System, method and apparatus for implementing business continuity in household network circumstance
A home network and business continuity technology, applied in the home network field, can solve the problems of loss of program content, inability to better adapt to different applications and users, and inability to obtain user attributes and business context information correlation, etc., to achieve a good experience. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0064] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention more clearly, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
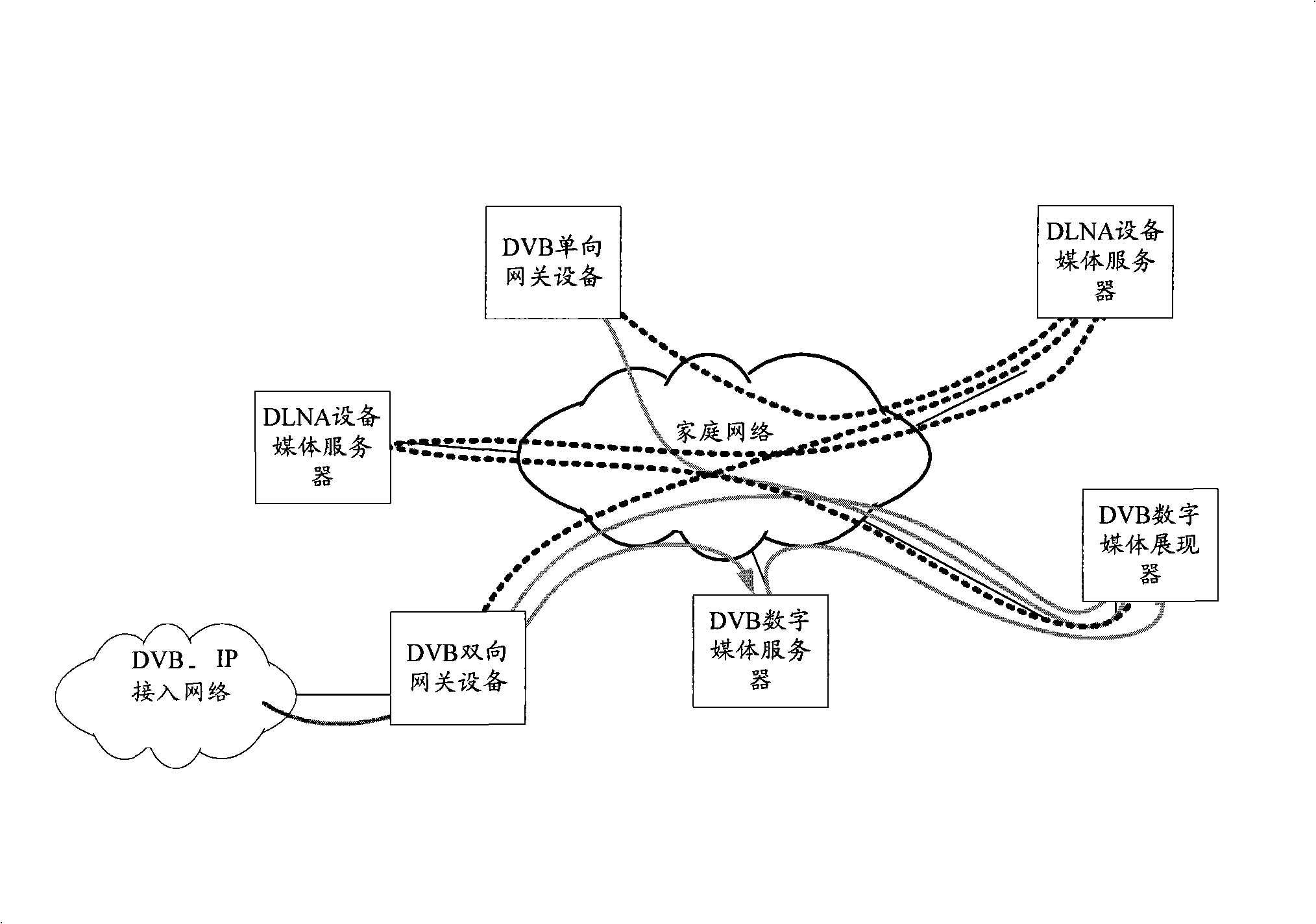
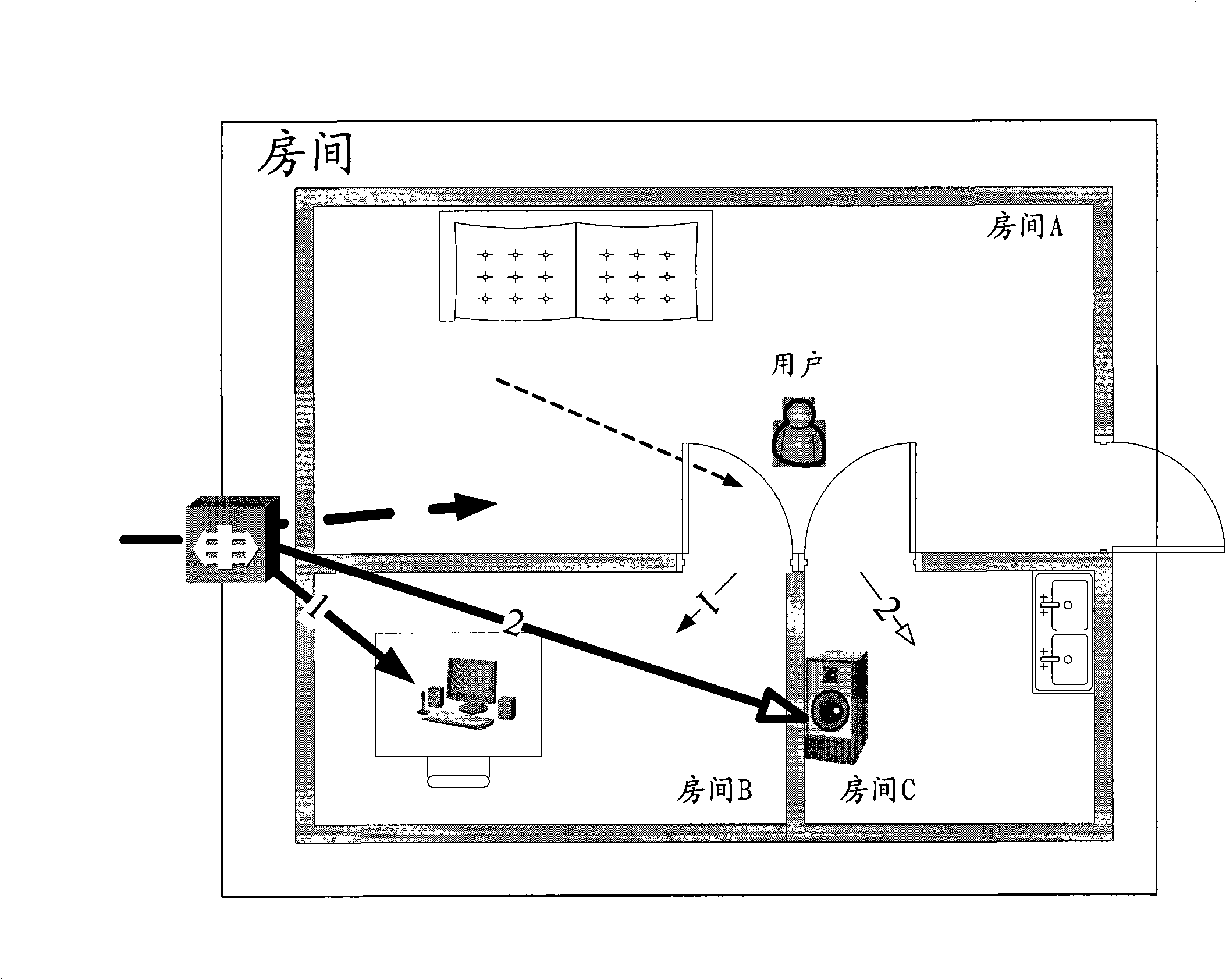
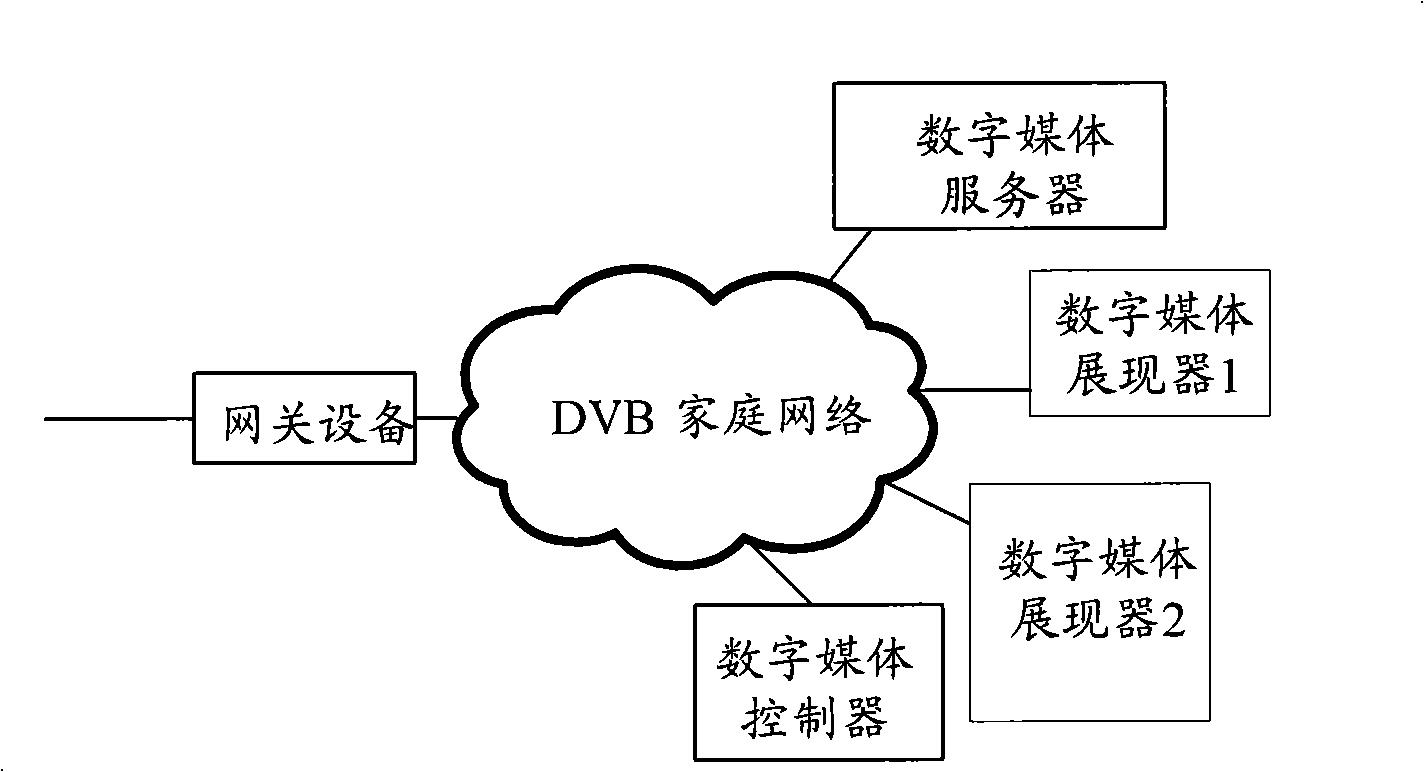
[0065] First, the concept of business continuity is explained. The continuous use of services among multiple devices refers to the continuous consumption of services for users. What users need is business continuity (delay, jitter, etc. are within a tolerable range), and they don't care about changes in underlying sessions. At the business session level, switching between devices will inevitably lead to changes in some session participating entities, paths, etc., the original session where these changes occur will end, and a related new session will also be generated.
[0066] The embodiment of the present invention is aimed at the home network environment, provides the function of automatically switching and using the service among ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com