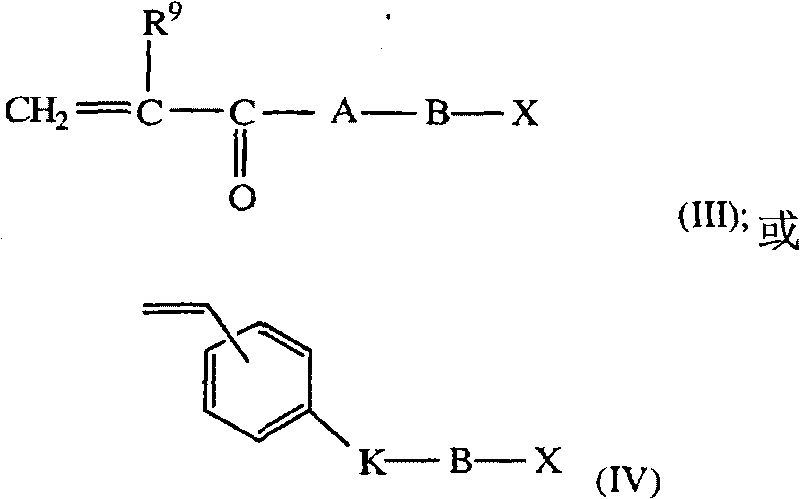
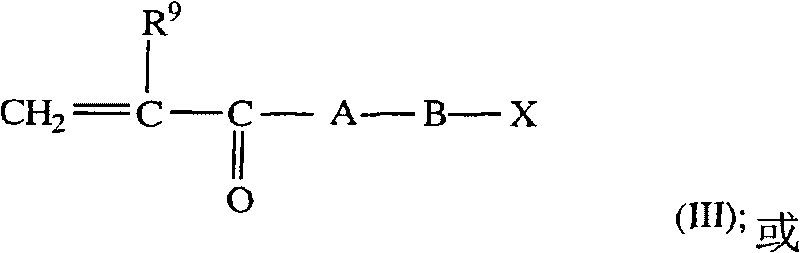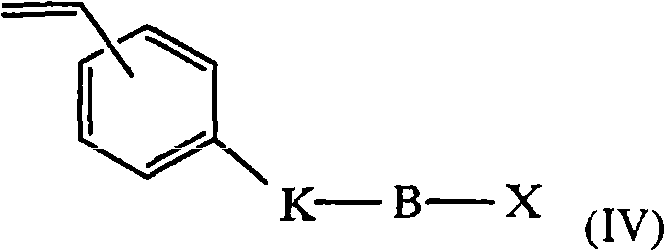Ophthalmic solutions
A solution, ophthalmic technology, applied in application, lens cleaning composition, packaging sterilization, etc., can solve the discomfort of lens wearers and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0173] Preparation of Silicone Hydrogel Lenses
[0174] A monomer mixture was prepared by mixing the ingredients in Table 1 below, where the amounts are parts by weight.
[0175] Table 1
[0176] Element
[0177] The resulting monomer mixture is cast into contact lenses by introducing the monomer mixture into a mold assembly consisting of two polypropylene mold parts, wherein the front mold part has a mold surface for forming the front surface of the contact lens, and the rear The mold part has a mold surface for forming the back surface of the contact lens. The molding part and monomer mixture are then exposed to ultraviolet light to induce free radical polymerization and cure the monomer mixture to form a contact lens. The resulting contact lens was removed from the mold assembly and extracted in a 60°C oven for 1 hour to release the dried lens from the mold.
Embodiment 2
[0179] The lenses of Example 1 were post-treated with a copolymer of NVP and dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, quaternized with a 20% aqueous solution of diethyl sulfate obtained from Aldrich Chemical Company (Milwaukee, Wisconsin).
[0180] Control lenses (Control Lenses) were prepared by plasma treating the lenses of Example 1 with ammonia gas, followed by extraction with isopropanol for 2 hours, hydration in deionized water, and autoclaving (121°C) in borate buffered saline . By plasma treating the lens of Example 1 with ammonia gas, followed by extraction overnight in a solution made of a mixture of deionized water (70 mL), acrylic acid (13.12 g), NaOH (8.526 g) and isopropanol (350 mL), Hydrate in deionized water containing 30 ppm of NVP and dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate copolymer, quaternize overnight with diethyl sulfate (Aldrich Chemical Company), store in borate buffered saline, and autoclave Sterilization (121° C.) to prepare test lenses according to the invention ...
Embodiment 3
[0199] Preparation of Copolymers of 3-Methacryloylaminopropyl-Dimethyl(3-sulfopropyl)ammonium Hydrochloride (MAPSA) and Glyceryl Methacrylate (GM)
[0200] MAPSA (0.925 g, 3.163 mmol, from Aldrich Chemical Company) was dissolved in 50 ml of deionized water. Into a 250ml three-neck flask equipped with a stir bar and a condenser (connected to an oil bubbler) was added deionized water (150ml), GM (4.963g, 31.02mmol) (via syringe), MAPSA solution and azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN, 0.050 g). The reaction mixture was sparged vigorously with nitrogen for 20 minutes with stirring, after which the nitrogen flow was reduced. The reaction mixture was heated to 70°C with an oil bath and maintained at this temperature for 48 hours under a continuous nitrogen purge. Store the product in deionized water.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com