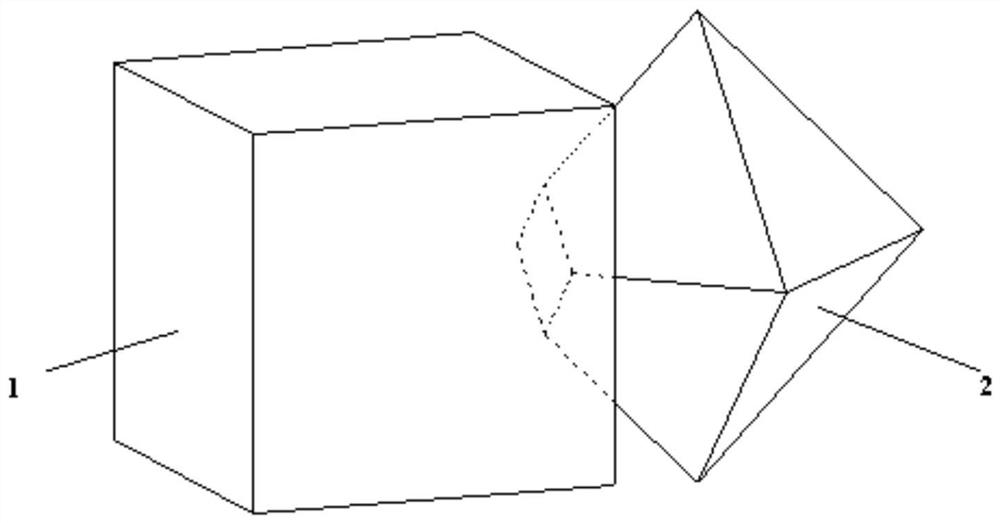
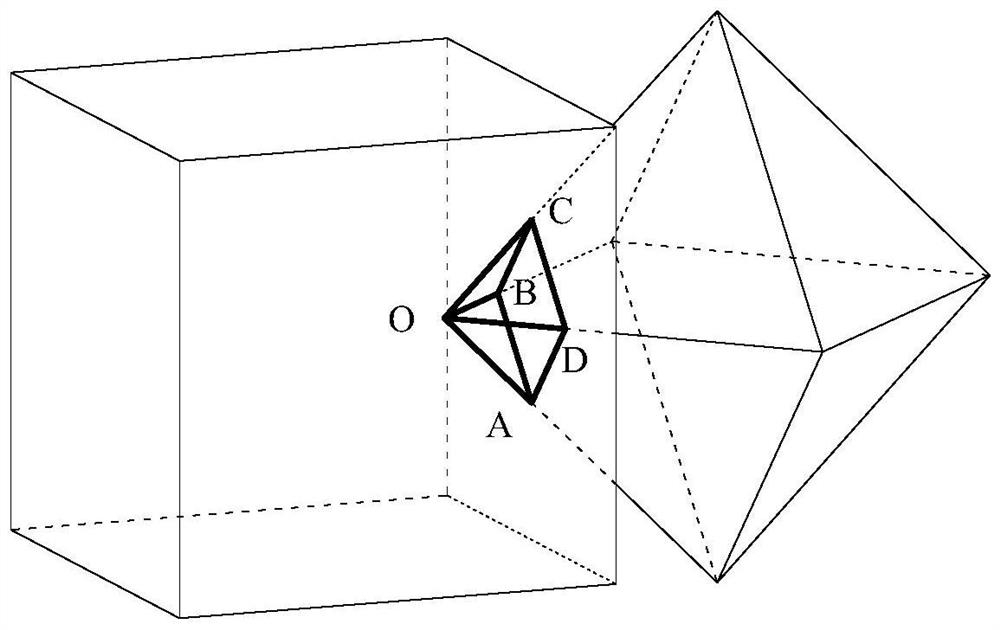
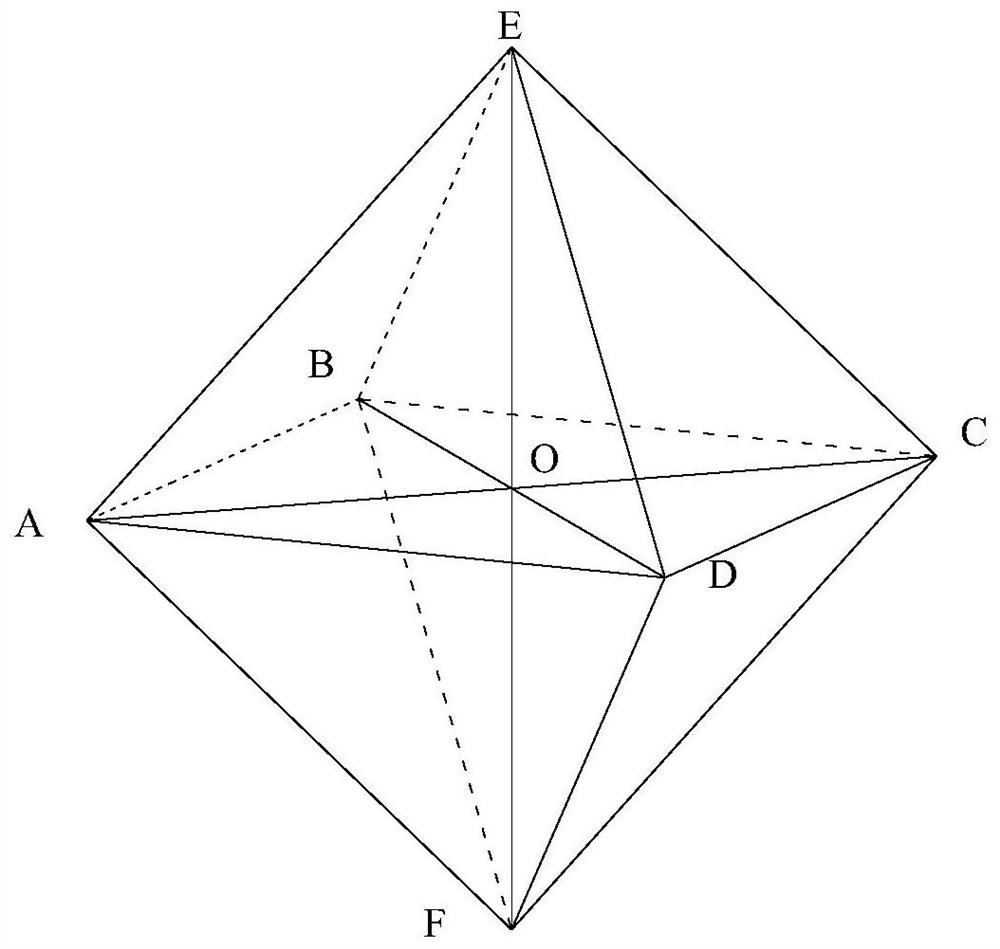
A Discrete Element Method for Three-Dimensional Arbitrary Convex Polygonal Blocks Based on Distance Potential Function
A convex polygon and potential function technology, applied in the field of block discrete elements, can solve problems such as single form, influence of element stiffness and contact force, and uniform element size.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0216] Due to the existence of weak interlayers inside a certain rock slope, under the influence of external conditions such as earthquakes and rainfall, it may cause geological disasters such as landslides. Adopt the method provided by the invention, set up the discrete unit model for the rock slope, such as Figure 6 As shown, a total of 2653 discrete units are divided.
[0217] Figure 6 is the state when the rocky slope is stable, Figure 7 to Figure 9 It is the movement process of landslide along the sliding surface under the influence of external conditions. Based on the three-dimensional block discrete element method of the distance potential function provided by the present invention to simulate the rock slope landslide process, it can clearly describe the failure process of the rock slope along the sliding surface under the influence of unfavorable loads, and can analyze the rock slope very well. Whether the slope is safe under load, the failure process of the land...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com