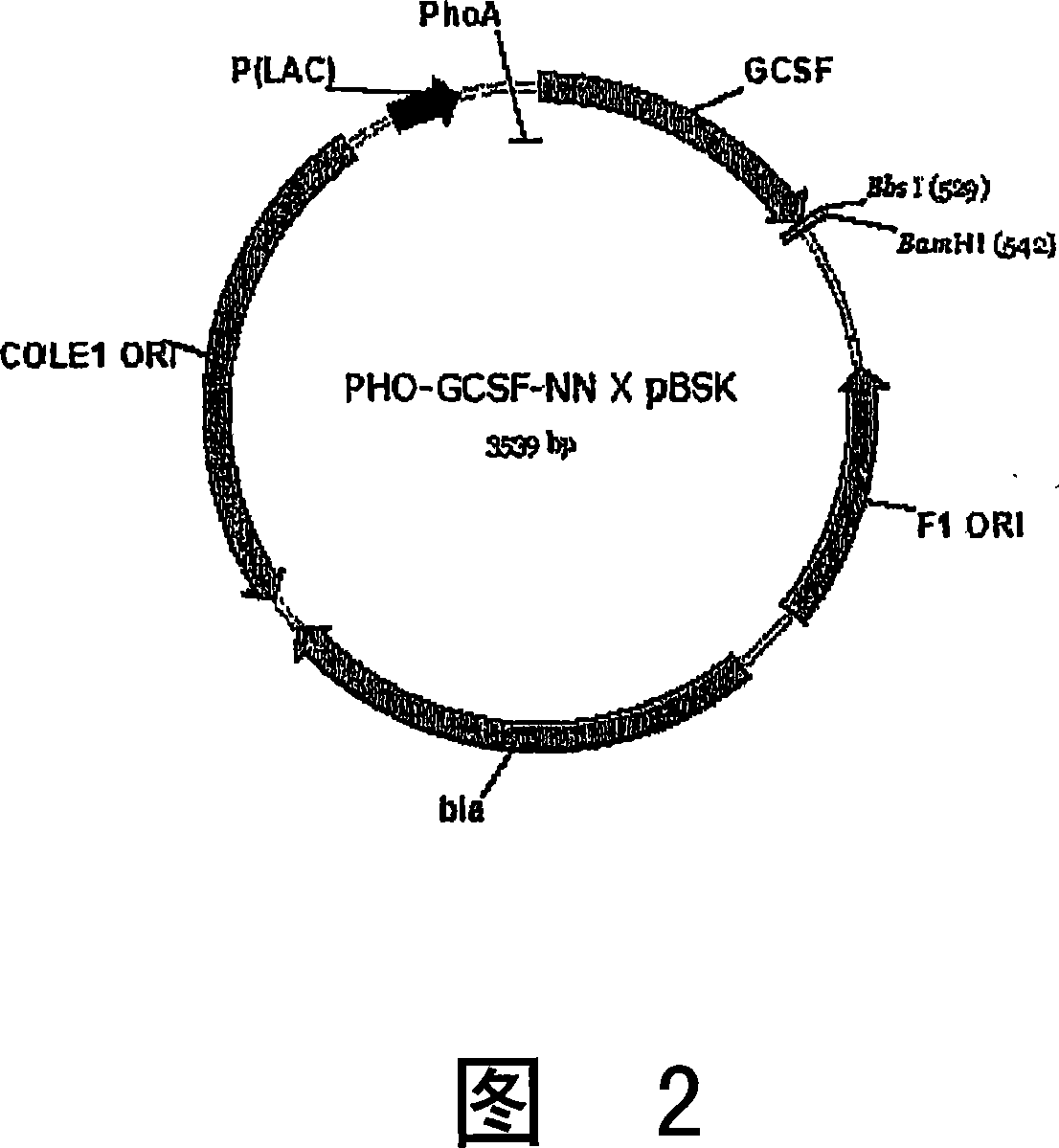
[0078] To facilitate downstream protein purification, it was decided to secrete the G-CSF-polymer protein into the cell culture medium. Previous experience with various cytokine-polymer constructs and bacterial (ST2) secretion signals has shown that they are secreted inefficiently in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. However, the Schizosaccharomycen pombe secretion signal sequence using pho1 + acid phosphatase (PHO) is known to enable secretion of heterologous proteins (GFP and HPV 16 E7) into the medium. Therefore, this secretion signal was tested in the CHO cell expression system with the G-CSF-polymer construct described below. Synthetic vectors for production of G-CSF-polymer constructs and expression of G-CSF-polymer are also described below.
