Autostereoscopic display device and corresponding terminal equipment
A naked-eye three-dimensional display device technology, applied in three-dimensional systems, static indicators, optics, etc., can solve the problems of audience dizziness, rough picture, affecting picture clarity, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing graininess and eliminating moiré
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
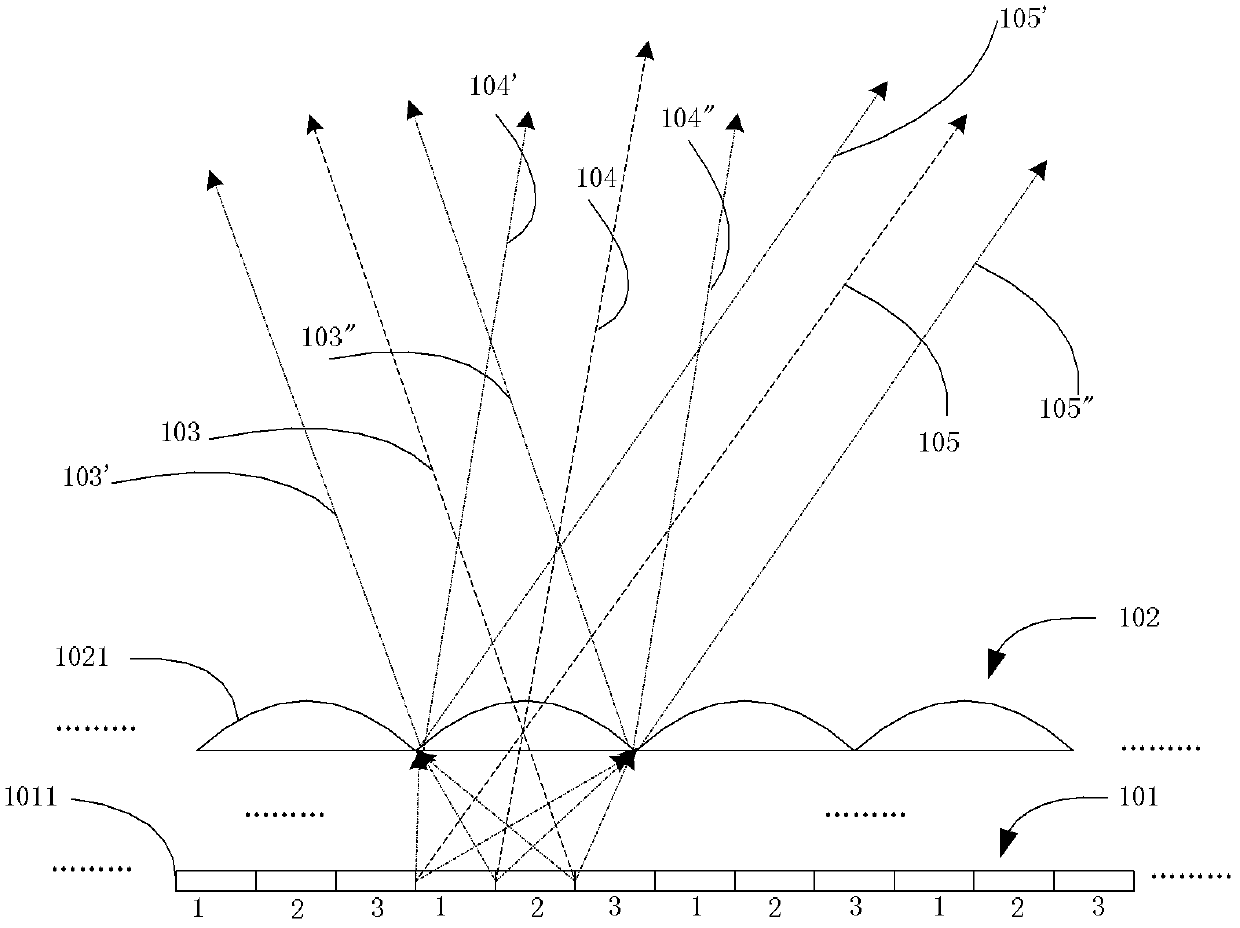
[0066] This embodiment provides a naked-eye three-dimensional display device, which includes a display panel and a light-splitting device. The display panel is composed of a series of display units for providing image display; Directional transmission to achieve light splitting. Different from the existing naked-eye three-dimensional display device, the naked-eye three-dimensional display device of this embodiment also includes a directional dimmer, which is made of a transparent material and placed on the side of the light splitting device away from the display panel. , comprising a plurality of dimming units capable of refracting light, and said dimming units will only deviate from the original light path in one direction after refracting one light. Herein, for a dimming unit, the plane perpendicular to its extending direction is called a radial plane, and the cross-sections of the dimming unit on each radial plane are the same. For the light splitting device, the plane per...
