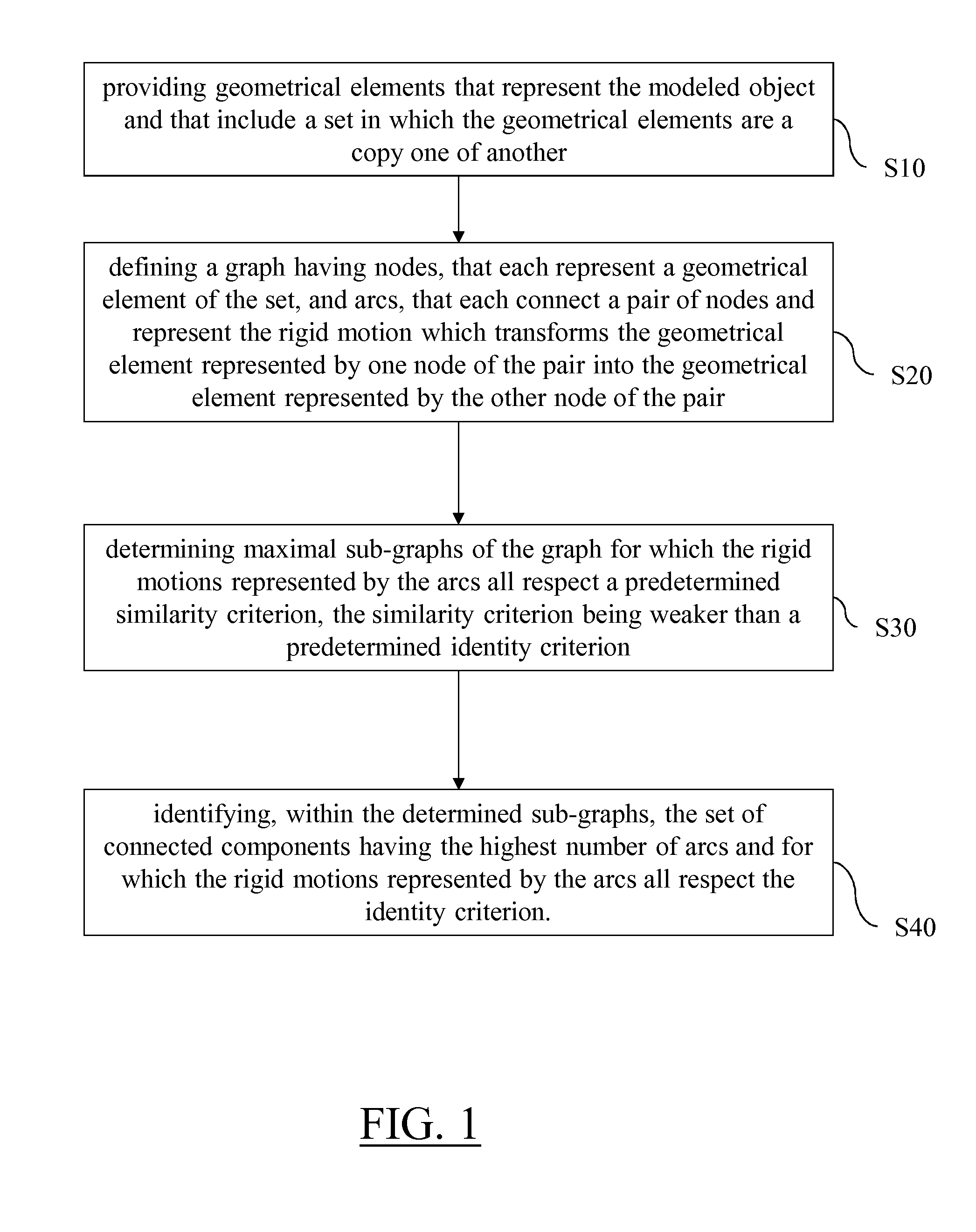
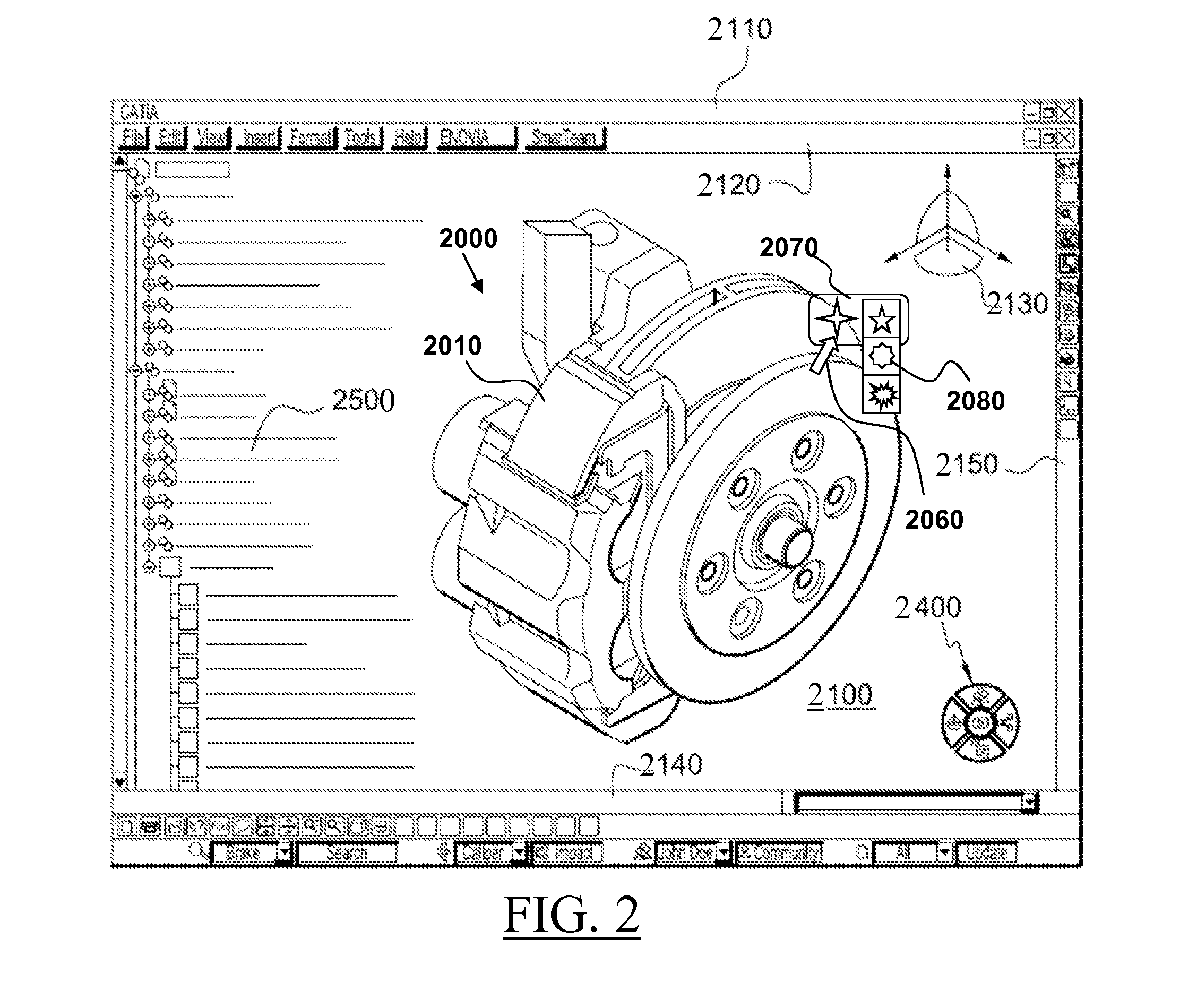
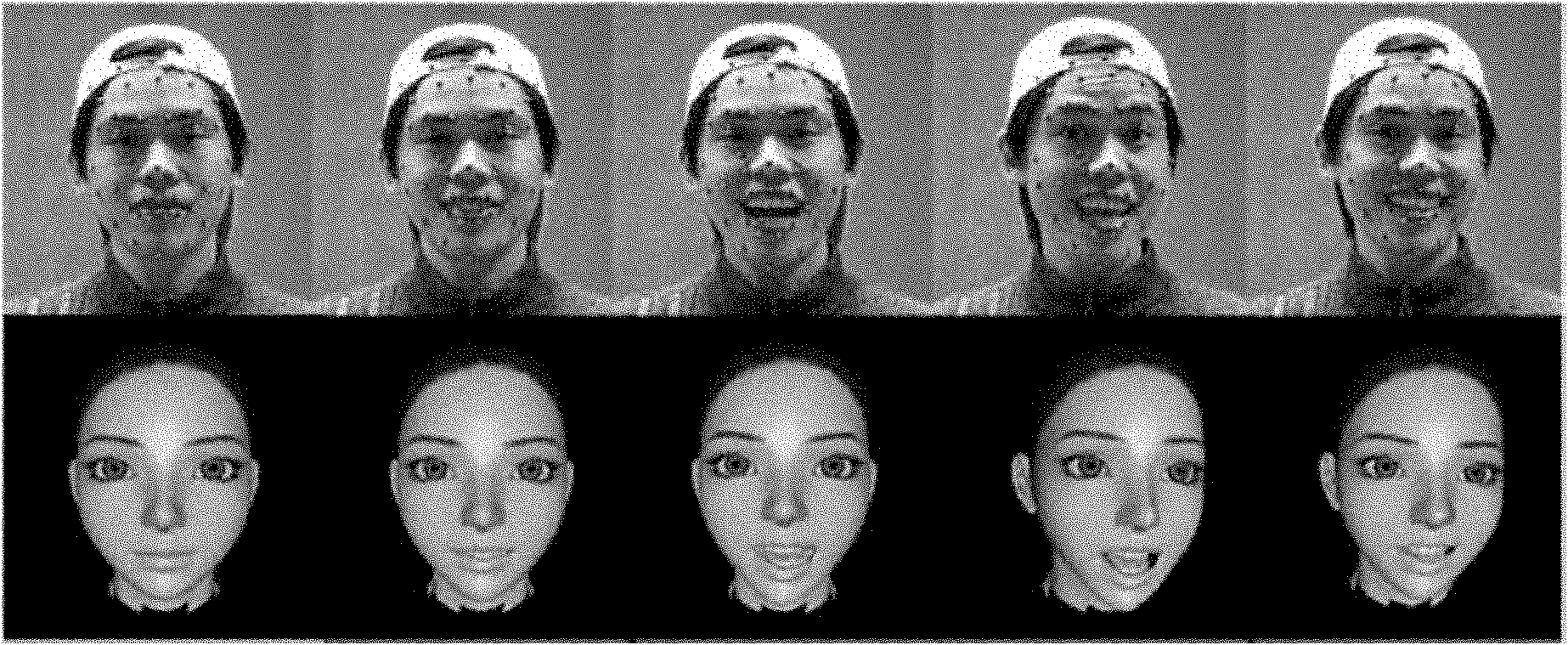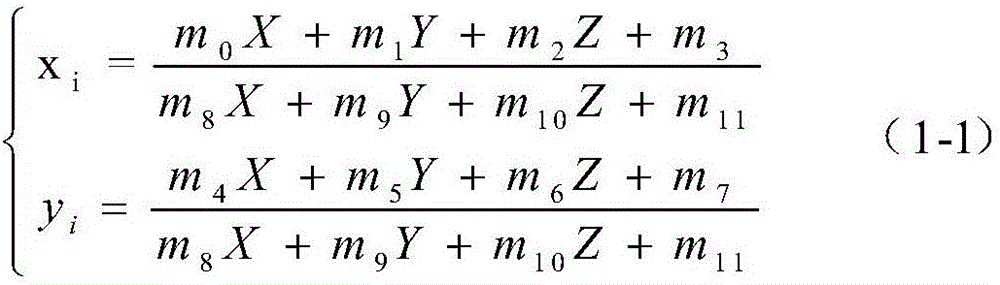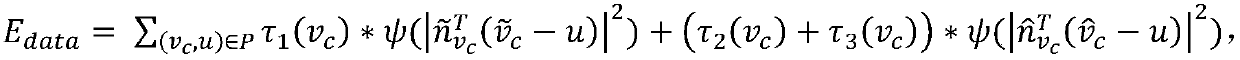Patents
Literature
124 results about "Rigid motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A rigid motion of the plane ( or an isometry ) is a motion which preserves distance. There are four basic rigid motions: (1) Re°ection (2) Glide Re°ection (3) Rotation (4) Translation Theorem 2. The above list contains all rigid motions of the plane.
