Additive manufacturing management of large part build mass
A technique for additive manufacturing, parts, applied in the field of laser construction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
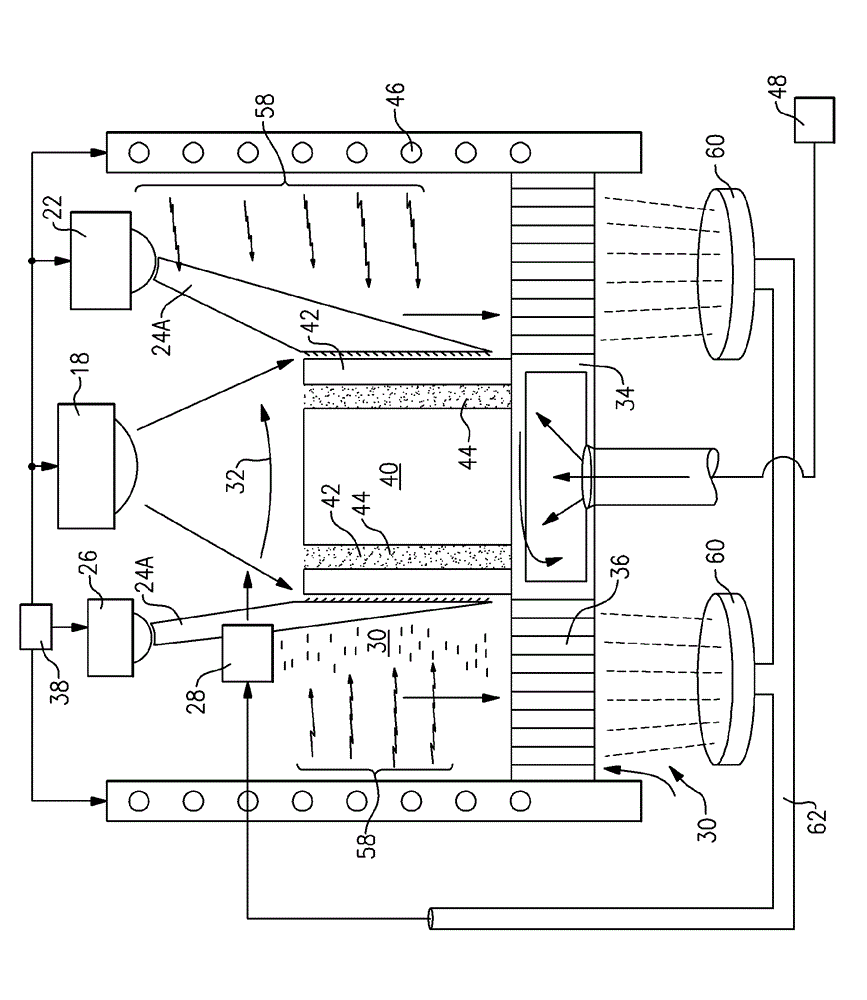
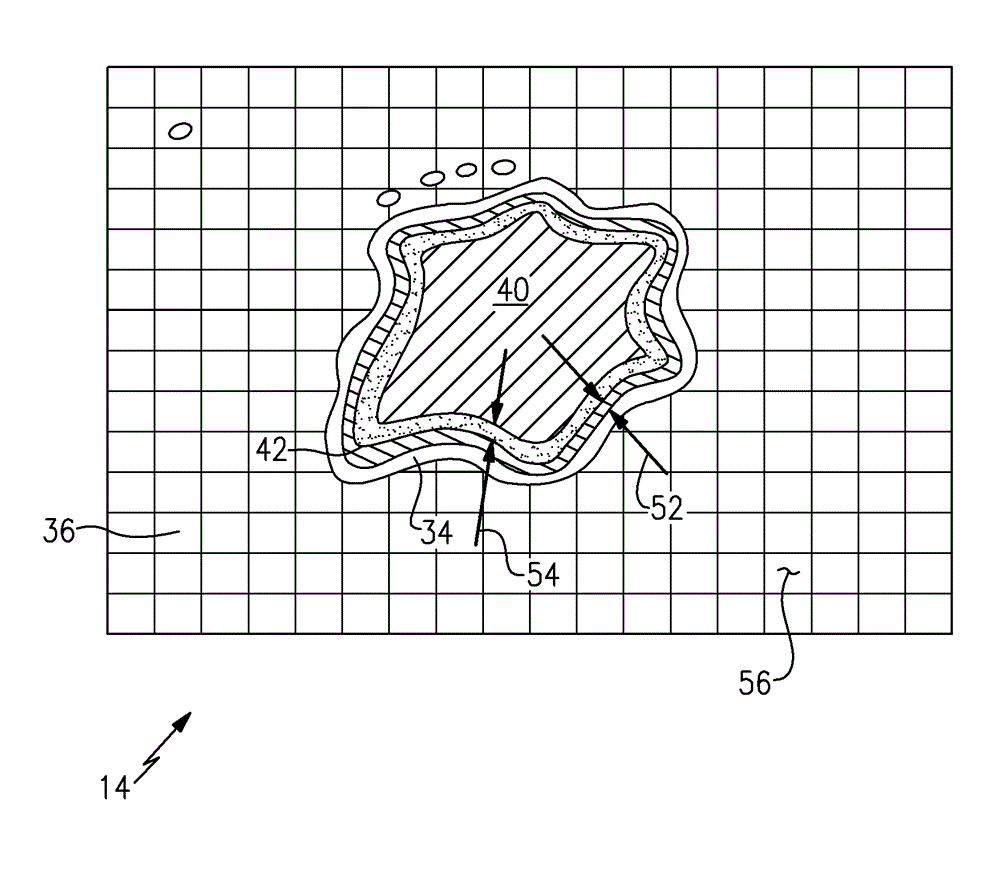
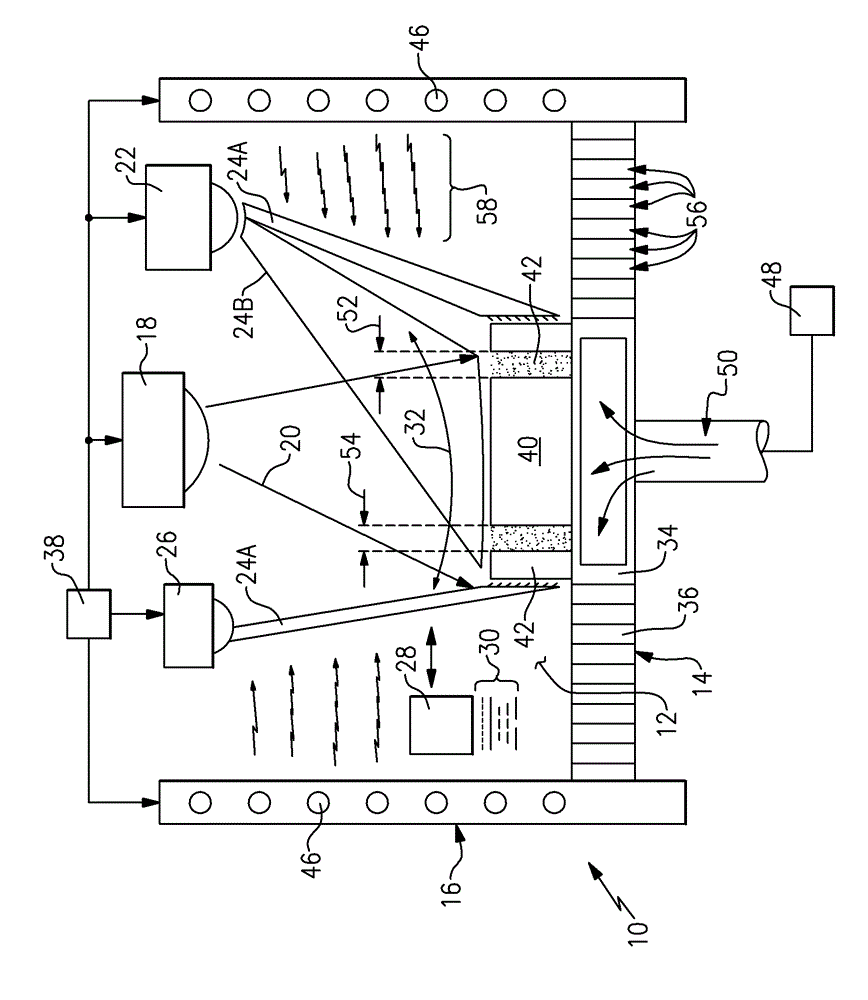
[0029] Referring to FIG. 1 , an additive manufacturing machine 10 includes a workspace 12 that supports an energy emitting device 18 and a substrate 14 on which a part 40 is supported during manufacture. In this example, energy emitting device 18 emits laser beam 20 that melts material 30 deposited by material applicator 28 . An exemplary material 30 is a metal powder that is applied in layers on the substrate 14 and subsequent layers are applied to produce the desired configuration of the part 40 . The laser beam 20 directs energy that melts the powder material into a configuration that forms the desired part dimensions.
[0030] The additive manufacturing process employs a material 30 that is applied to form multiple layers on top of the substrate 14 . Selective portions of the layer are subsequently melted by the energy emitted from the laser beam 20 . Energy focused on the top layer of part 40 generates the desired heat to melt portions of the powder metal. Heat conduct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com