Three-dimensional strain tensor change observing method
A strain tensor, three-dimensional technology, used in measuring devices, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of convenient self-inspection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
[0039] Utilize 9 wire strain sensors, arranged in the following way:
[0040] Establish a Cartesian coordinate system XYZ;
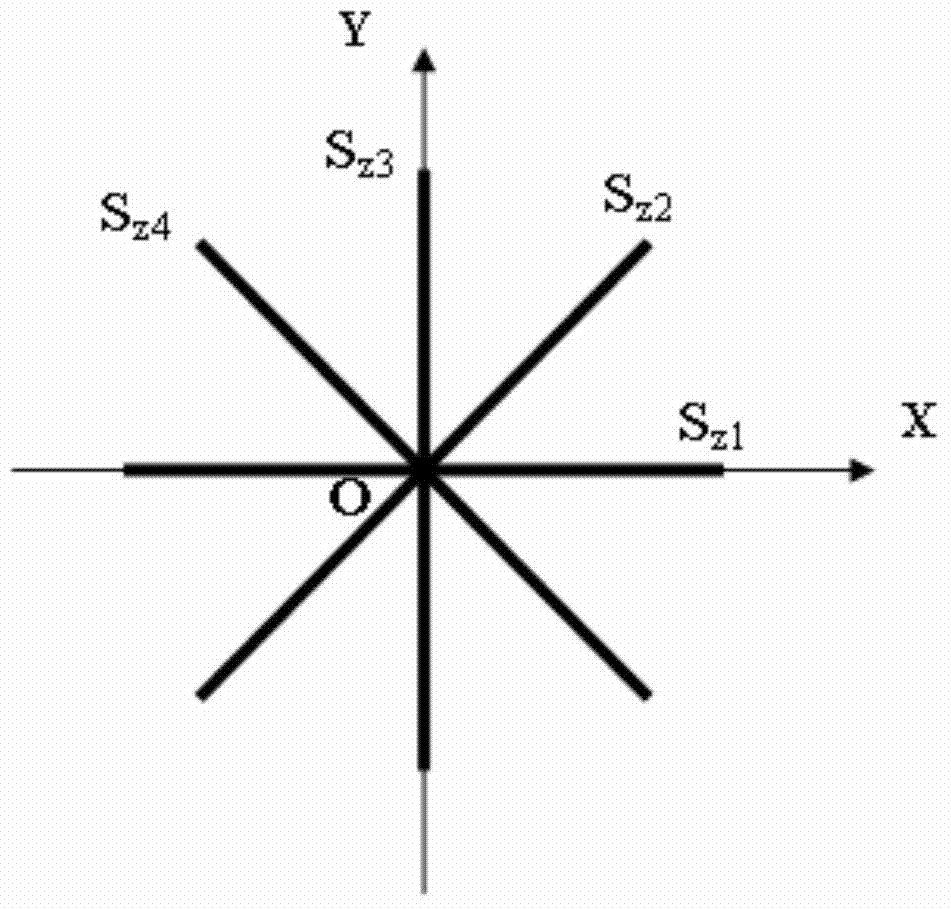
[0041] Arrange 4 linear strain sensors in the XY plane, and observe the linear strain s in 4 directions at equal intervals of 45° z1 , s z2 , s z3 and s z4 , where s z1 and s z3 Coincident with the X-axis and Y-axis respectively (attached figure 1 );
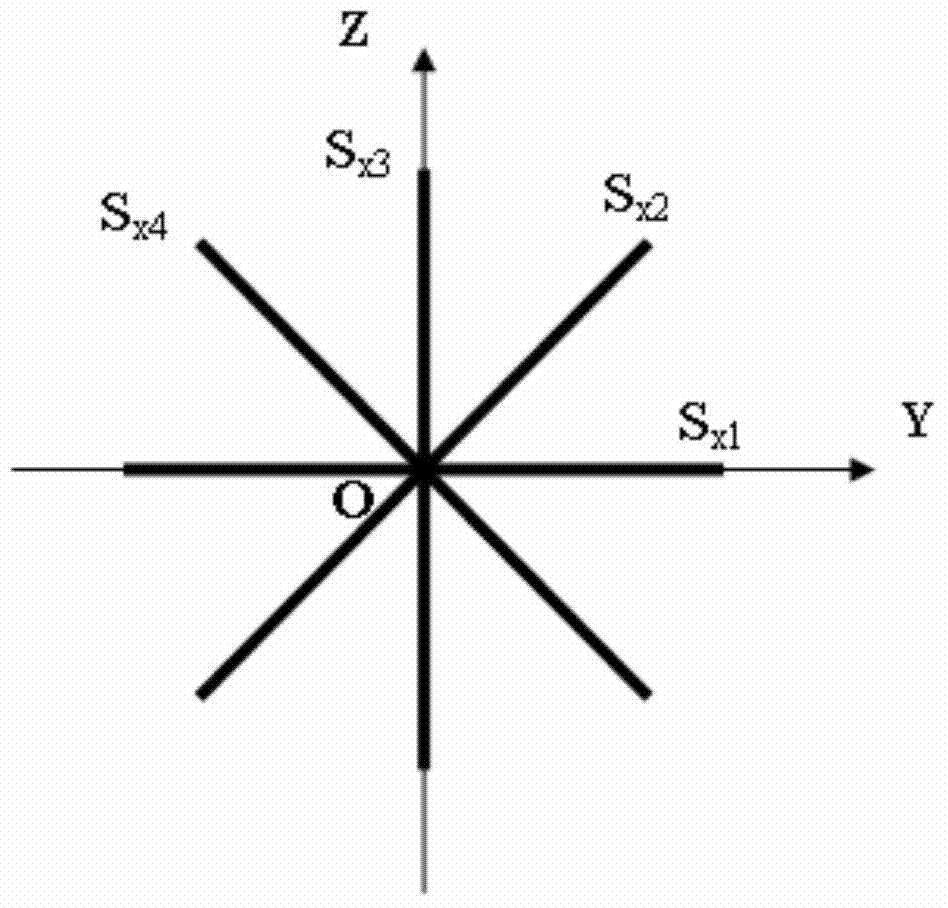
