Method for compressing, storing and restoring pixel information of RGB (Red, Green and Blue) space image region
A technology of RGB space and image area, applied in the field of RGB space image area pixel information compression, storage and restoration, can solve problems such as affecting operation efficiency, and achieve the effect of saving storage space and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
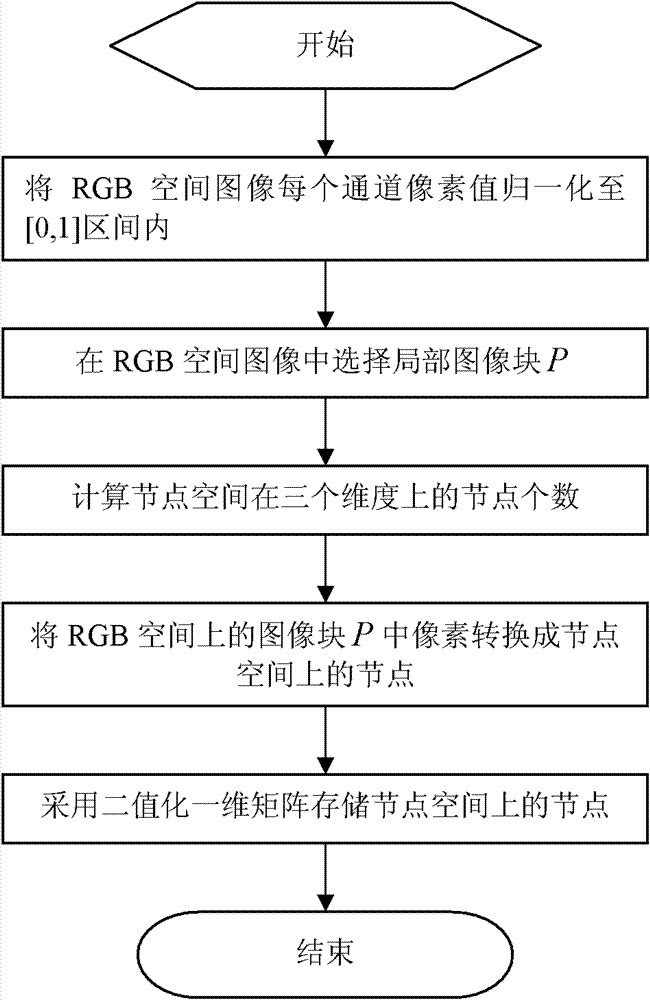
[0050] This embodiment describes a method for compressing and storing pixel information of an RGB spatial image region. Such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0051] (1) Normalize the pixel value of each channel of the RGB space image to the [0, 1] interval.
[0052] (2) Select a local image block P in the RGB space image.
[0053] Assume that the local image block P contains a total of S pixels, and each pixel has a value of three channels of RGB. First use a matrix vecP with S rows and 3 columns to temporarily store the values of three channels of S pixels, each row stores a pixel, and each column stores a channel value of a pixel.
[0054] (3) Calculate the number of nodes in the three dimensions of the node space according to the extreme values of the three-dimensional coordinates of the pixels in the image block P in the RGB space.
[0055] In order to ensure the compression effect, the total number of nodes in the node space is set ...
Embodiment approach 2
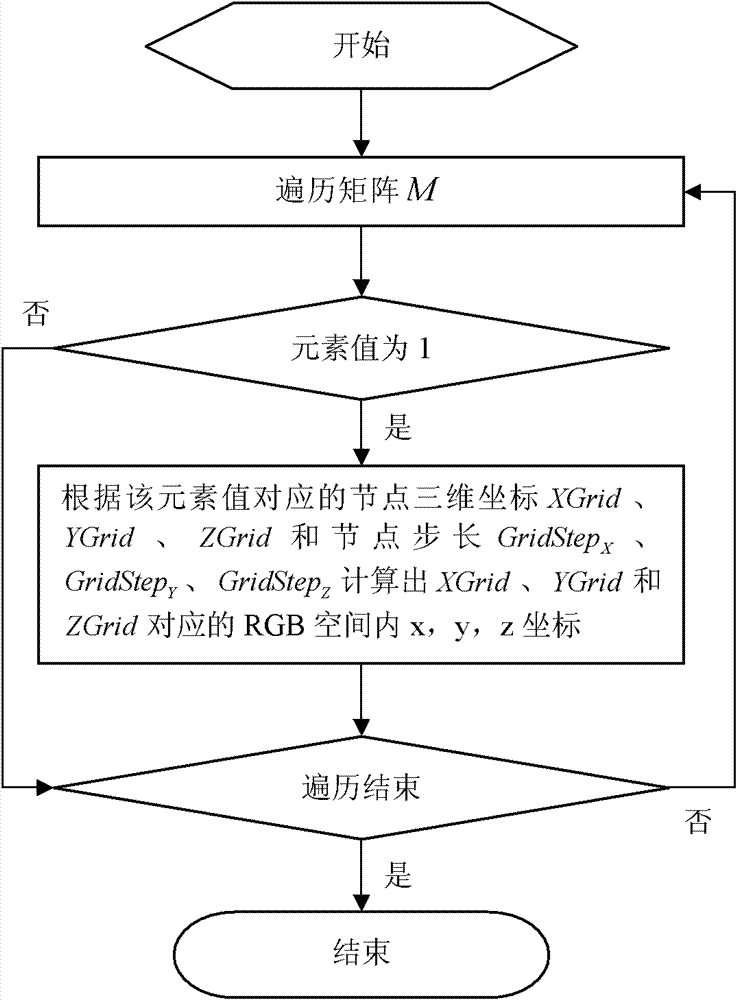
[0080] This embodiment describes the restoration method of the RGB spatial image area pixel information stored by the method described in Embodiment 1, as follows figure 2 shown. Traverse each node in the node space point by point, if the node is set to 1, then the pixel in the RGB space of its corresponding position is also marked. Specifically, a certain point in the node space Grid pAs an example.