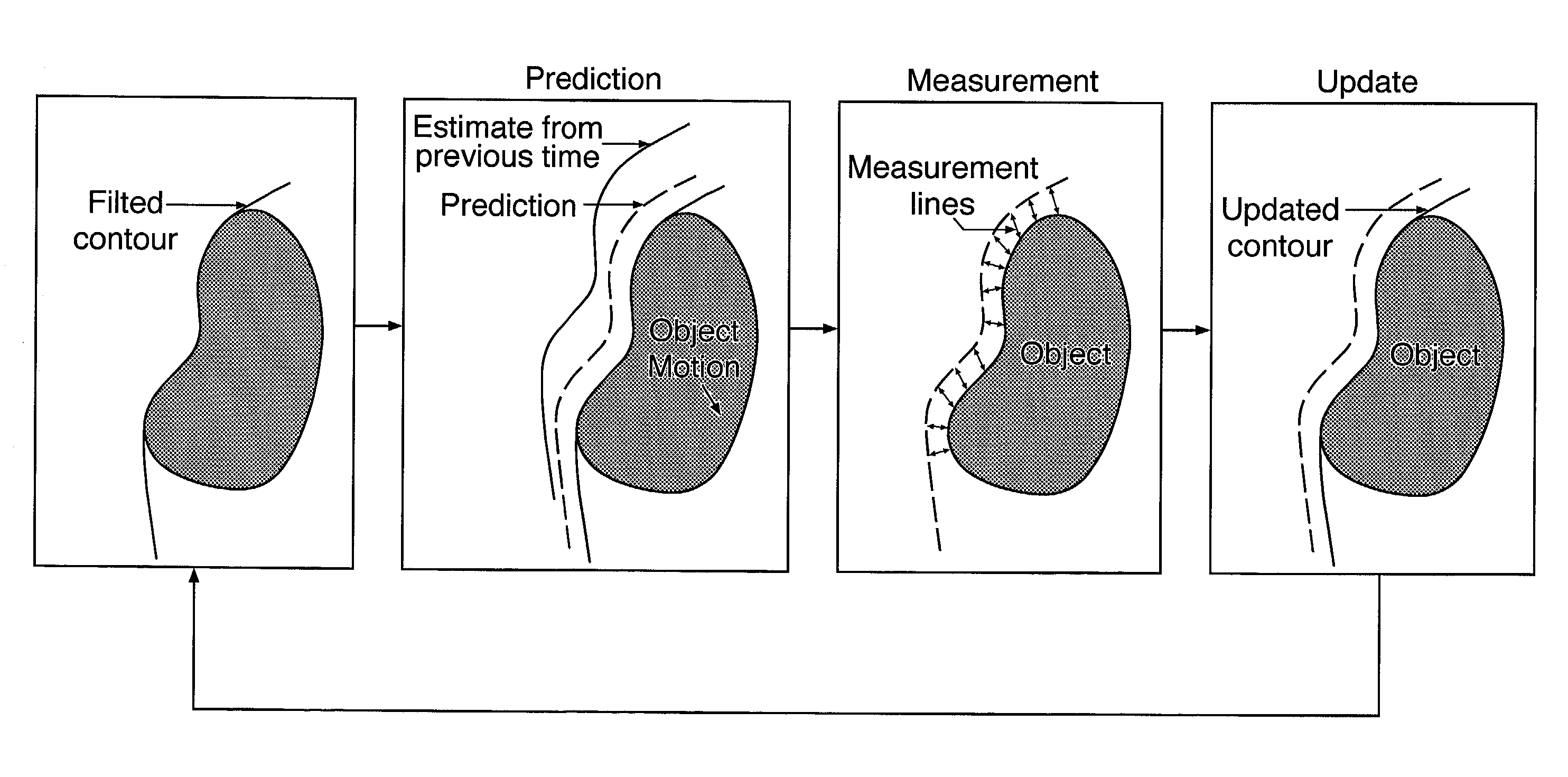
Non-rigid motion image analysis
InactiveUS7043063B1The solution result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisRigid motion