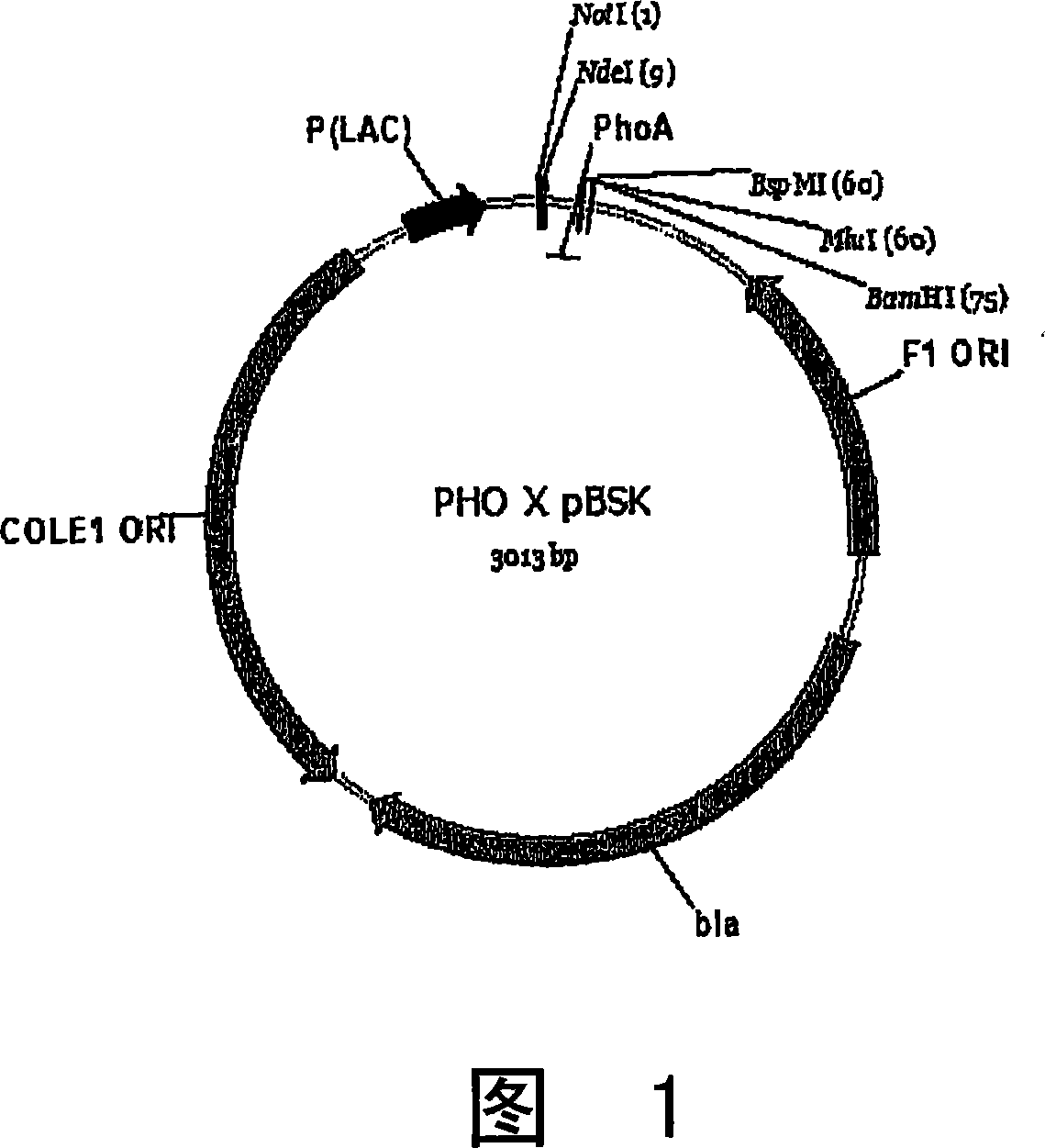
[0079] 1.A. Generation of PHO x pBSK constructs
[0080] PHO x PBSK construct
[0081] The first construct synthesized was simply the PHO leader cloned into the bacterial cloni...
