A Discrete Element Method for Arbitrary Convex Polygon Block Based on Distance Potential Function
A technique of discrete element method and potential function, which is applied in the fields of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as ambiguity in physical meaning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
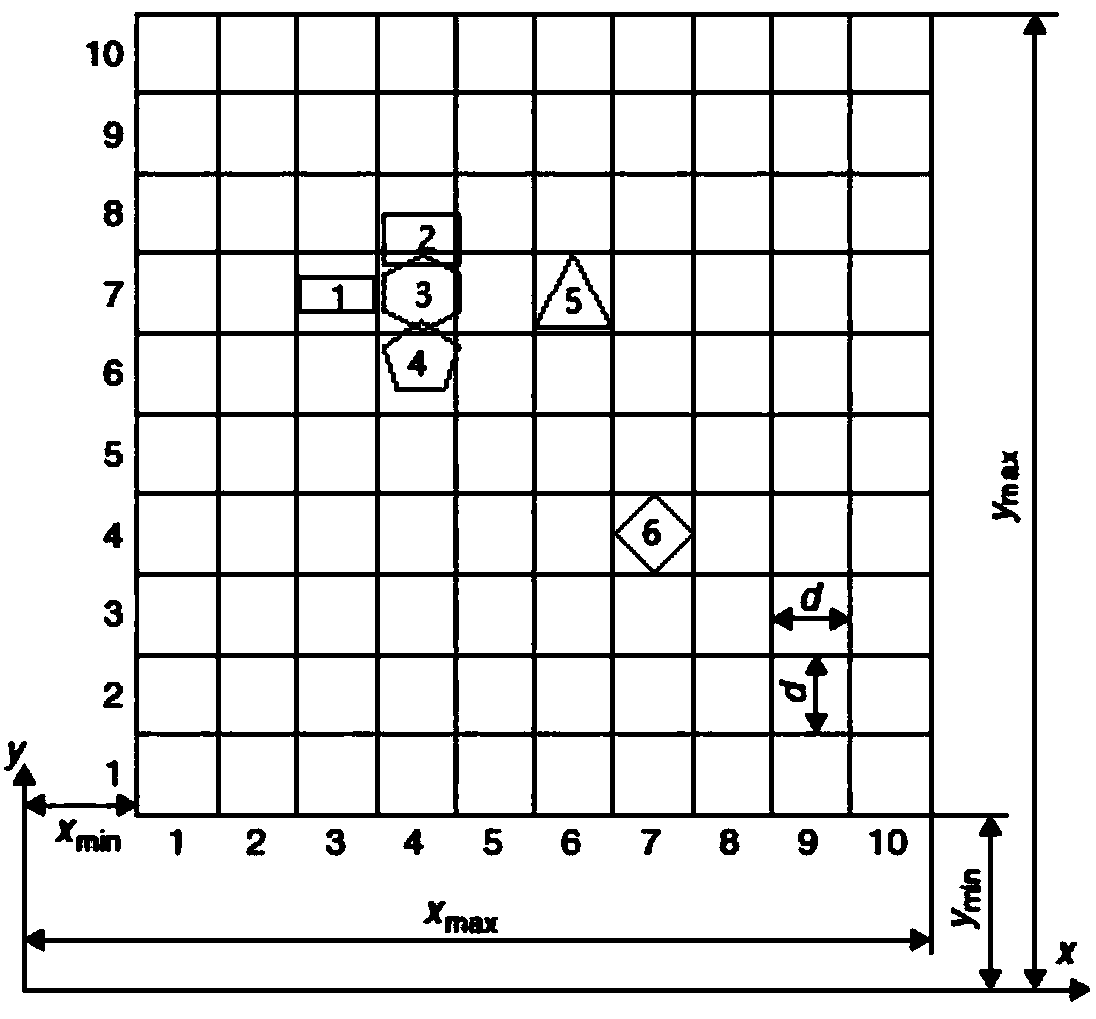
[0169] The movement form of the ore falling into the trough frame at a certain speed, the trough frame is a rectangular frame, that is, the movement form of the polygonal ore block unit within a certain shape boundary, such as Figure 5As shown, four ore blocks move downward at a speed of 0.08m / s. Using the method provided by the present invention, a discrete element model is established for the ore-boundary. Now the four ore blocks are divided into 35 block discrete units , that is to calculate and analyze the movement of 35 block units.
[0170] Figures 6 to 10 It is the movement process diagram of the ore block after the ore block starts to contact the tank frame. In the discrete element model, all block units move downward at a speed of 0.08m / s. When the lowermost block unit contacts the boundary, the distance between the block unit and the block unit and between the block unit and the boundary Due to the contact force and moment generated by the contact, the resultant ...
Embodiment 2
[0174] The funnel of a mining site is filled with collapsed and irregular ores of different sizes. Open the gate of the funnel, and under the action of self-weight, the movement form of the ore after it is released from the funnel, that is, the polygonal ore block unit is within a certain shape boundary The motion form of the ore, using the method provided by the present invention, establishes a discrete element model for the ore-boundary, such as Figure 12 As shown, a total of 309 ore body discrete units are divided, 162 funnel and trough frame discrete units are divided, and the funnel and trough frame are fixed.
[0175] Figure 12 is the initial state of the ore in the hopper, Figure 13 to Figure 19 After the gate of the funnel mouth is opened, it is the geometric shape when drawing ore. The ore bodies are affected by gravity and contact each other, resulting in contact force and moment, the speed and acceleration of the ore body change accordingly, and the ore body mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com