[0081] Traverse the matrix M in the order of X, Y, and Z, and set the node Grid p The corresponding three-dimensional coordinates are XGrid, YGrid and ZGrid respectively. As described in Embodiment 1, the value of the Lth element in the matrix M is Grid p The corresponding node value.
[0082] When traversing to the element value, if the value is 0, it means that there is no corresponding node in the node space at this position. If it is 1, it means that the node exists, and further calculate its corresponding coordinate value in the RGB space. Let the coordinates in the...
Embodiment approach 3
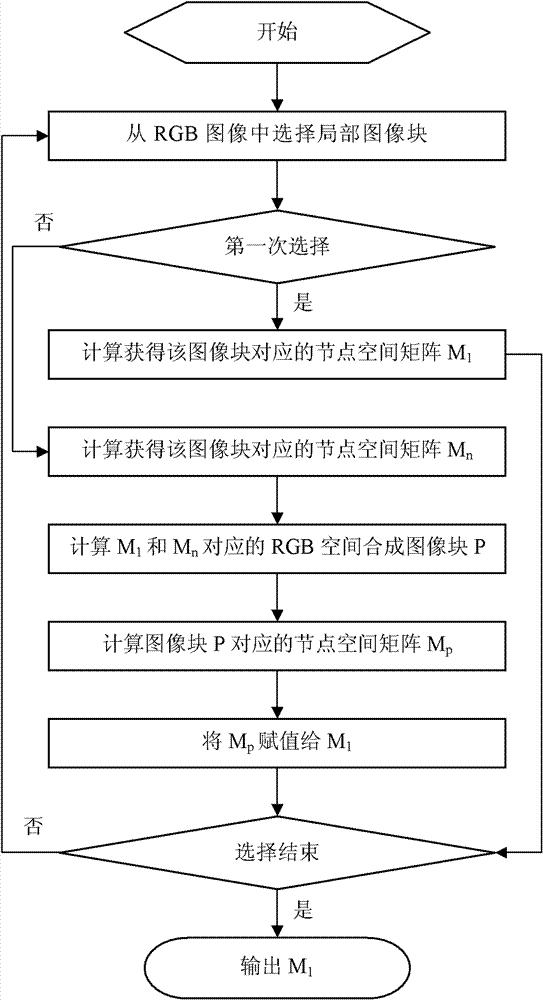
[0086] This embodiment describes a method for compressing and storing pixel information in multiple regions of an RGB spatial image, such as image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0087] (1) Select the local image block P of the pixel block for the first time 1 , using the method described in Embodiment 1 to calculate and obtain the matrix M 1 ;
[0088] (2) Then select the local image block P 2 , using the method described in Embodiment 1 to calculate and obtain the matrix M 2 ;
[0089] (3) Using the method described in Embodiment 2 to convert M 1 and M 2 At the same time, the transformation from the matrix to the RGB space is performed to obtain the local image block P 3 ;
[0090] (4) For local image block P 3 , using the method described in Embodiment 1 to calculate and obtain the storage matrix M 3 , the M 3 assigned to M 1 ;
[0091] (5) If no new local image blocks are selected, output M 1 ; If a local image block is selected again, go to step (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com