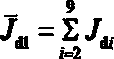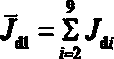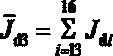Aeroengine Simulation Test Bench Based on Double Rotor Simplified Dynamic Model Design
An aero-engine and dynamics model technology, applied in simulators, instruments, control/regulation systems, etc., can solve problems such as complex model structure, difficult qualitative analysis, and low efficiency of quantitative analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] A kind of aero-engine simulation test bench based on double-rotor simplified dynamics model design, its composition comprises: test bed frame, described frame adopts the structure supporting low-pressure rotating shaft 31 of 6-point support and the high-pressure rotating shaft that is sleeved on the outside of low-pressure rotating shaft 32;
[0072] The dual-rotor system of an aero-engine adopts a 6-point support structure, in which the high-pressure rotor system adopts a two-point structure and adopts a 1-0-1 support method; the low-pressure rotor system adopts a four-point structure and adopts a 1-2-1 support method; The bearing supports in the dual-rotor system are numbered 1-6 from left to right, and bearing 5 is an intermediate bearing 33 . According to the support structure and working principle of the aero-engine dual-rotor system, a relatively accurate complex dynamic discrete model Model A of the aero-engine dual-rotor system with a 6-point support structure i...
Embodiment 2
[0108] According to the aeroengine simulation test bench designed based on the simplified dynamic model of the dual rotors described in Example 1, the critical speeds of the three models and the relative errors between the simplified model and the complex model under different elastic support coefficients. The support is an isotropic elastic support. In this paper, the dual-rotor system model is discretely modeled and simplified. Here, it can be assumed that all supports have the same stiffness, and the elastic support coefficient is 1*10 4 N / m changes to 2*10 for approximately rigid support 9 N / m. representing different models i order critical speed, where ,Model B and model C First i The order critical speed relative to the model A No. i critical speed error Expressed as
[0109] (11)
[0110] Figure 4 to Figure 11 When the system rotates in the same direction and the high-voltage rotor is the main excitation, the comparative analysis diagrams of the first ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com