Gastro-resistant enzyme pharmaceutical compositions
A composition and gastric juice-resistant technology, applied in drug combination, drug delivery, pharmaceutical formulation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0082] Example 1: Digestive Enzyme Tablets Without Excipients
[0083] Table I
[0084] Excipient-free tablet (500 mg tablet)
[0085] (obtained by direct compaction at 2.5T)
[0086]
[0087]
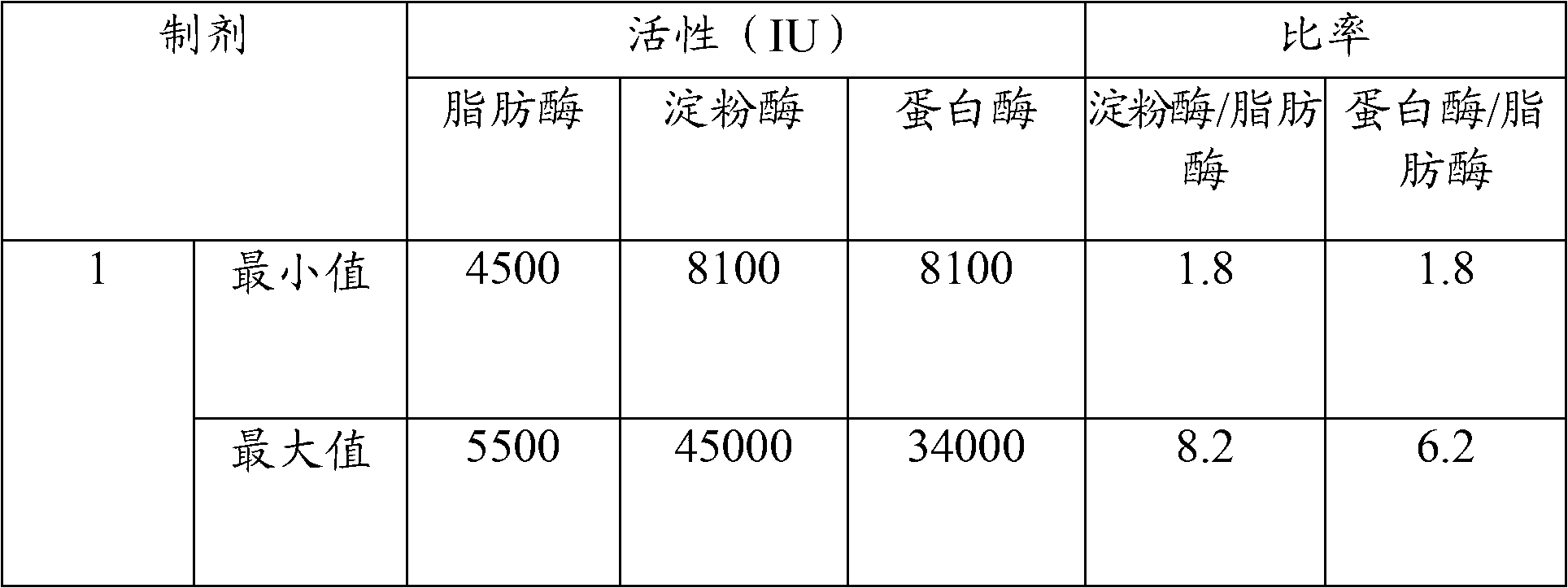
[0088] Tablets without excipients were prepared by direct compression of 500 mg of active substance (with lipase, protease and amylase enzyme activities as mentioned in Table 1 ) in a mold with a diameter of 9.7 mm.
