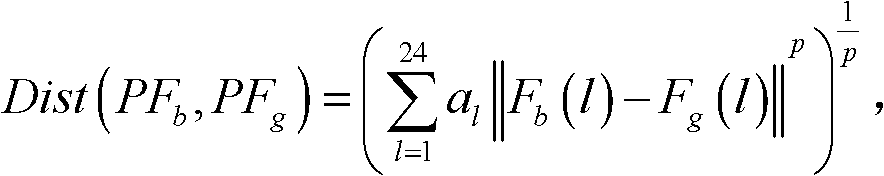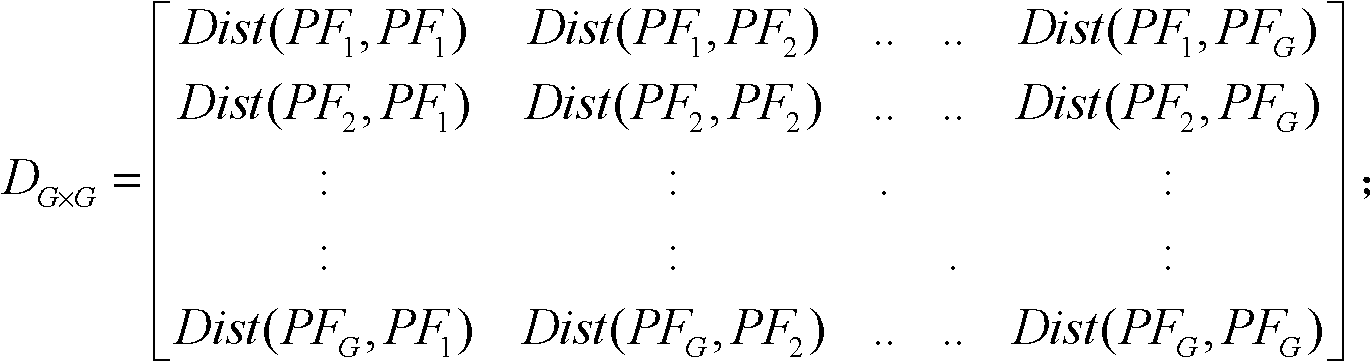Method for identifying abnormality of customers in futures market
An identification method and customer technology, applied in the information field, can solve the problems of high misjudgment, low efficiency, abnormal identification method, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
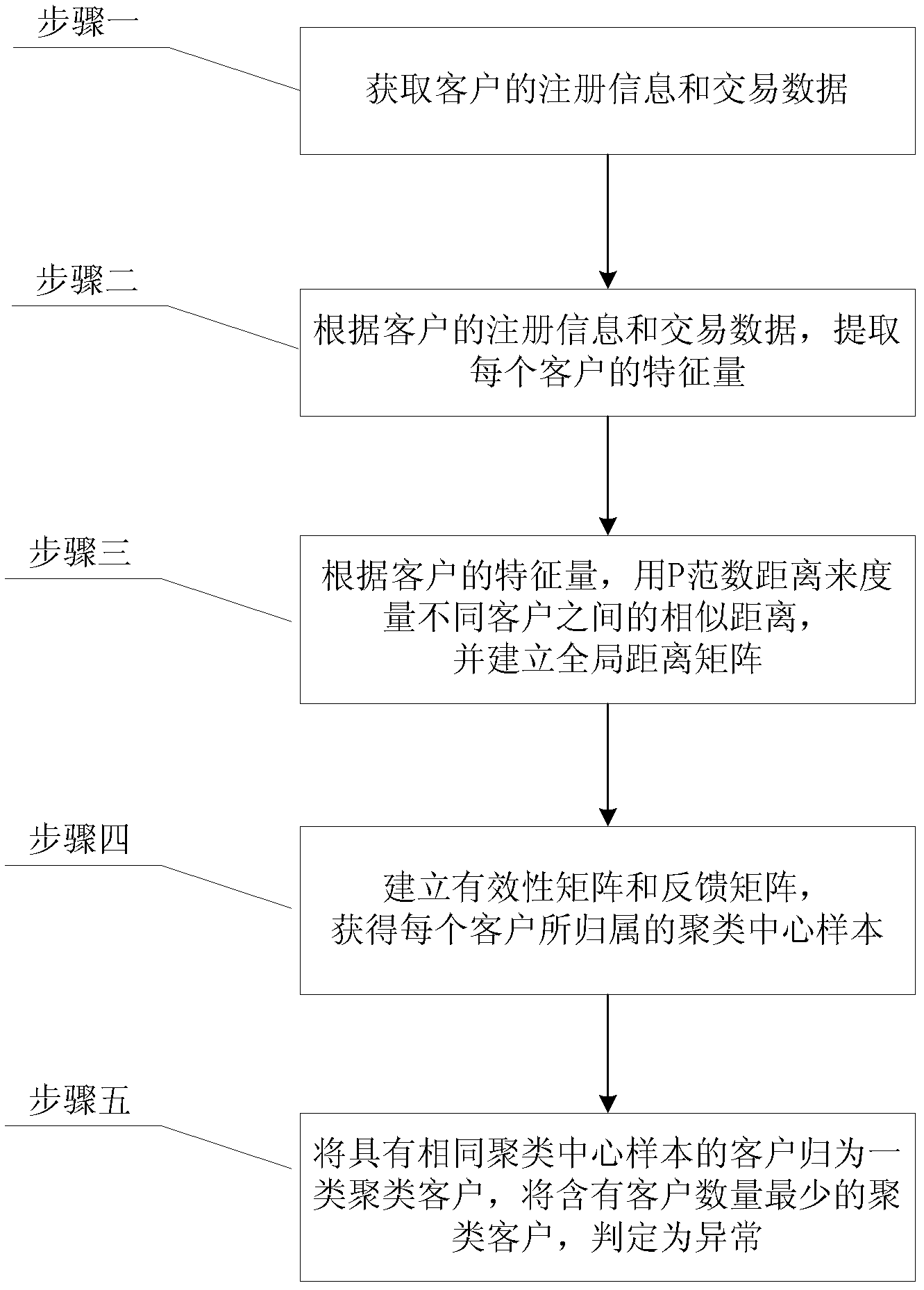
[0044] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 Describe this implementation mode, this implementation mode comprises the following steps:
[0045] Step 1: Obtain the registration information and transaction data of G customers, PF k Indicates the kth customer, G is an integer greater than 600, k=1, 2, 3...G;
[0046] Step 2: According to the registration information and transaction data of G customers, extract the feature quantity F of each customer k (l), wherein l is an integer, l=1,2,3...24;
[0047] Step 3: According to the customer's characteristic quantity F k (l), using p-norm distance to measure customer PF b and customer PF g The similarity distance between Dist(PF b , PF g ):
[0048] Dist ( PF b , PF g ) = ( Σ ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0059] Specific implementation mode 2: This implementation mode is a further description of implementation mode 1. In the step 4, the PF of each customer is obtained k The cluster center sample fc to which it belongs k The specific method is:
[0060] Step 41: From the global distance matrix D G×G Get customer PF b and customer PF g The similarity between Sim(b, g), establish a global similarity matrix S G×G :
[0061] S G × G = Sim ( 1,1 ) Sim ( 1,2 ) · · · · · · ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0068] Specific embodiment three: this embodiment is a further description of embodiment two, the feedback matrix R after LT times of iterative update is obtained in the step four or three G×G and validity matrix A G×G The specific process is:
[0069] Step 431: The feedback matrix R obtained in step 42 G×G All elements of r(i, j) are updated to r(i.j) * =λr tmp (i,j)+(1-λ)r old (i,j),
[0070] where λ is the update coefficient, r old (i, j) is the r(i, j) obtained from the previous iteration update, r tmp (i, j) is shown in the following formula:
[0071] r tmp ( i , j ) = Sim ( i , j ) - max ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com