Embodiment 2
[0152] Transformation of host cells and expression of chimeric DNA molecules
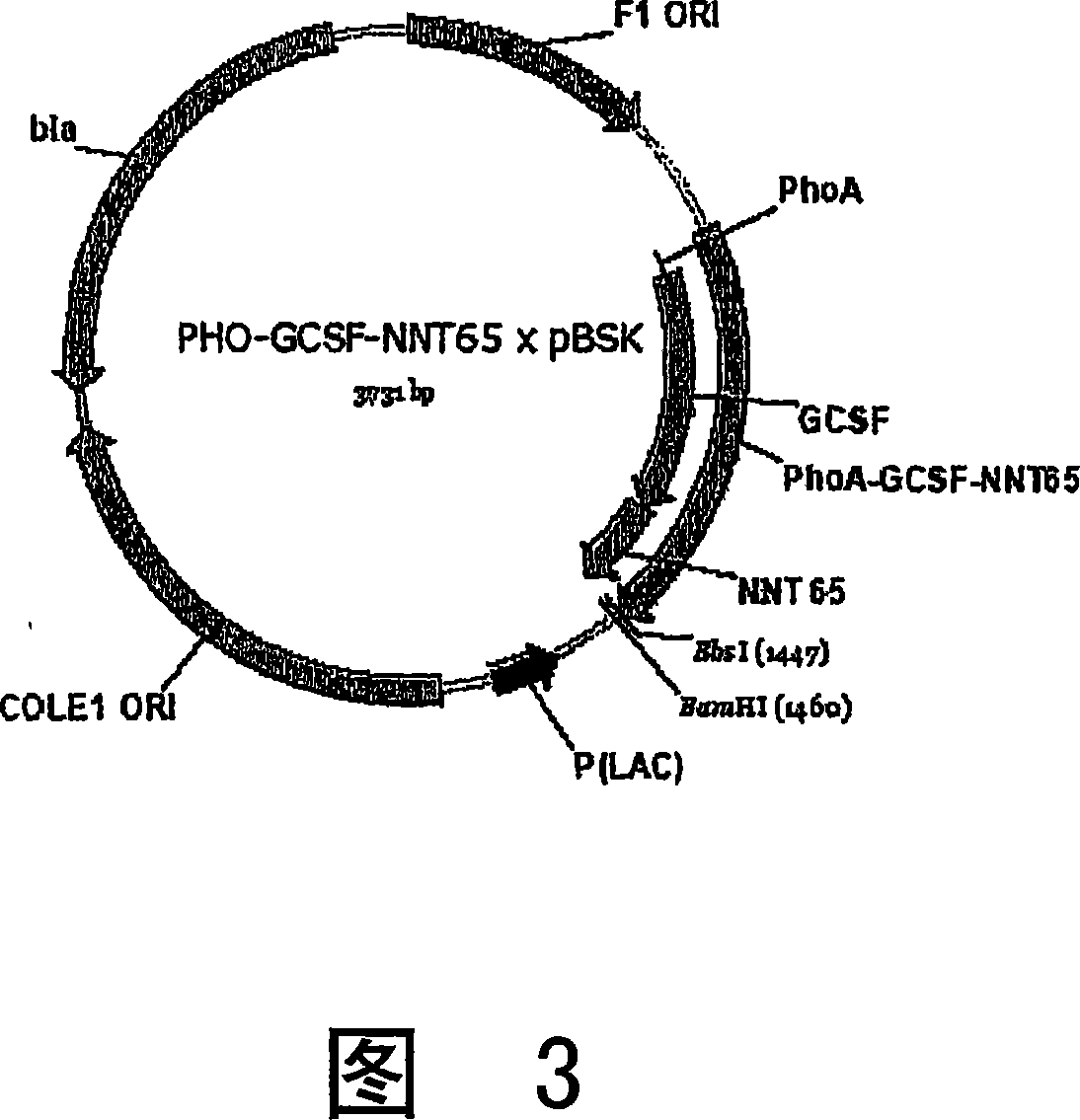
[0153] 2. A. Generation of PHO-G-CSF-(NNT)155 x pCE2 construct
[0154] Preparation of vector pCE2
[0155]Plasmid pCE2 was generated from plasmid pREP7b by the following operation. First, a 2000 bp EBNA coding region was deleted. Second, pBR322ori was replaced with pKS-ori. Then, the RSV promoter region was replaced with the CMV enhancer and elongation factor-1a (EF-1a) promoter and intron.
[0156] The CMV enhancer was derived from a 380 bp XbaI-Sph1 fragment generated from pCEP4 (Invitrogen, San Diego, CA) by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with the following primers:
[0157] 5'-GGCTCTAGAT ATTAATAGTA ATCAATTAC-3'; and
[0158] 5'-CCTCACGCAT GCACCATGGT AATAGC-3'.
[0159] The EF-la promoter and intron (Uetsuki et al., J. Biol. Chem. 264:5791-5798 (1989)) were derived from a 1200 bp SphI-Asp718I fragment generated by PCR from human genomic DNA using the following primers:
[0160] 5'-GGTG...
Embodiment 3
[0192] Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of G-CSF-(NNT)155 Conjugates
[0193] The pharmacokinetic parameters of the G-CSF-(NNT)155 protein conjugate were evaluated. Three other compounds were included as positive controls. Controls were Neulasta (PEG-G-CSF), Neupogen (rh-G-CSF) and G-CSF compounds. The compound was tested by a single intravenous (i.v.) administration to mice and blood was collected 72 hours post-dose. Plasma was analyzed by ELISA.
[0194] 3.A. Analysis method
[0195]The assay employs a quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique. Microplates were pre-coated with G-CSF-specific monoclonal antibodies. Add standards and samples to each well. The immobilized antibody binds the G-CSF present. After washing away unbound material, a G-CSF-specific enzyme-linked polyclonal antibody was added to each well. After washing away unbound antibody-enzyme reagent, the substrate solution is added to each well, producing a color proportional to the amount of G-CSF bo...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap