Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli inactivated vaccine and preparation method thereof
A technology of poultry pathogenic Escherichia coli, which is applied in the field of poultry pathogenic Escherichia coli inactivated vaccine and its preparation, to achieve the effect of preventing infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Rejuvenation and identification of candidate strains for seedling production in embodiment 1
[0036] The candidate strain APCE94 for producing seedlings of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli of O78 serotype was obtained through screening in the previous research of the present invention, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.10602.
[0037] After the strain was rejuvenated in susceptible ducks, the strain morphology, virulence factor detection and immune protection rate identification were carried out. The rejuvenated bacterial strain was passed on LB liquid and LB agar plate for 50 times, and the morphology of the bacterial strain (round convex, smooth, moist, translucent, off-white colonies), biochemical reaction characteristics (fermented lactose and Sorbitol; does not decompose sucrose; does not produce hydrogen sulfide; does not decompose urea; both indole and methyl red tests are positive; VP test and citrate utilization test are negative), molecular biological ...
Embodiment 2
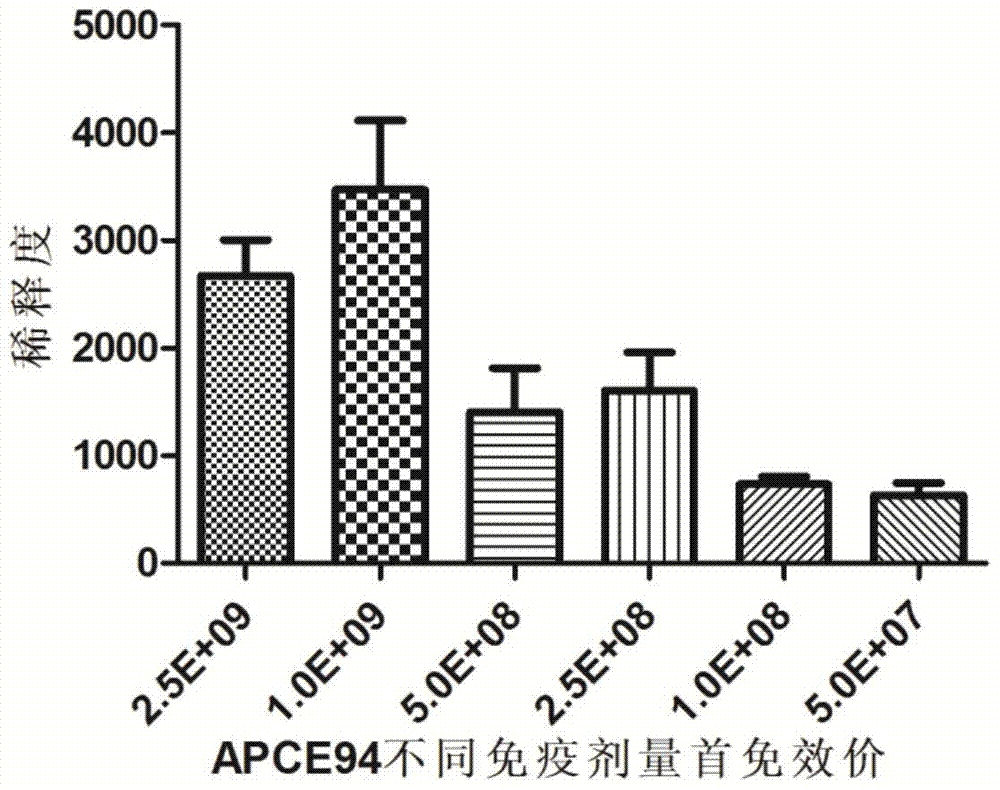
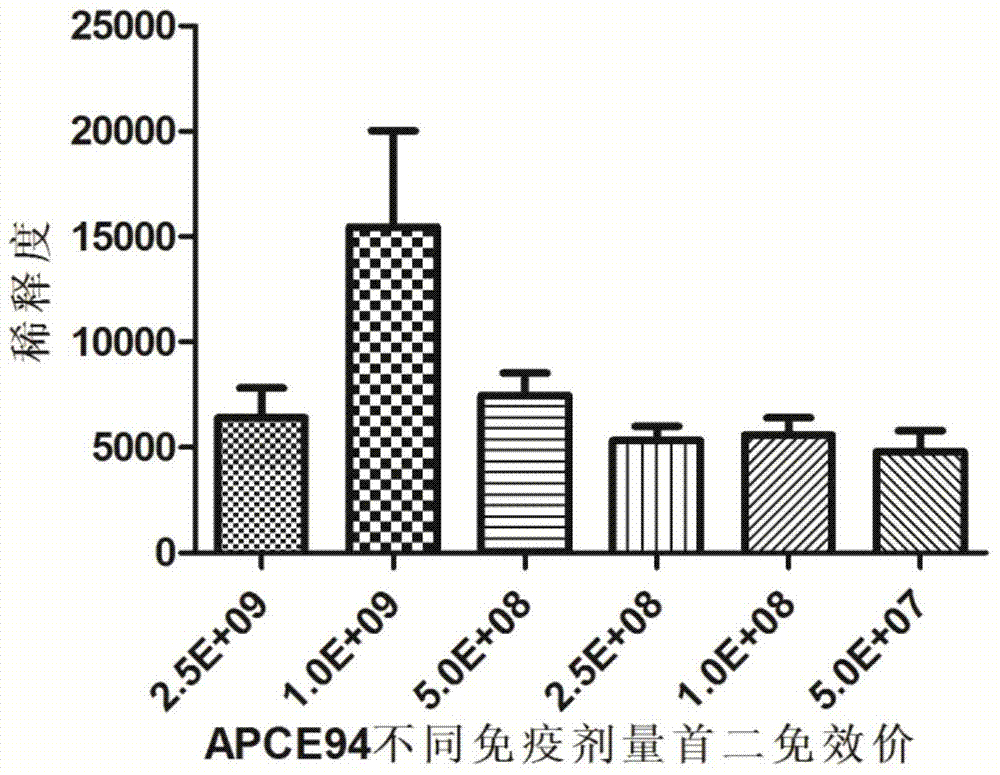
[0038] The optimal bacterial content selection of embodiment 2 poultry pathogenic Escherichia coli inactivated vaccine
[0039] 192 10-day-old Cherry Valley ducks were randomly divided into 4 groups, 48 per group, two vaccine immunization test groups and two control groups. The two test groups were randomly divided into 6 subgroups, 10 rats / group, and the immunization dose was 2.5×10 9 CFU / piece, 1×10 9 CFU / piece, 5×10 8 CFU / piece, 2.5×108 CFU / piece, 1×10 8 CFU / piece, 5×10 7 CFU / only and non-immunized control group.
[0040] The vaccines of each group were inoculated subcutaneously in the neck of the corresponding number of Cherry Valley ducks according to the corresponding dose, and the control group did not receive any vaccination treatment. Two weeks later, each group was boosted with the same method once.
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, 14 days after the first immunization and the second immunization, the blood was collected from the jugular vein to separate t...
Embodiment 3
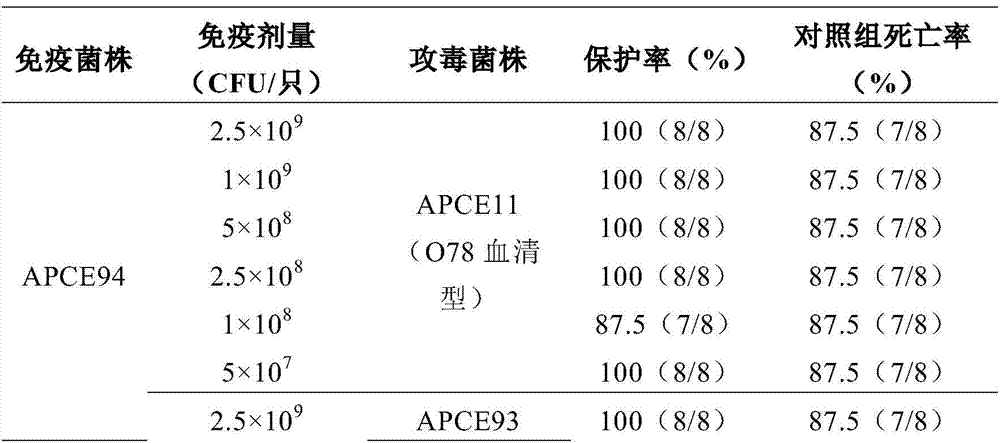
[0047] Embodiment 3 prepares O78 serotype avian pathogenic Escherichia coli inactivated vaccine
[0048] O78 serotype APEC inactivated oil emulsion vaccine strain APCE94 was resuscitated, grown, inactivated, and tested as described above, and an inactivated vaccine was prepared.
[0049] The method is: take the bacteria content 3.33×10 9 Add 7 parts of Montanide ISA70 VG adjuvant or Montanide ISA 71 VG adjuvant to 3 parts of CFU / mL APCE94 inactivated bacteria liquid, mix well, stir and emulsify at high speed for 1 minute / time×2 times to kill pathogenic Escherichia coli live vaccines. Aliquot 100mL / bottle and store at 4°C.
[0050] The bacterial content of 0.5mL vaccine is 5×10 8 CFU, 0.5mL per mouse was subcutaneously inoculated in the neck during immunization.
[0051] 90 10-day-old unimmunized healthy susceptible Cherry Valley ducks (Qingyang Duck Farm, Wuxi City) were randomly divided into 3 groups, 30 / group, coded as A and B, and group A was given inactivated vaccine a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com