Method for predicting shutdown probability of power grids under combined effect conditions of extreme high temperatures and forest fire
A forest fire and outage probability technology, applied in forecasting, data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to calculate line failure probability, inability to calculate conductor temperature, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
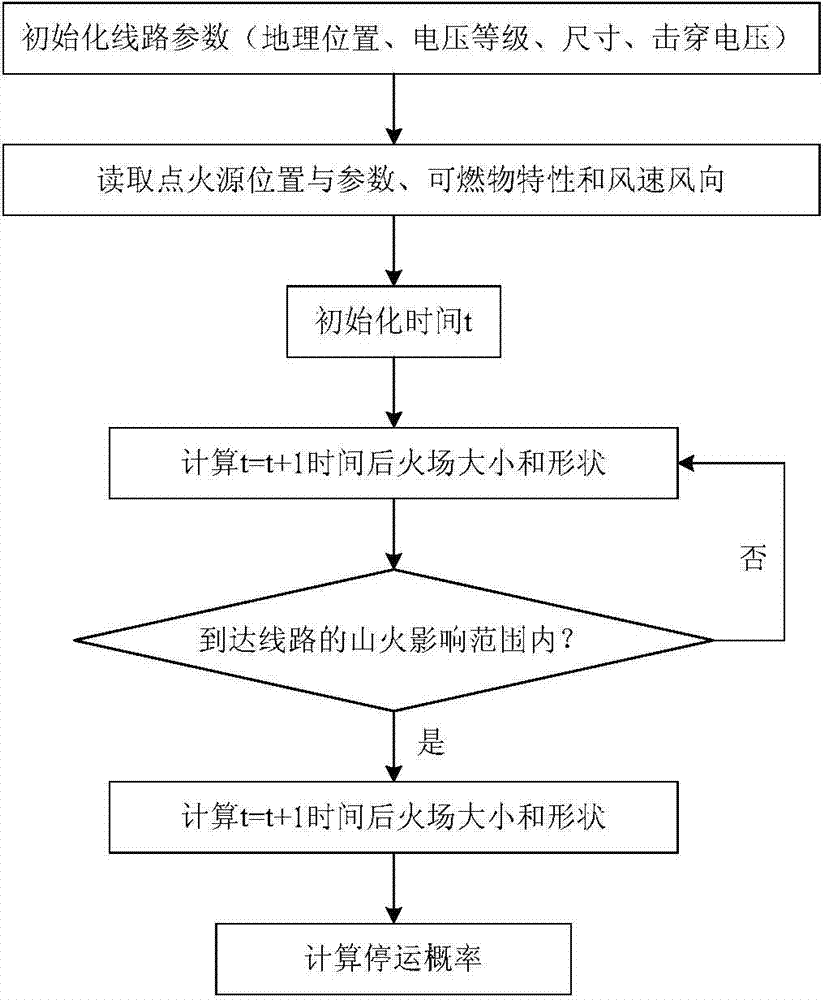
[0034] Specific implementation mode one: The method for predicting the probability of power grid outage under the combined action of extreme high temperature and forest fires in this embodiment is implemented in the following steps:
[0035] 1. Calculate the probability of short-circuit failure of the wire caused by insulation breakdown P(electricbreakdown|fire);
[0036] 2. Calculate the failure probability P(HighTemp|fire)×P(fault|HighTemp) caused by the high temperature of the wire caused by the combined action of extreme high temperature and forest fire;
[0037] 3. Calculate the probability of power grid outage under the combined action of extreme high temperature and forest fire
[0038] P c =P(electricbreakdown|fire)+P(HighTemp|fire)×P(fault|HighTemp)
[0039] where P c Indicates the power grid outage probability;
[0040] P(electicbreakdown|fire) indicates the probability of wire short-circuit failure caused by insulation breakdown;
