Apparatus and method for reducing gaseous inclusions in a glass
An inclusion, gaseous technology, used in glass furnace equipment, glass manufacturing equipment, feed troughs, etc., to solve problems such as high disposal cost waste, limiting clarifier clarification and oxygen reabsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
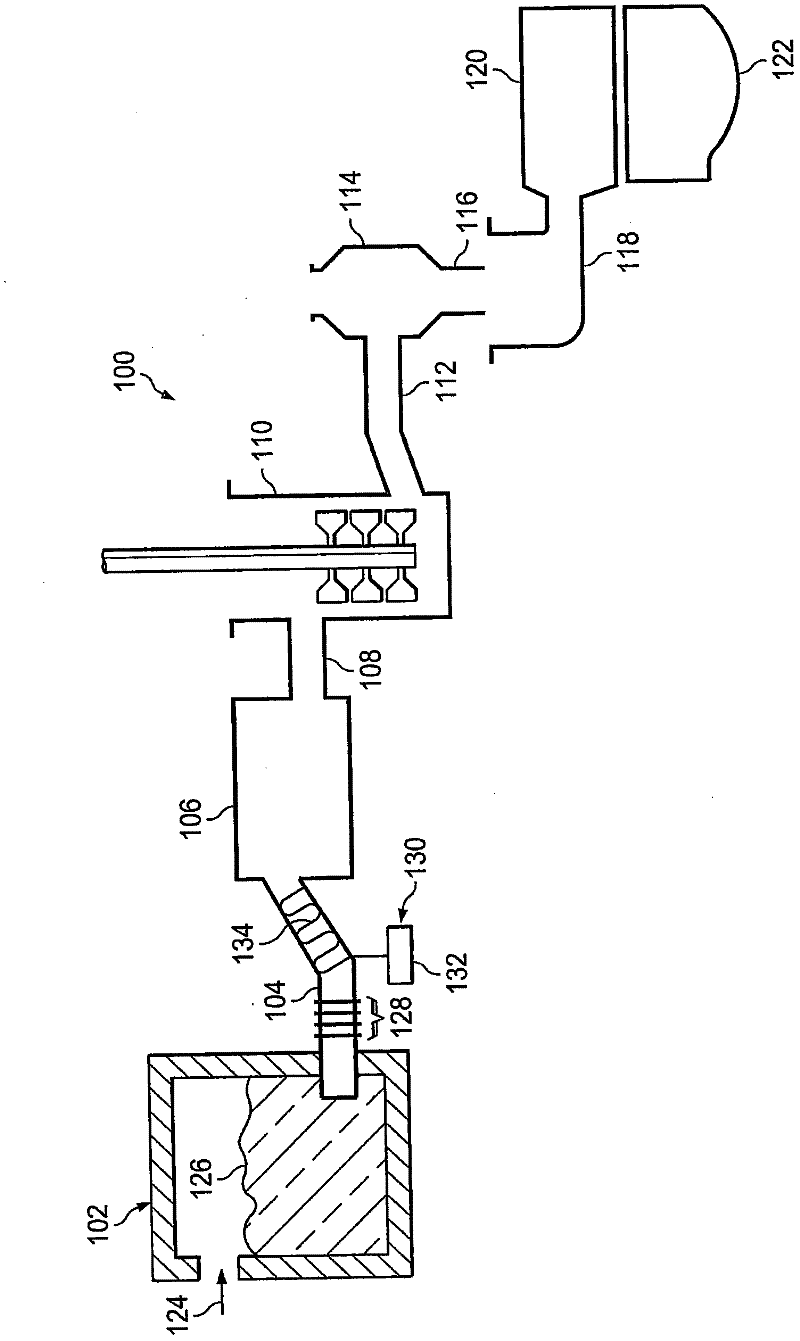
[0056] In the clarification step, the oxygen released by the clarifier at high temperature can promote the growth of bubbles through the diffusion of dissolved gas into the bubbles. In the fining vessel 406 , the gas bubbles float to the free surface of the molten glass 426 where they break up and the gas is expelled from the molten glass 426 .
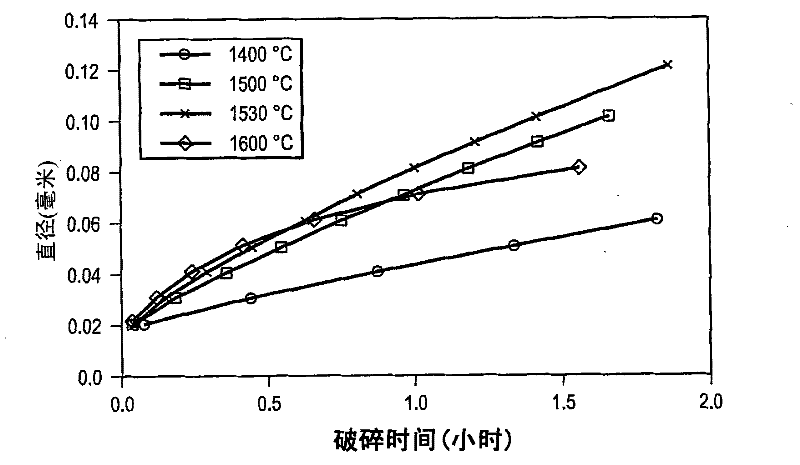
[0057] Once the clarification of the molten glass 426 is completed, the molten glass 426 flows into the cooling refractory tube 408 and is cooled to the cooling temperature T C , the cooling temperature is lower than the clarification temperature (T F ), shifting equation (2) to the left, consuming oxygen in the molten glass 426 and reducing the size of the bubbles. Eventually, the bubble shrinks to a certain size and collapse occurs simultaneously. Because this embodiment of the invention (as well as previous embodiments) relies on bubble collapse rather than gas escape, no melt free surface is required, but if a melt free surface ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com