Double-wire welding control method
A control method and filler wire technology, applied in welding equipment, manufacturing tools, arc welding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of complex welding torch structure, high price, and high price, and achieve the effect of simple discrimination means
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
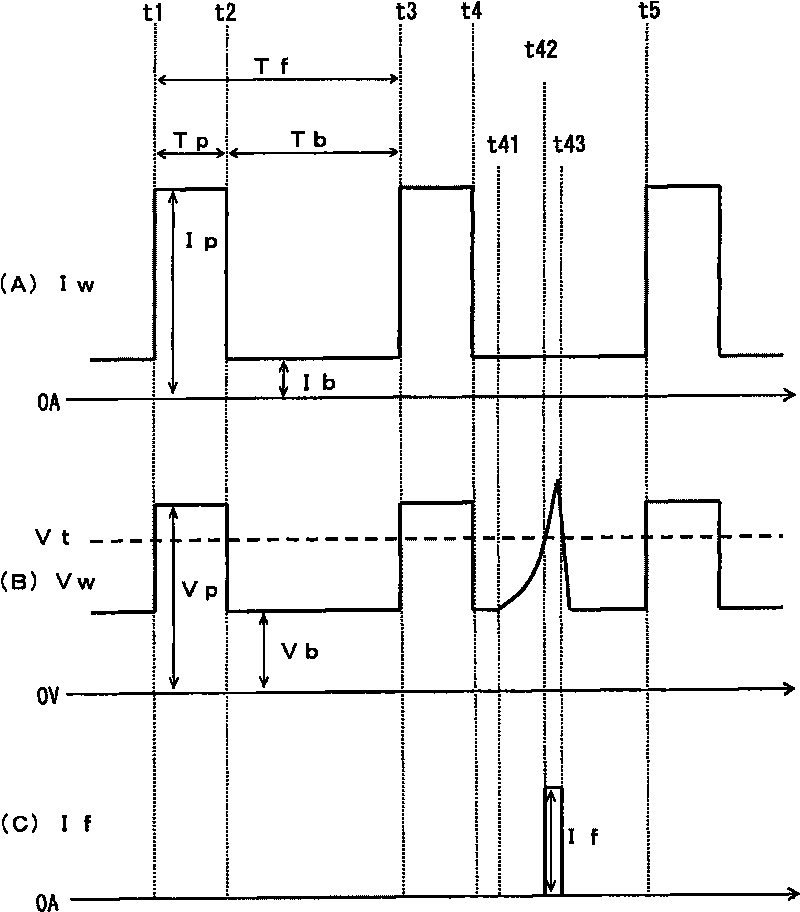
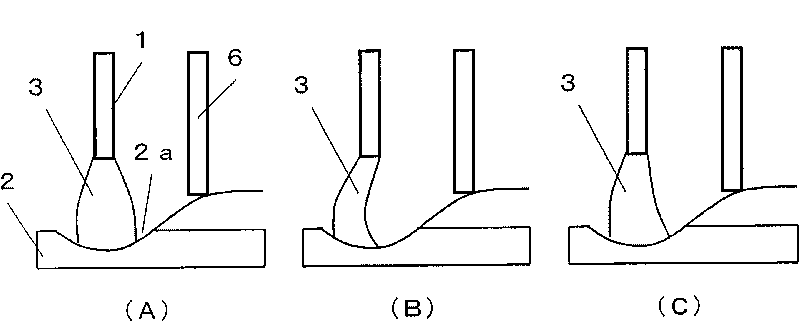
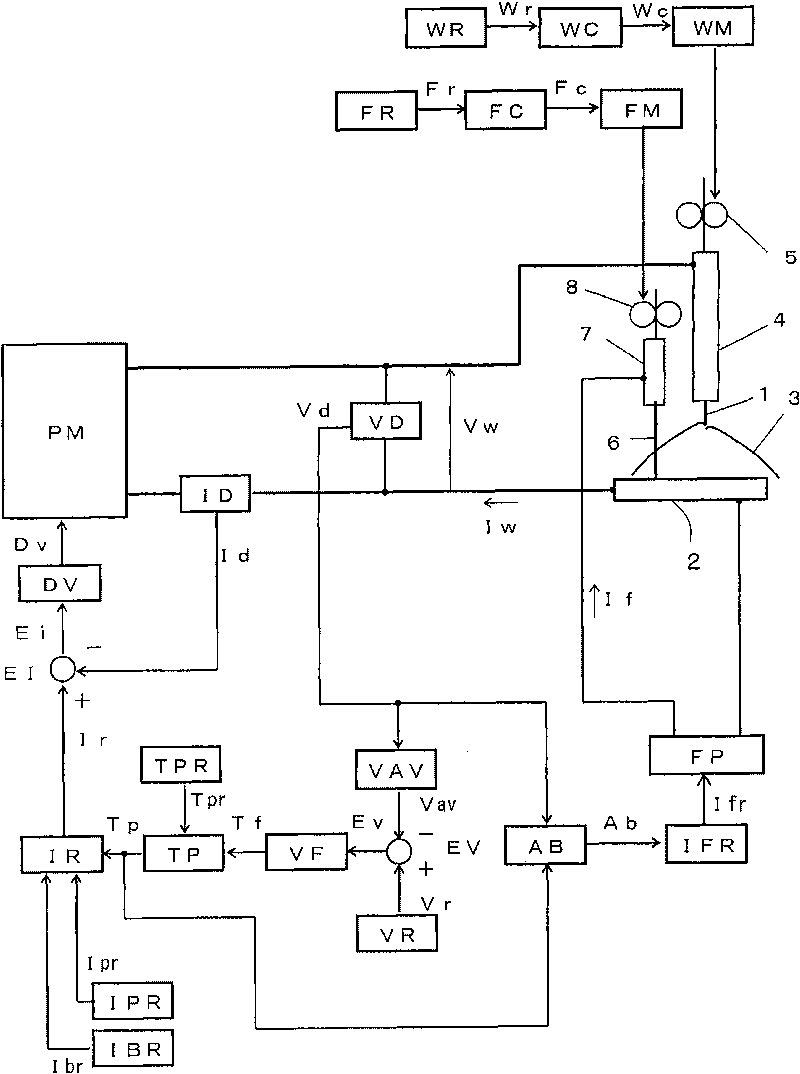
[0034] (Embodiment 1) figure 1 It is a current / voltage waveform diagram showing the twin wire welding control method according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The same figure (A) shows the change with time of the welding current Iw, the same figure (B) shows the change with time of the welding voltage Vw, and the same figure (C) shows the current If passed through the filler wire. In the same figure, in the pulse period from time t1 to t3, the stable welding state without arc deflection is shown, and in the following pulse cycle from time t3 to t5, the welding state in which arc deflection has occurred is shown. when. Hereinafter, the arc deflection countermeasure of the present embodiment will be described with reference to the same drawings.
[0035] During the pulse period from time t1 to t3, arc deflection does not occur, and thus the welding state is stable. During the peak period Tp from time t1 to time t2, as shown in (A) the peak current Ip is passed, and...
Embodiment approach 2
[0053] (Embodiment 2) Embodiment 2 differs from Embodiment 1 described above in the following points. That is, in Embodiment 1, when the occurrence of arc deflection is determined based on the rise of the base voltage Vb, the filling wire current If is started to flow. This