A six-stage modeling method for the characterization of gas-water distribution in water-bearing carbonate gas reservoirs
A technology of carbonate rocks and modeling methods, applied in 3D modeling, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of large differences in gas-water interface, do not consider the control of gas-water interface, and only focus on sedimentary facies modeling, etc. problem, to achieve a widely applicable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] In order to make the technical means, creative features, goals and effects achieved by the present invention easy to understand, the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific embodiments.
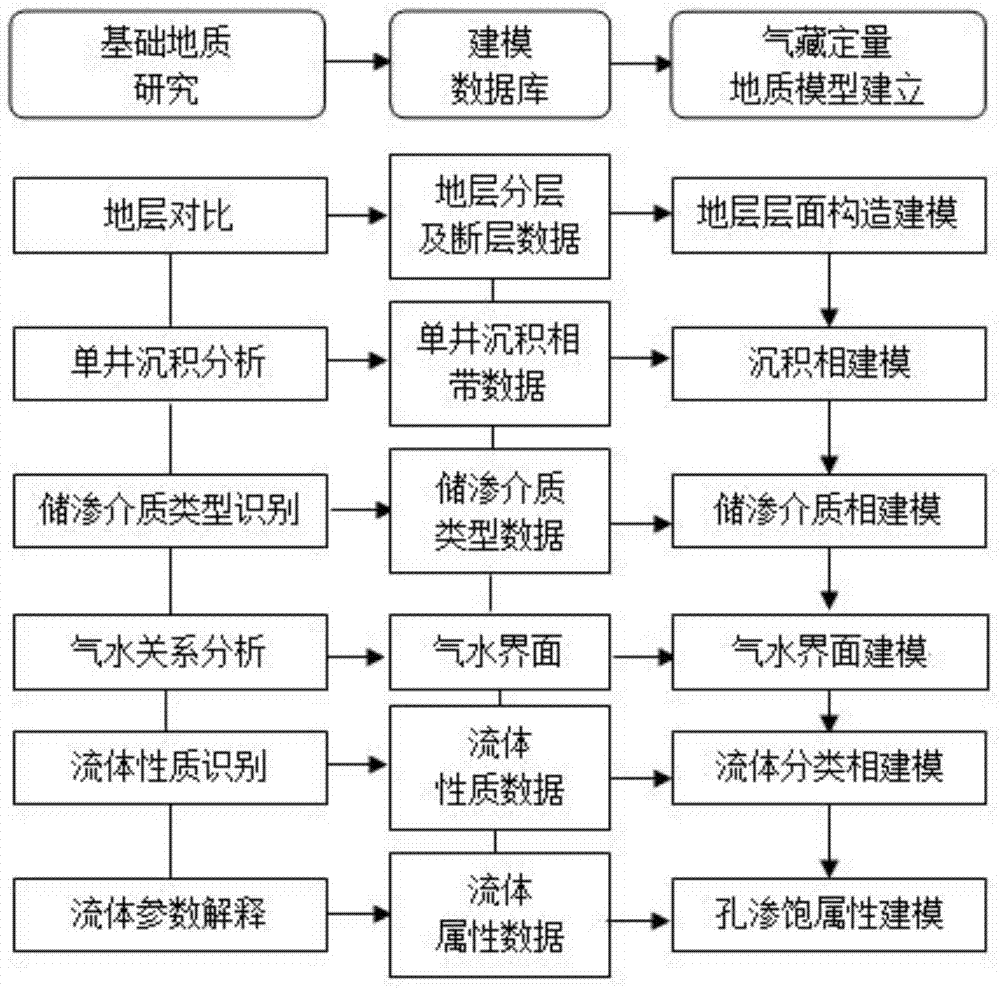
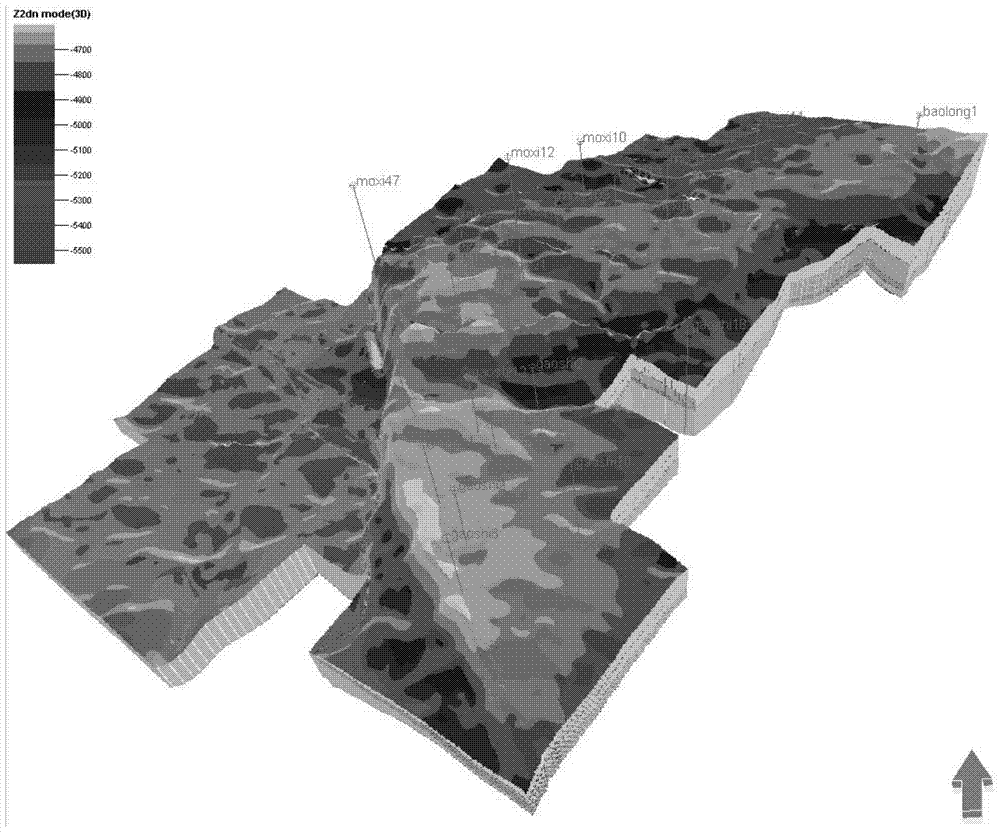
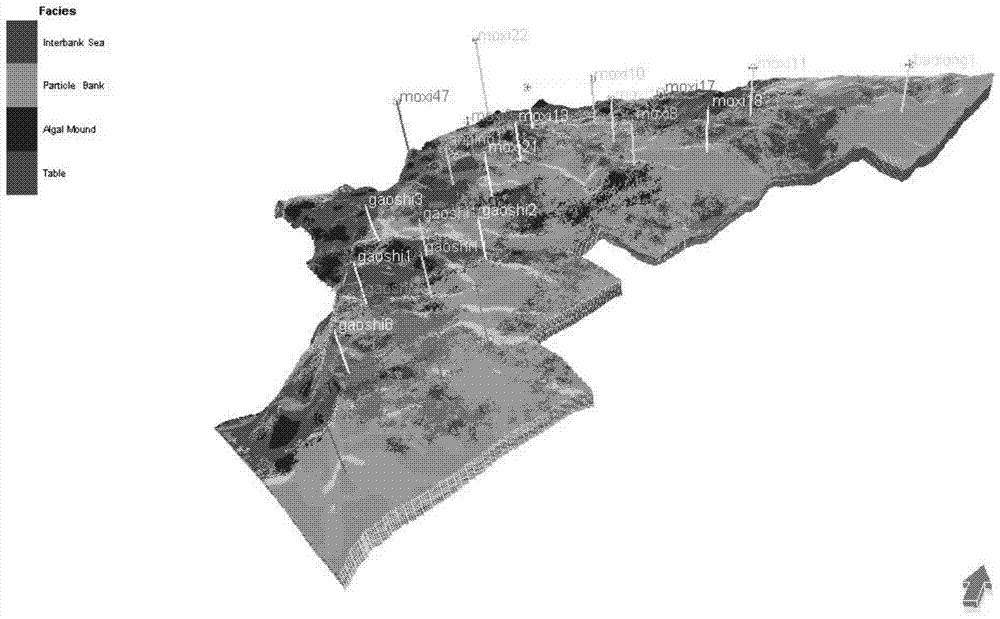
[0034] refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation method adopts the following technical solutions: the present invention develops around pores, caves and fractures in carbonate gas reservoirs with water, the spatial combination types of pores, caves and fractures are complex, layered edge water and uneven bottom water Coexistence, complex gas-water relationship and other characteristics, proposed six stages of formation layer structure modeling-sedimentary facies modeling-storage medium facies modeling-air-water interface modeling-fluid classification facies modeling-pore seepage and saturation attribute modeling The modeling method system realizes the accurate and quantitative characterization of gas-water distribution in three-dimensional s...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap