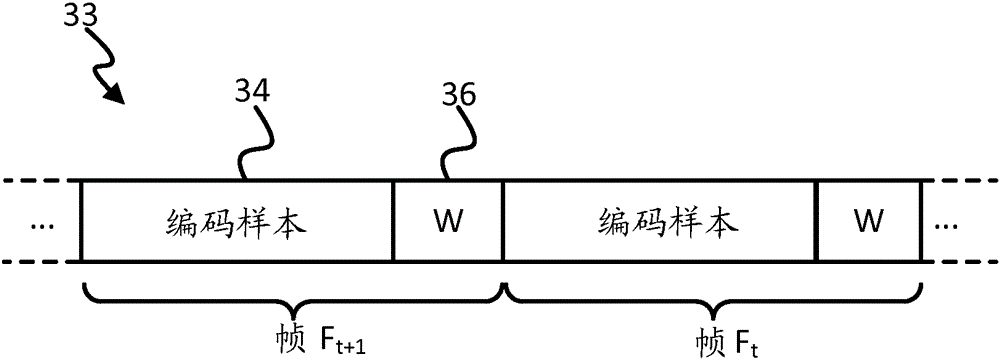
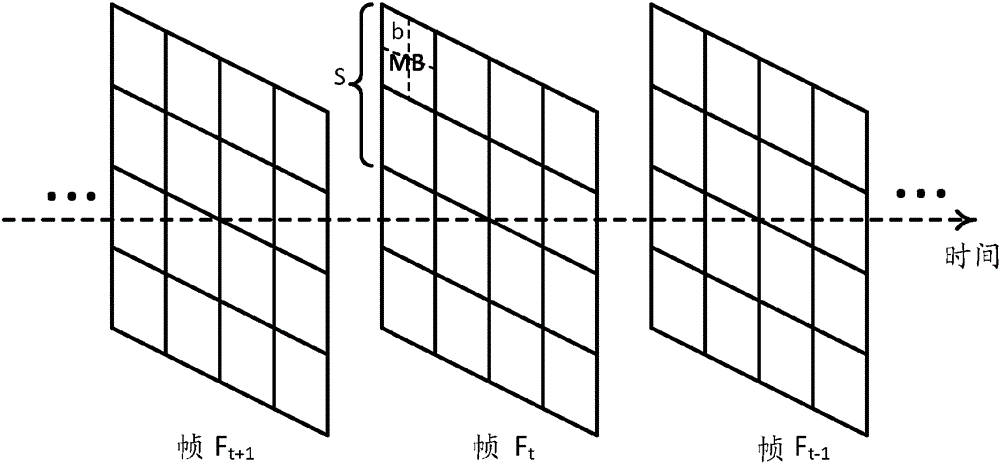
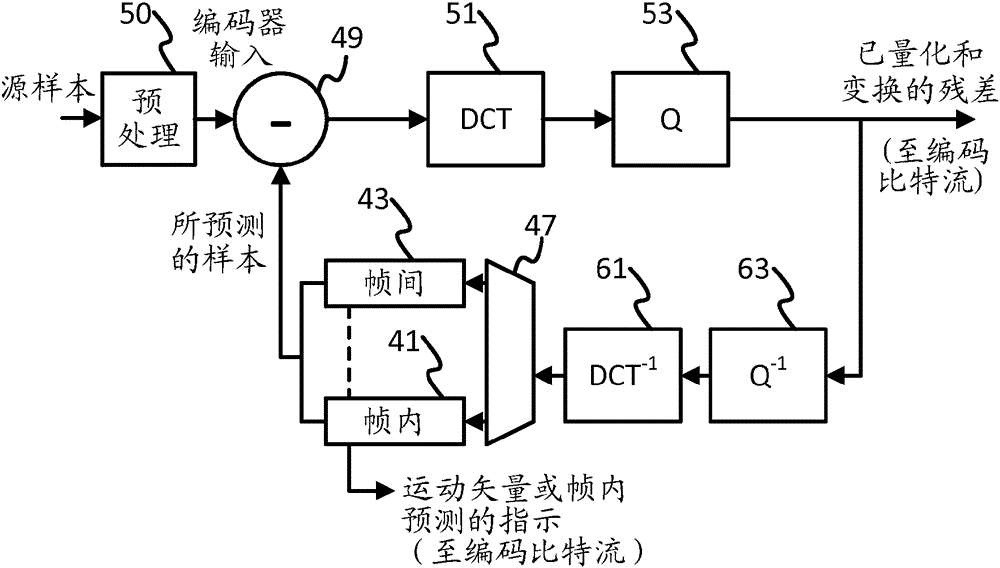
Spatially adaptive video coding
A coding and spatial technology, applied in image coding, digital video signal modification, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as packet loss, distortion, delay, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] At low bit rates, it may be beneficial to reduce the video resolution to reduce the distortion introduced by encoding. Frames can contain objects with different resolution sensitivities, such as faces in the foreground and less important backgrounds. When reducing the resolution, important details in the face as well as communication cues can be lost. Therefore, it may be beneficial to give faces a higher resolution compared to the background.
[0016] One option could be to transmit two separate streams with different resolutions. This can be complex in terms of implementation, and it might not be very efficient either.
[0017] According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the solution is to "warp" the video frame at the sender side such that faces or other regions of interest (ROIs) are stretched out while the background is reduced. In an embodiment, the output may be a rectangular frame suitable for encoding with an existing encoder standard such as H.264...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com