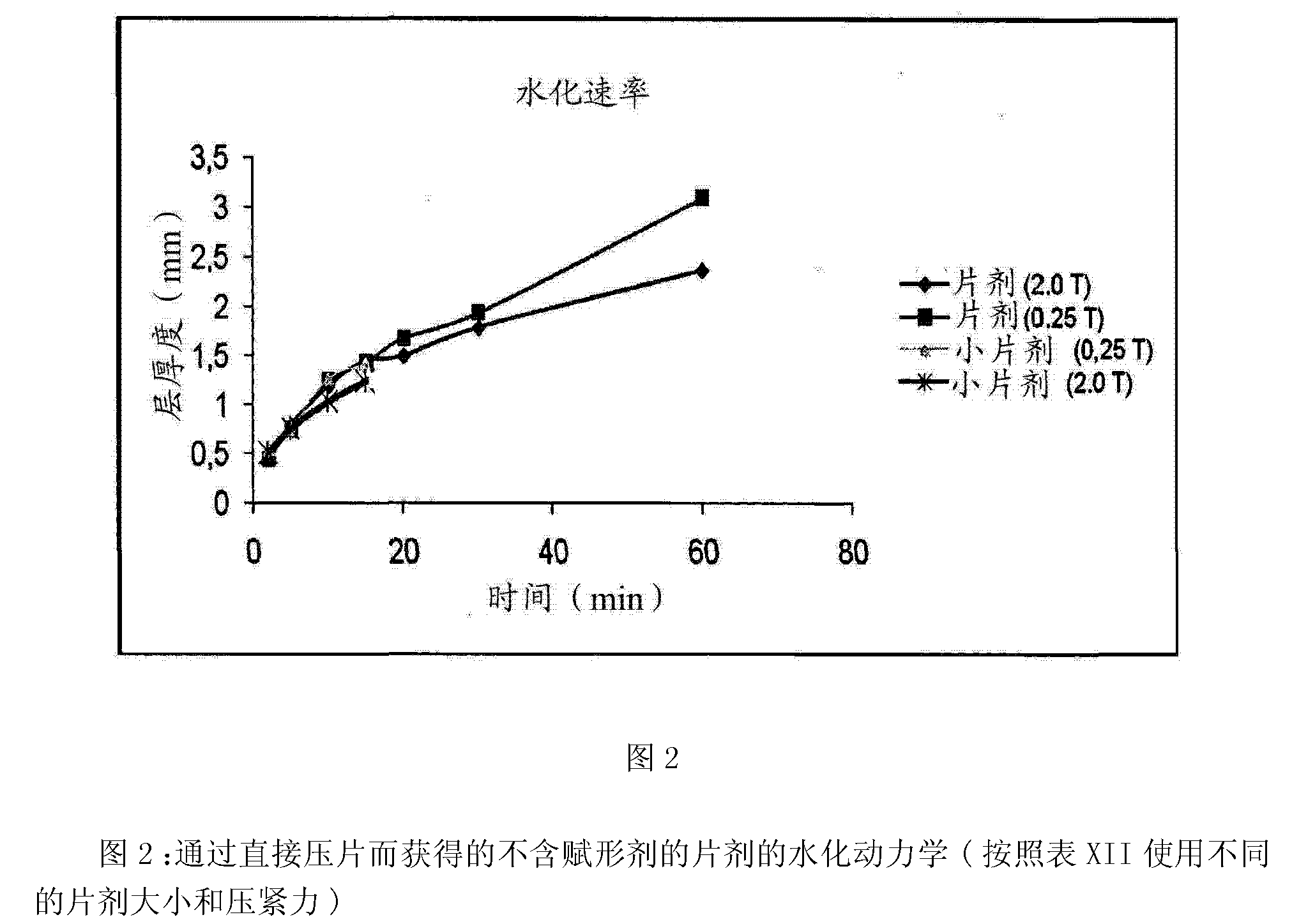
[0089] Smaller tablets were also prepared as indicated below. Smaller tablets of each size were prepared in sufficient numbers such that they together had a total mass of approximately 500 mg (equivalent to one 9.7 mm tablet).
[0090] Tablet 2.0mm (34 small tablets)
[0091] Tablet 4.0mm (8 tablets)
[0092] Tablet 6.0mm (4 tablets)
[0093] Tablet 9.7mm (1 tablet)
example 2
[0094] Example 2: Evaluation of Pancreatic Enzyme Tablets Without Excipients and Reference Tablets Containing 40% w / w Excipients in Simulated Gastric and Intestinal Fluids
[0095] The excipient-free tablets of Example 1, as well as the uncoated reference formulation containing excipients, were evaluated for enzymatic activity in simulated gastric fluid (SGF) and simulated intestinal fluid (SIF) as described below. The reference formulation contained 8,000 USP units of lipase, 30,000 USP units of amylase, and 30,000 USP units of protease and approximately 40% w / w pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. Reference preparations were prepared by direct compression. Results are shown in Tables II-V.
[0096] method
[0097] Tablets were maintained in a solution of SGF (50 mL) at pH 1.2 or SIF (50 mL) at pH 6.8 at room temperature with constant rotary agitation (50 rpm). The lipase, amylase, and protease activity of each sample was measured over time using the inner portion of th...
example 3
[0112] Example 3: Evaluation of whole tablet lipase activity measured after exposure to SGF for various time intervals.
[0113] Tablets prepared in Example 1 and a reference preparation as described in Example 2 were exposed to SGF for 30, 60 and 120 minutes and the lipase activity of the whole resulting tablets was evaluated. The results are shown in Table V below.
[0114] Table V
[0115] Tablets containing no excipients containing 500 mg tablets obtained by direct compression at 2.5T
[0116]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com