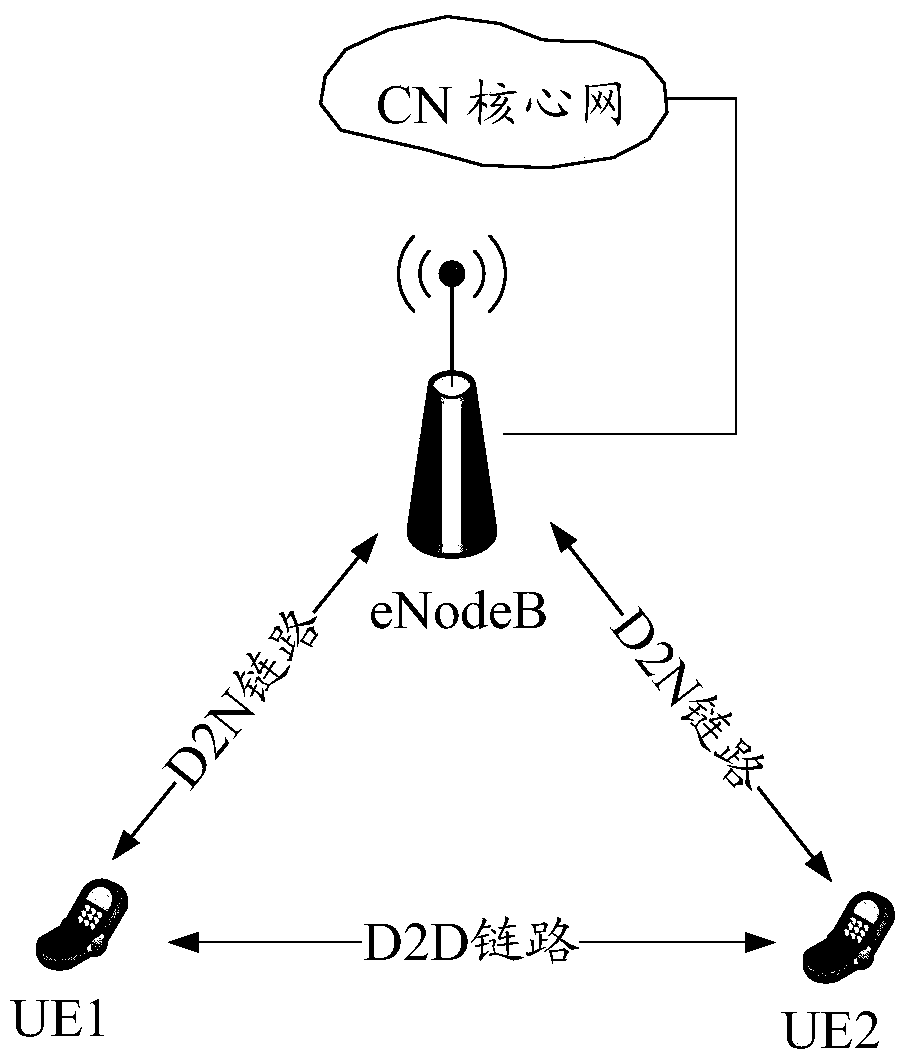
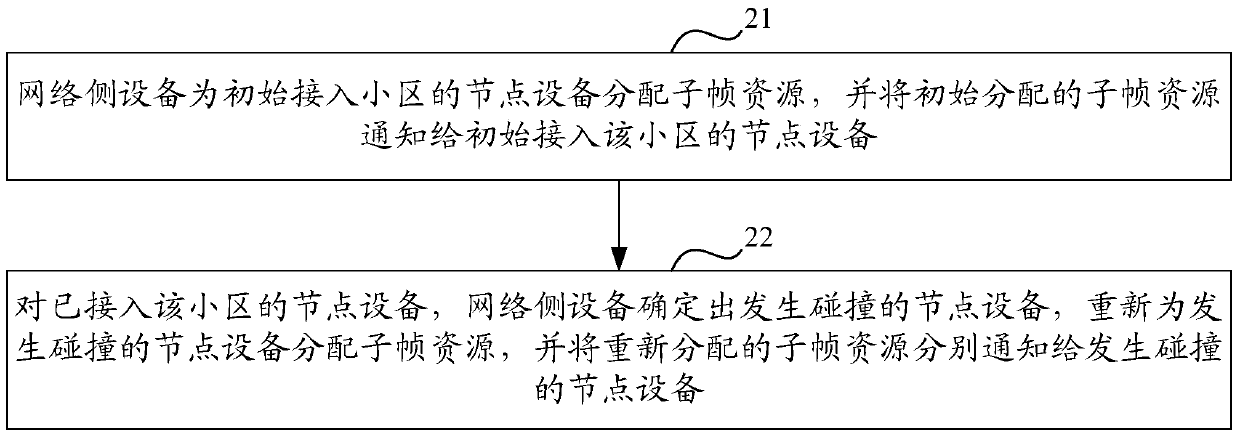
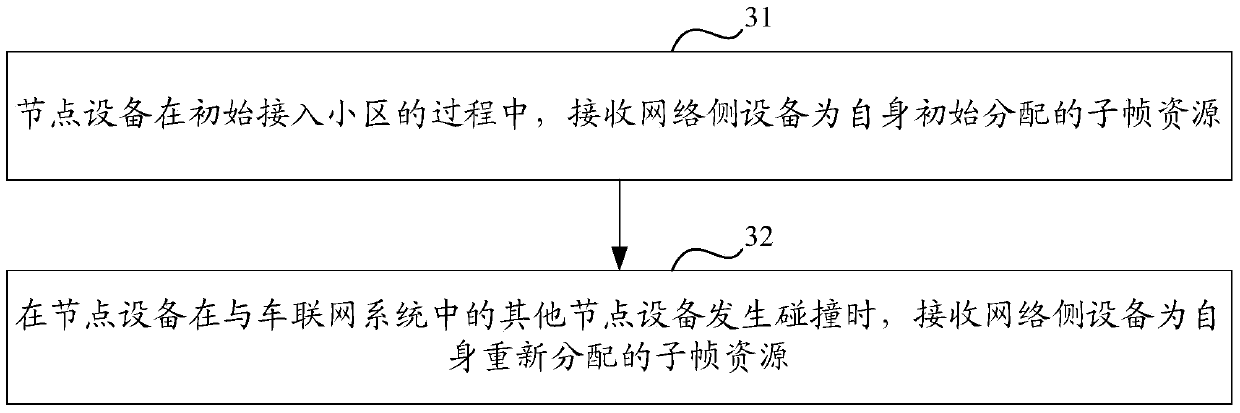
A method and device for information reporting and resource allocation in a vehicle networking system
A resource allocation and vehicle networking technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as poor security and node device collisions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0202] Embodiment 1: This embodiment mainly describes the processes of collision processing, reporting of strong interference by node devices (referred to as nodes), and re-allocation of subframe resources by the base station.
[0203] Assuming that node A, node B, and node C belong to the same base station, the distance between node A and node C is one hop, and the distance between node B, node A and node C is relatively far, and the base station allocates subframe resources for these three nodes, as Node A and Node B are allocated subframe 1 (node A and node B multiplex subframe 1), and node C is allocated subframe 2. Since node B is far away from node A and node C, it can be multiplexed with node A. Use subframe 1.
[0204] As the topology moves, the closer the node B is to the nodes A and C, the node A and the node B use the same subframe resource, causing some interference to the node C. When the signal strength from node B to node C is equal to the signal strength fro...
Embodiment 2
[0206] Embodiment 2: This embodiment mainly describes the resource adjustment process.
[0207] Assuming that node A and node B belong to the same base station, and the base station allocates subframe resources for these two nodes, since the distance between the two nodes is relatively long, the same subframe can be reused. With the movement of the topology, the distance between the two nodes is getting closer and closer, there is a possibility that there is a need for communication between the two nodes, and there are no other nodes between the two nodes, and the existence of the other node cannot be perceived through other nodes. A and Node B cannot receive each other's information.
[0208] In this case, the base station selects node A to continue using the existing subframe when it determines that the positions of the two nodes have reached the minimum distance for resource reuse based on the subframe resource information allocated to the node and the location information ...
Embodiment 3
[0209] Embodiment 3: This embodiment mainly describes the initial resource allocation process.
[0210] Node A initially accesses the base station, and applies for time slot resources through a Random Access (RA) process, wherein node A carries its own location information in the process of applying for resources.
[0211] The base station allocates time slot resources for node A according to the location information of node A. Prioritize the allocation of subframe resources that have not been allocated by the base station (that is, subframe resources in the idle state). If there are no subframe resources in the idle state, the base station searches for the node that occupies a certain subframe resource and is farthest from node A. Subframe resources are allocated to node A.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com