Identifying factorable code
A technology of factorization and coding, applied in the field of anti-piracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
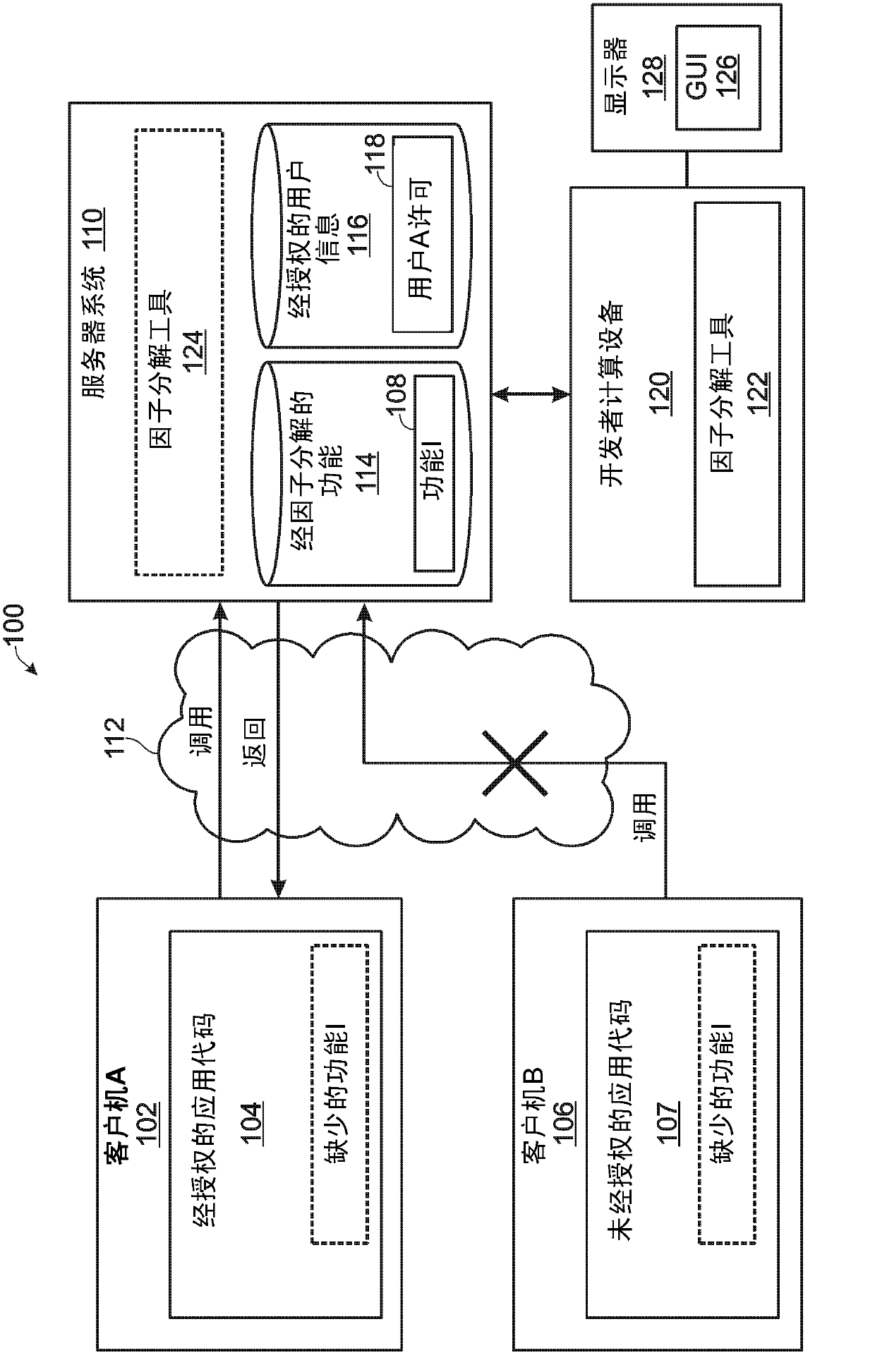
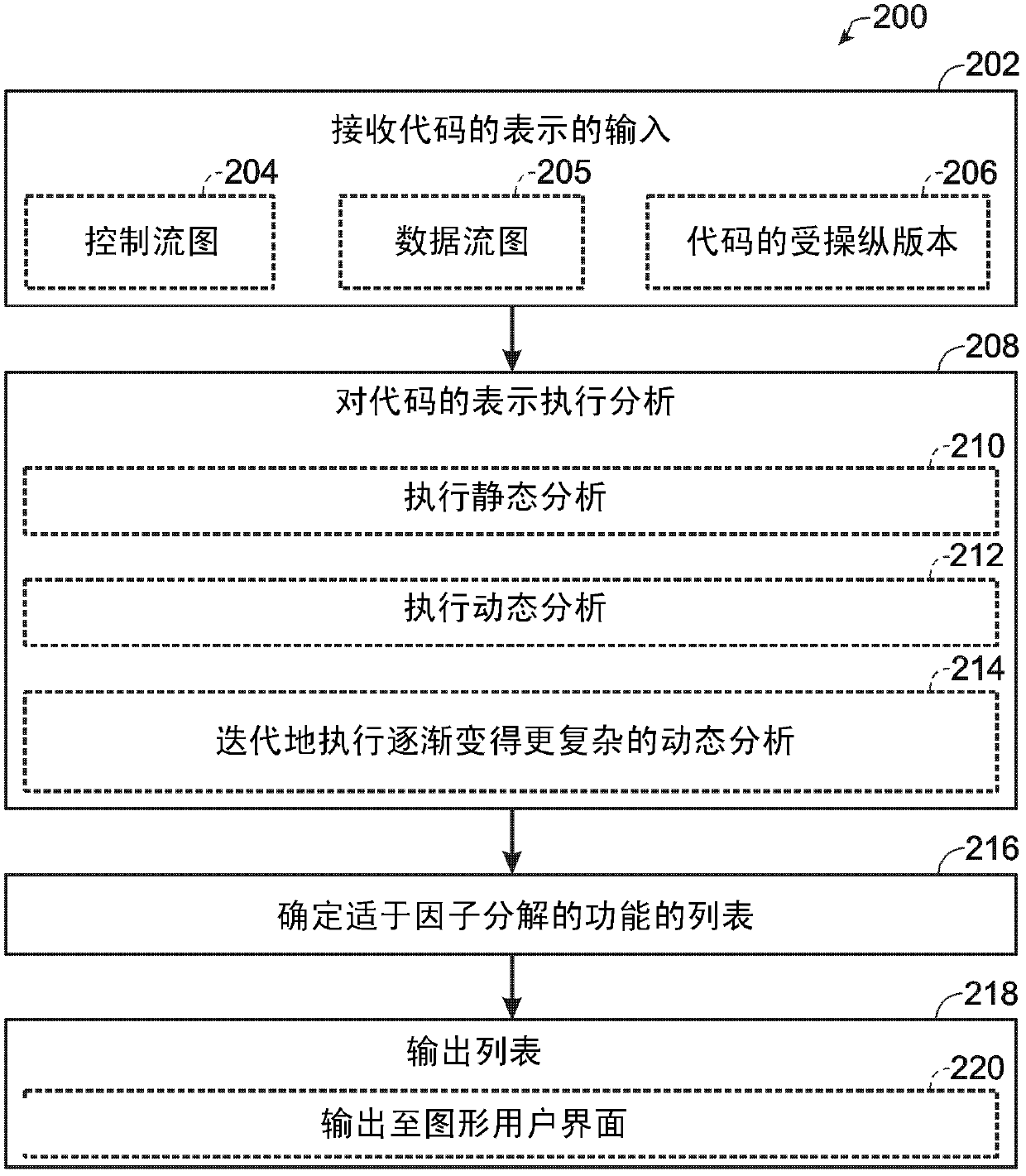
[0009] When looking for a part of code located remotely from another part of the code due to anti-piracy concerns, it may be difficult to locate when factored effectively to prevent piracy without affecting the performance of authorized versions of the program Harmful degree of code. This task is especially difficult for large, complex applications such as video games. For example, it is desirable for remotely located factored code to have functionality that is difficult to infer, such that when given a known input to the code, the code can provide an output that is not easily correlated with the input. Also, it is expected that there will be no factored code that has a sufficiently negative impact on program performance, since capturing such factored code would significantly degrade the quality of the user experience provided by the program. These concerns may favor factorization of relatively large and / or complex functions.
[0010] On the other hand, it is not desirable t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com