Embodiment 2
[0077] The difference between the naked-eye stereoscopic display device provided in this embodiment and the first embodiment is that a prism array is used instead of a lens array as a directional dimmer.
[0078] Such as Figure 4a with Figure 4b As shown, the directional dimmer 401 replaces the lens array in the first embodiment with a prism array, and the dimming unit on the directional dimmer 401 is a prism unit 4011, and the prism unit 4011 and the lens unit in the first embodiment scatter light The basic principle is the same. After refracting a ray, it will only deviate from the original optical path in one direction, and the ray after refracting the incident ray on the radial plane is still on the radial plane. At the same time, for the incident light incident on the same dimming unit at the same angle and different positions on the same radial plane, the refracted outgoing angles are not exactly the same, which also plays a role of "scattering". For dimming units su...
Embodiment 3
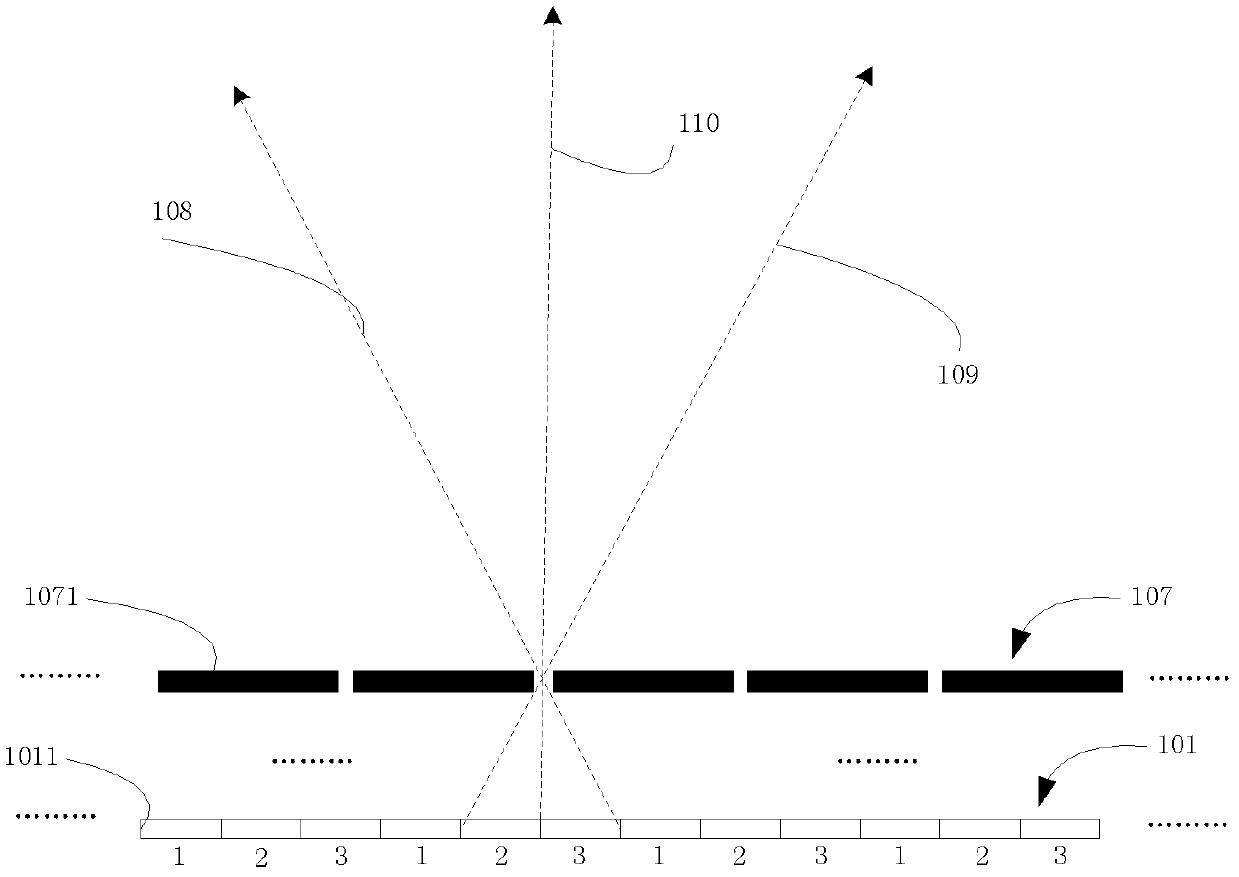
