Detailed correlation medium and small breakpoint identification method for delta front deposit
A technology of small and medium breakpoints and deltas, applied in the direction of earthwork drilling and production, wellbore/well components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult identification, difficult judgment, strong subjectivity, etc., achieve scientific enhancement, emphasize objectivity, and clear operation steps reasonable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] In order to make the above and other objects, features and advantages of the present invention more comprehensible, preferred embodiments are listed below and described in detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
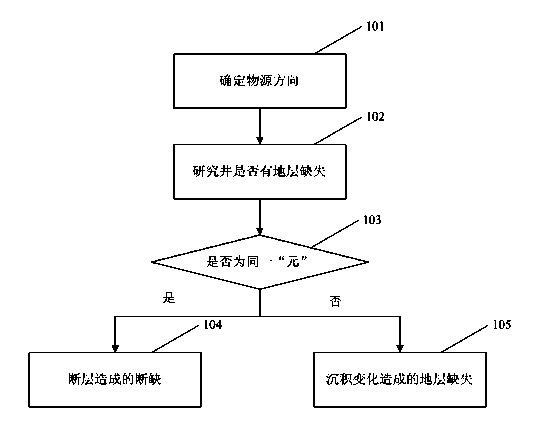
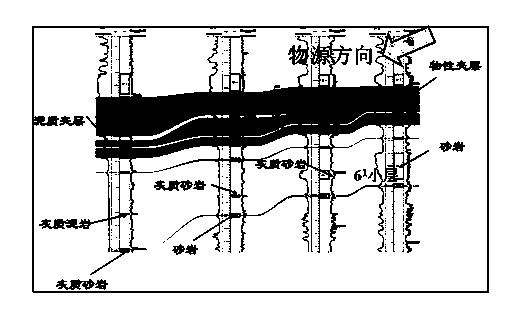
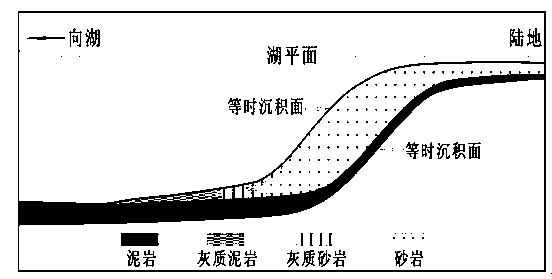
[0021] The method for identifying small breakpoints in the delta front sedimentary sublayer comparison in the present invention establishes the delta front isochrone body through the field outcrop observation description of the delta front, the actual data statistics of the oil field and the theoretical analysis of the sedimentary differentiation principle (i.e. a small layer or a single sand body) along the source direction of the lithological evolution model: "sand-lime-mud ternary model", that is, a small layer or a single sand body along the source direction will sequentially appear sandstone, lime sandstone , and gradually evolved into calcareous mudstone until pure mudstone. As an interlayer deposit, its lithological change is similar to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com