operation is also the same in Embodiment 2. Furthermore, in Embodiment 1, when it is determined that the arc deflection is eliminated based on the drop in the base voltage Vb, the supply of the filler wire current If is stopped. On the other hand, in Embodiment 2, the filler wire current If is supplied only for a predetermined period after occurrence of arc deflection is determined. Hereinafter, Embodiment 2 will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0054] Figure 4 It is a waveform diagram showing the current / voltage of the twin wire welding control method according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The same figure (A) shows the time change of the welding current Iw, the same figure (...
Embodiment approach 3
[0061] (Embodiment 3) Embodiment 3 differs from the above-mentioned Embodiments 1 and 2 in the following points. That is, in Embodiments 1 and 2, when the occurrence of arc deflection is determined from the rise of the base voltage Vb, the supply of the filler wire current If is started. This operation is also the same in Embodiment 3. Furthermore, in Embodiment 1, when it is determined that the arc deflection is eliminated from the drop in the base voltage Vb, the supply of the filler wire current If is stopped. In addition, in Embodiment 2, the supply of the filler wire current If is stopped after a predetermined period of time elapses from the time when the generation of arc deflection is discriminated. On the other hand, in Embodiment 3, the fill current If is supplied during the period from when arc deflection is detected to when the next cycle of peak voltage Vp is applied to the welding wire (supply of peak current Ip). Hereinafter, Embodiment 3 will be described with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com