[0041] P(HighTemp|fire) repre...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0058] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in the step 1, the probability of short-circuit failure caused by insulation breakdown is calculated as follows:
[0059] Power frequency breakdown voltage U of air gaps under forest fire conditions 1 for
[0060] U 1 =K t K p U 0
[0061] K p is the smoke concentration correction factor, and the power frequency breakdown voltage of the air gap is U 0 , the atmospheric correction factor K t , K t =K d K h , where K d is the air density correction factor, K h is the air humidity correction factor;
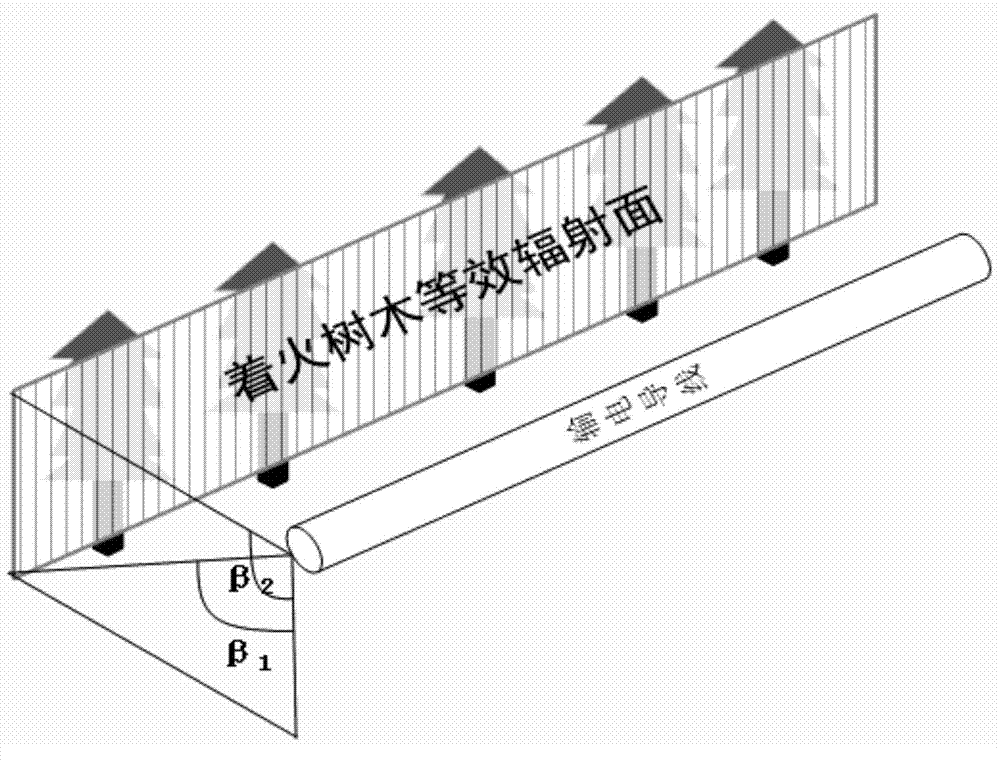
[0062] The short-circuit failure probability caused by edge breakdown during forest fire is expressed as
[0063] P ( U ) = 1 0.04 2 π U 50 e ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
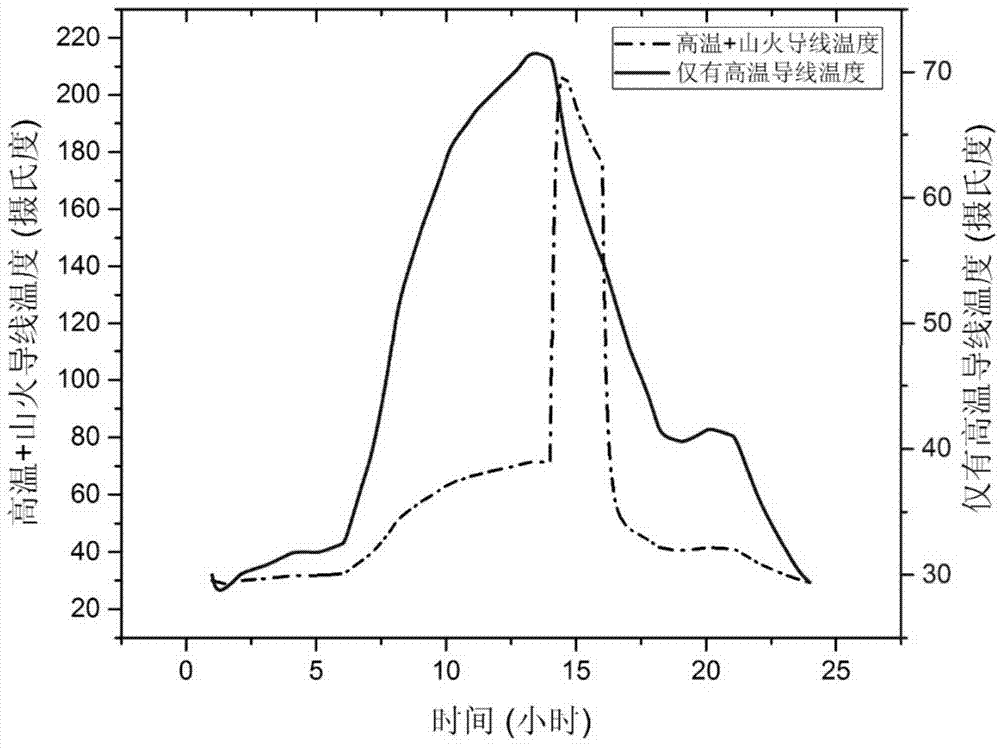
[0066] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 or 2 in that: in the second step, P(HighTemp|fire) is monitored by using modern remote sensing technology, and P(HighTemp|fire) is taken when the forest fire passes through the transmission line. 1, otherwise 0.
[0067] Other steps and parameters are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com