[0042] Arrange 4 linear strain sensors in the YZ plane, and observe the linear strain s in 4 directions at equal intervals of 45° x1 , s x2 , s x3 and s x4 , where s x1 and s x3 Coincident with the Y-axis and Z-axis respectively (attached figure 2 ).
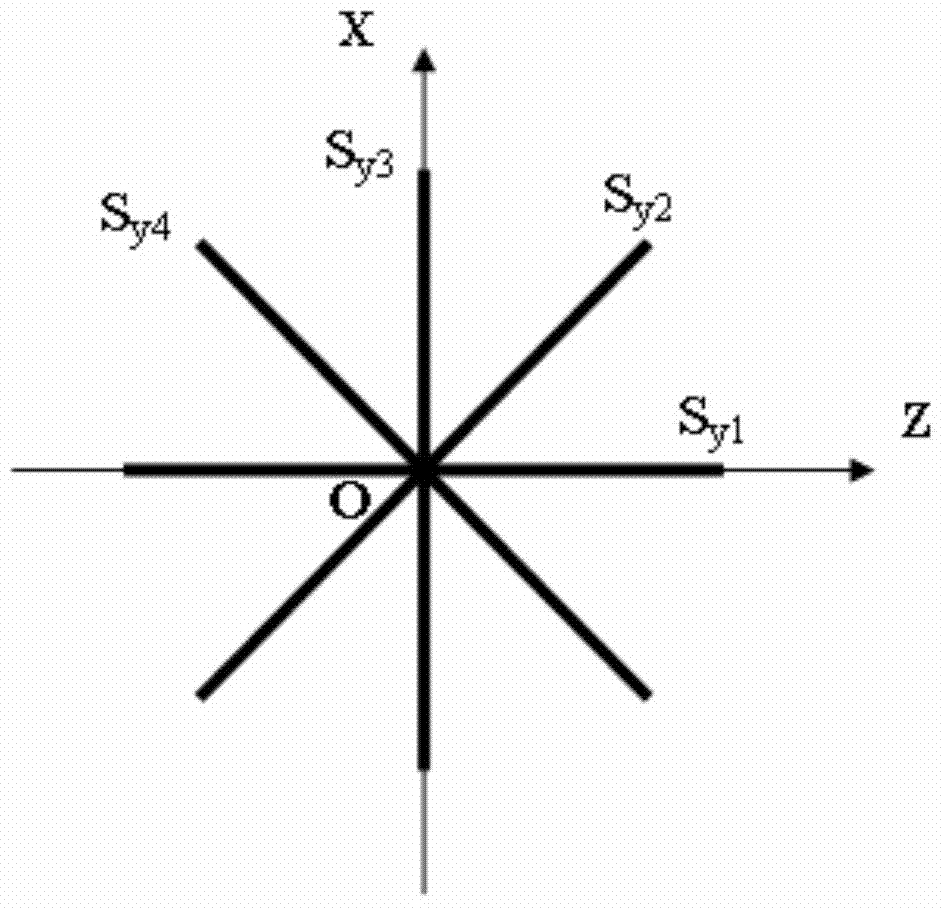
[0043] Arrange 4 linear strain sensors in the ZX plane, and observe the linear strain s in 4 directions at equal intervals of 45° y1 , s y2 , s y3 and s y4 , where s y1 and s y3 Coincident with the Z axis and X axis respectively (attached image 3 );
[0044] In fact, there are only 9 line strain observations, and the following equival...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com