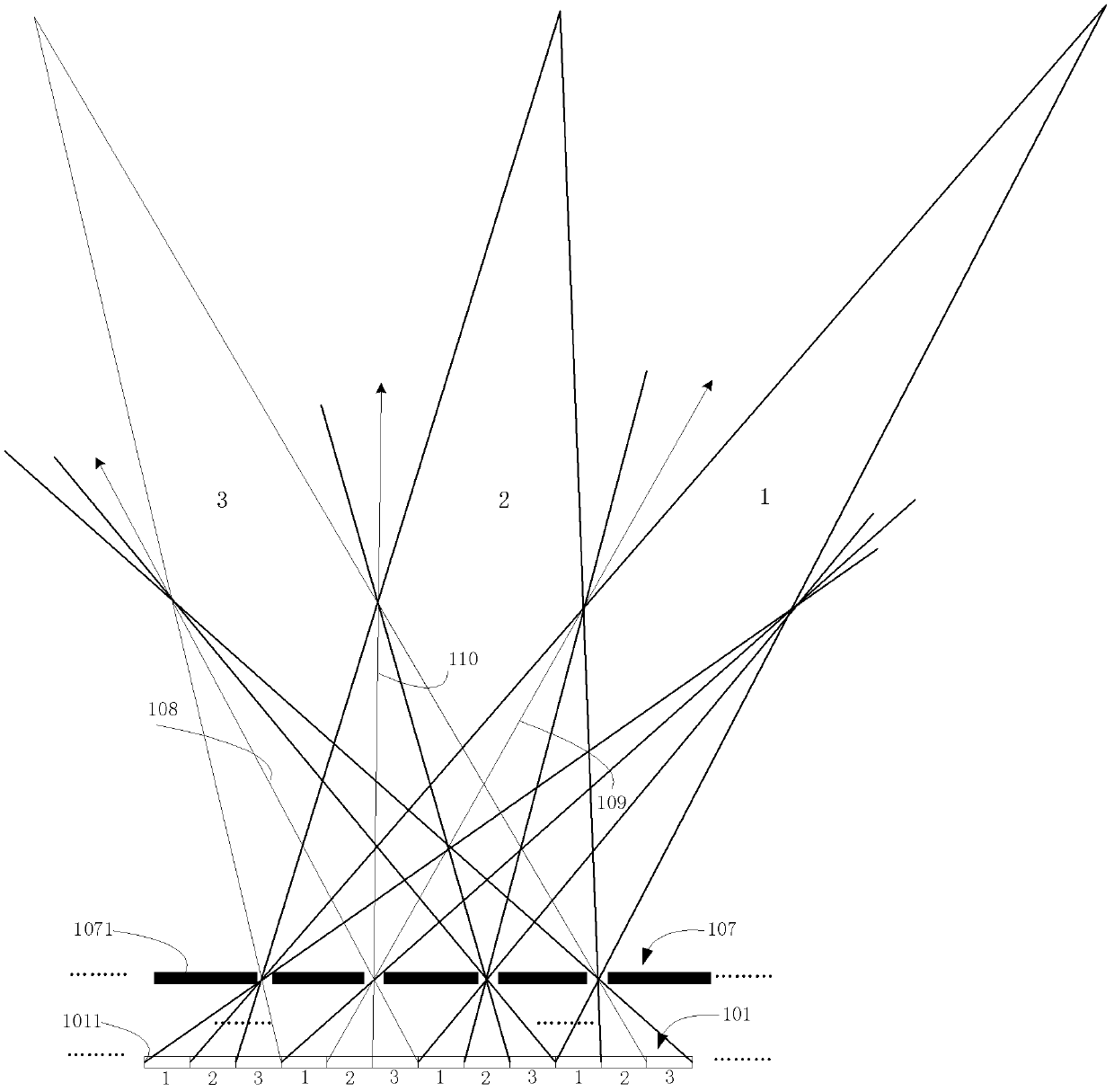
[0081] In the above two embodiments, the directional dimmer is placed on the side of the light splitting device away from the display panel. In this embodiment, the directional dimmer is placed between the light splitting device and the display panel. The directional dimmer may use a lens array or a prism array, and the light splitting device may use a lens array or a barrier array. Figure 5a It shows the structure and optical path changes when both the directional dimmer 201 and the light splitting device 102 use a lens array, Figure 5b It shows the structure and optical path changes when the directional dimmer 201 adopts a lens array and the light splitting device 107 adopts a barrier array, Figure 6a It shows the structure and optical path changes when the directional dimmer 401 adopts a prism array and the light splitting device 102 adopts a lens array, Figure 6b It shows the structure and light path changes when the directional dimmer 401 adopts a prism array and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com