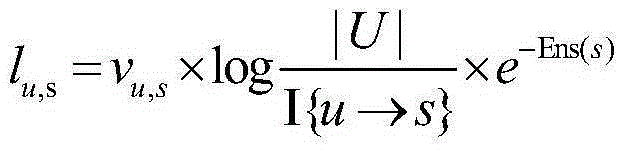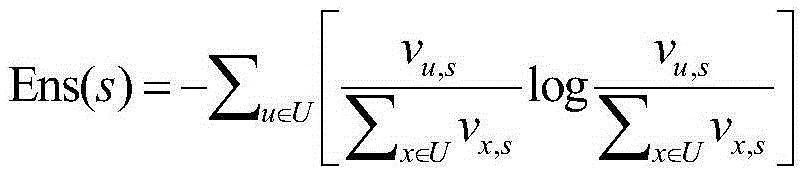Geographical social network based user similarity computation method
A user similarity and social network technology, applied in the field of public opinion monitoring, can solve the problems of not considering the strength in the statistical sense, not being able to identify, not considering the overall law of social work and rest, etc., to achieve better user classification effect, high accuracy, and user Classification effect is excellent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
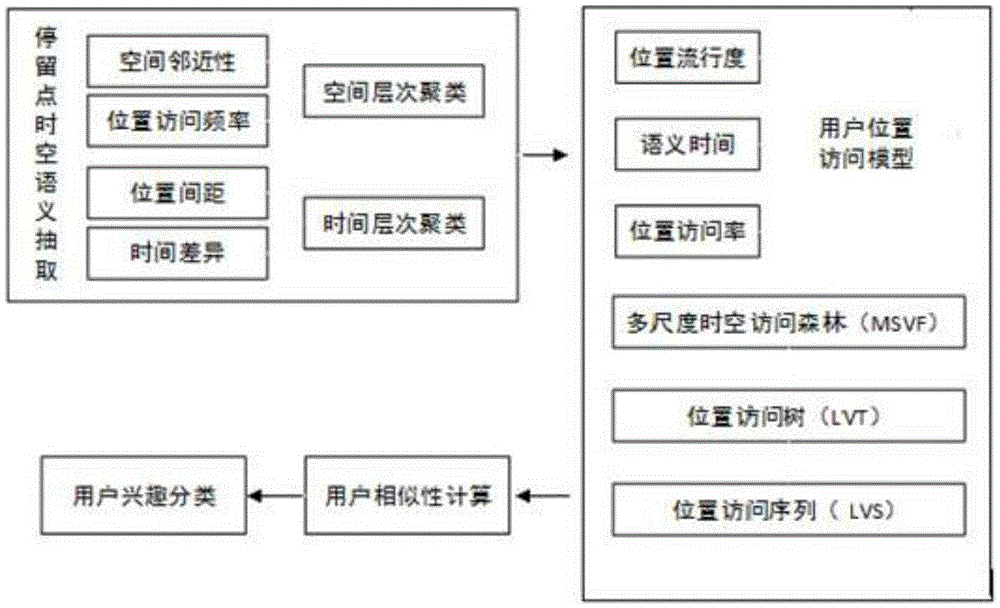
[0037] Step 1: Spatiotemporal Semantic Extraction
[0038] (1) Multi-scale spatial semantics
[0039] Using the VenueID in the Checkin data as a parameter, the POI name of the Checkin location can be obtained through Foursquare's RESTAPI, so as to obtain the lowest-level functional semantics of the location, such as "WuhanUniversity", and the RESTAPI can further obtain "WuhanUniversity" belonging to the "Education" category , so as to obtain the functional semantics of the Checkin position at a higher scale, and so on, so as to map all the Checkin positions of each user to the hierarchical POI classification structure to form a multi-scale semantic tree of positions.
[0040]In order to express the similarity of users’ stay at different spatial scales, we introduce the user’s access intensity to locations in the location semantic division based on geographical divisions, and perform spatial hierarchical clustering of locations based on the spatial distance between locations, s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com