A method of analysing a sequence of images of a deformable object in non-rigid motion involves modeling the boundary using a non-rigid contour. A representation of movement of the contour through the sequence of images is calculated using a tracking space shape. The calculated movement representation is decomposed using an interpretational space shape that is different than the tracking space shape.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
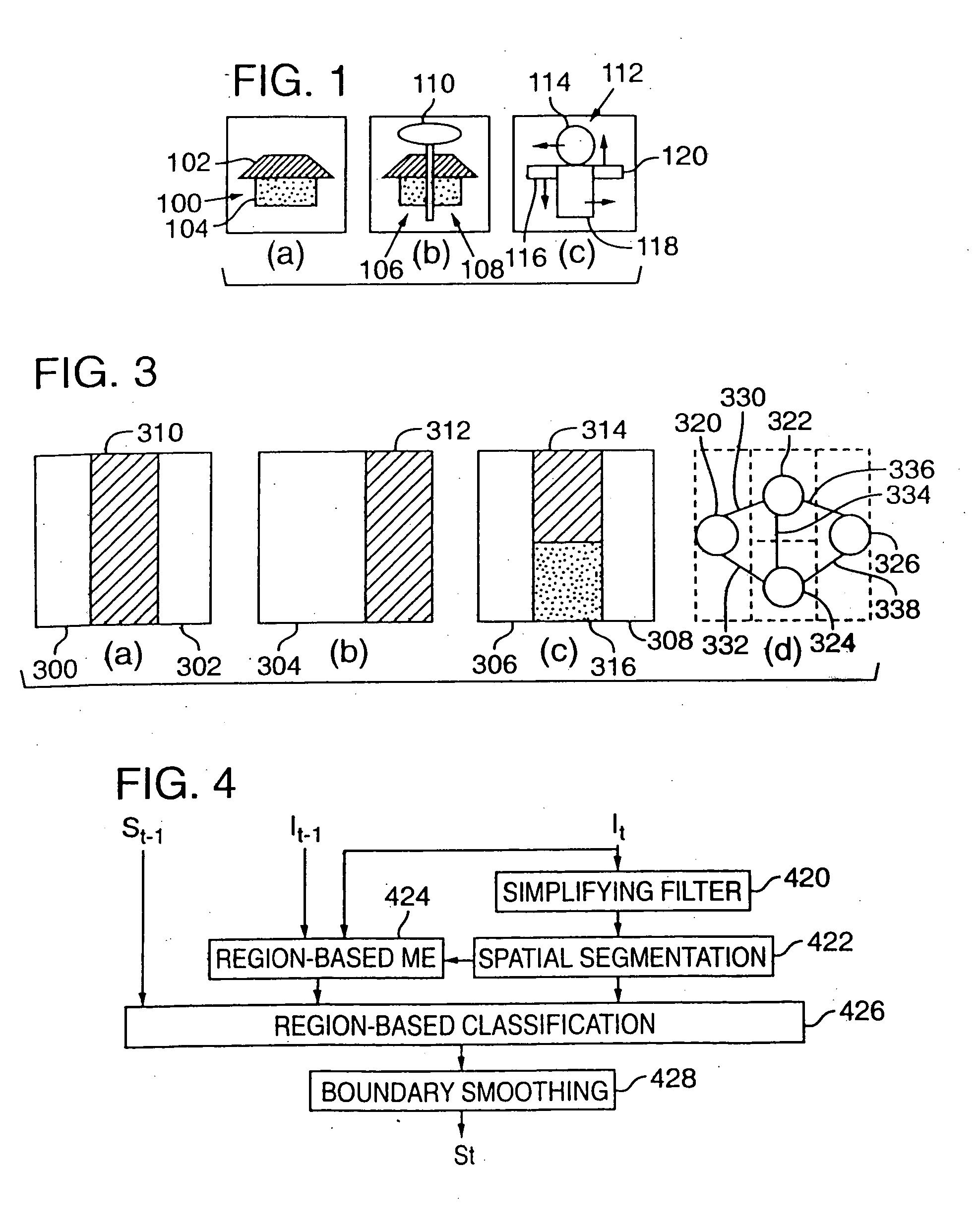
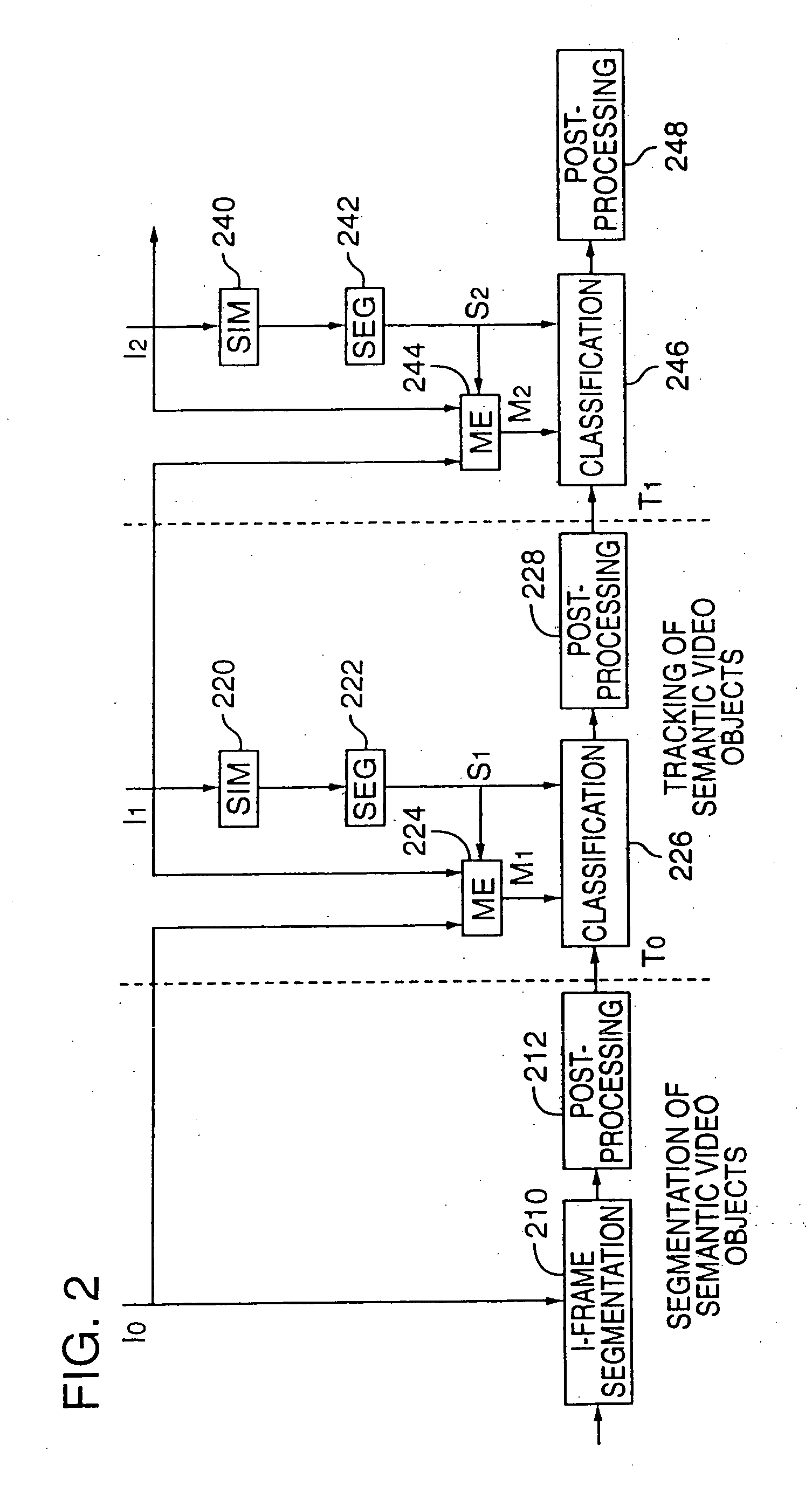
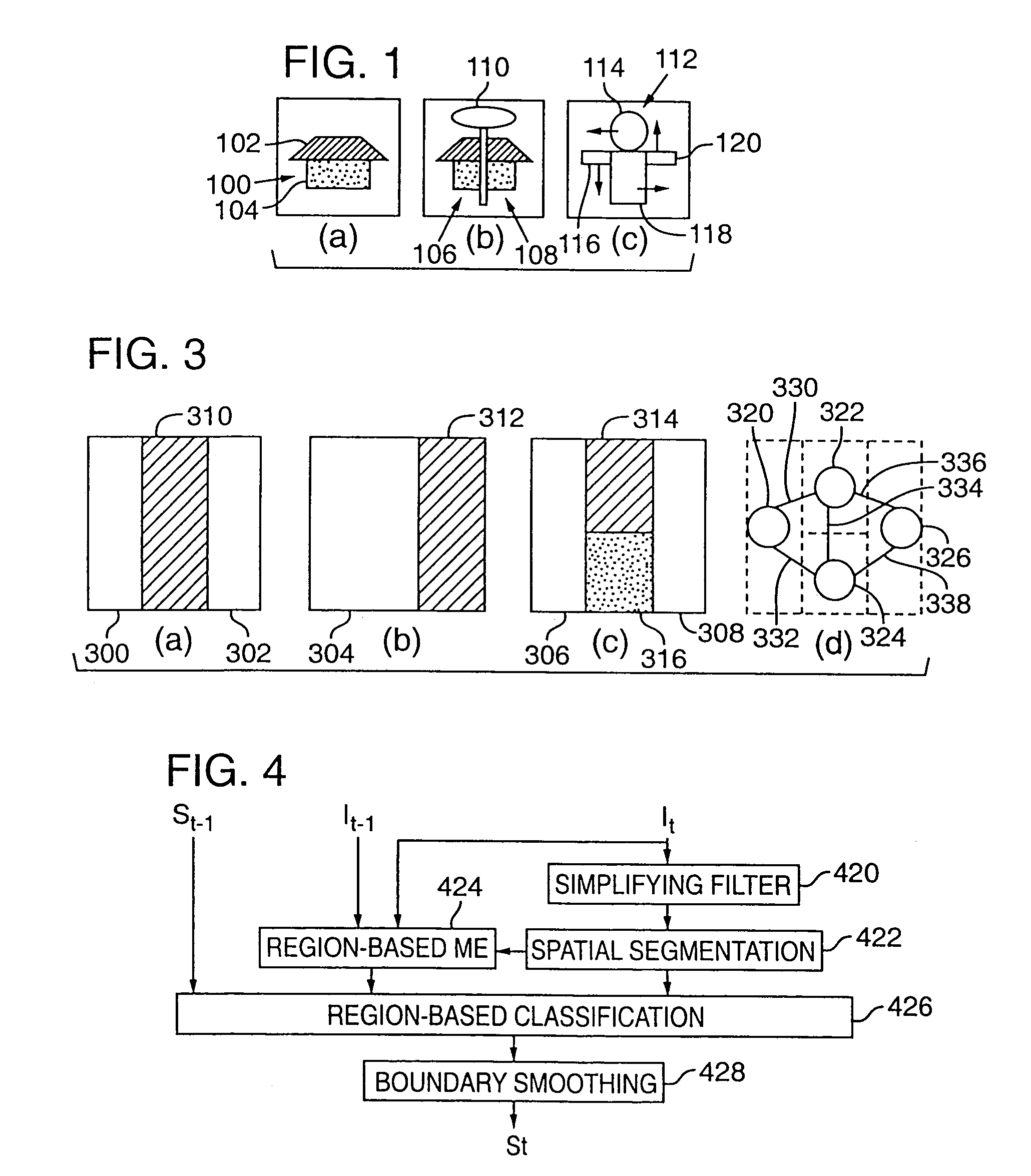
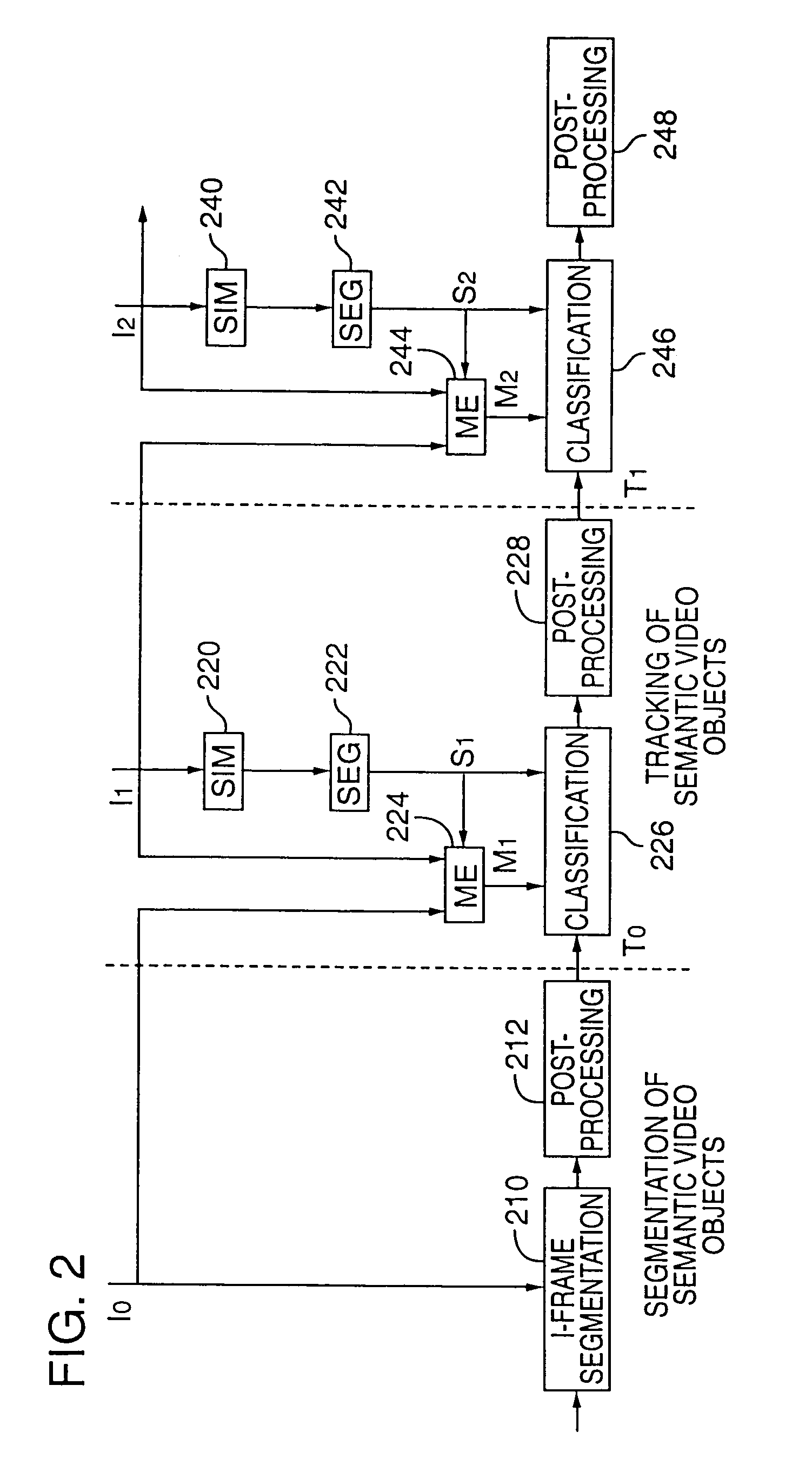
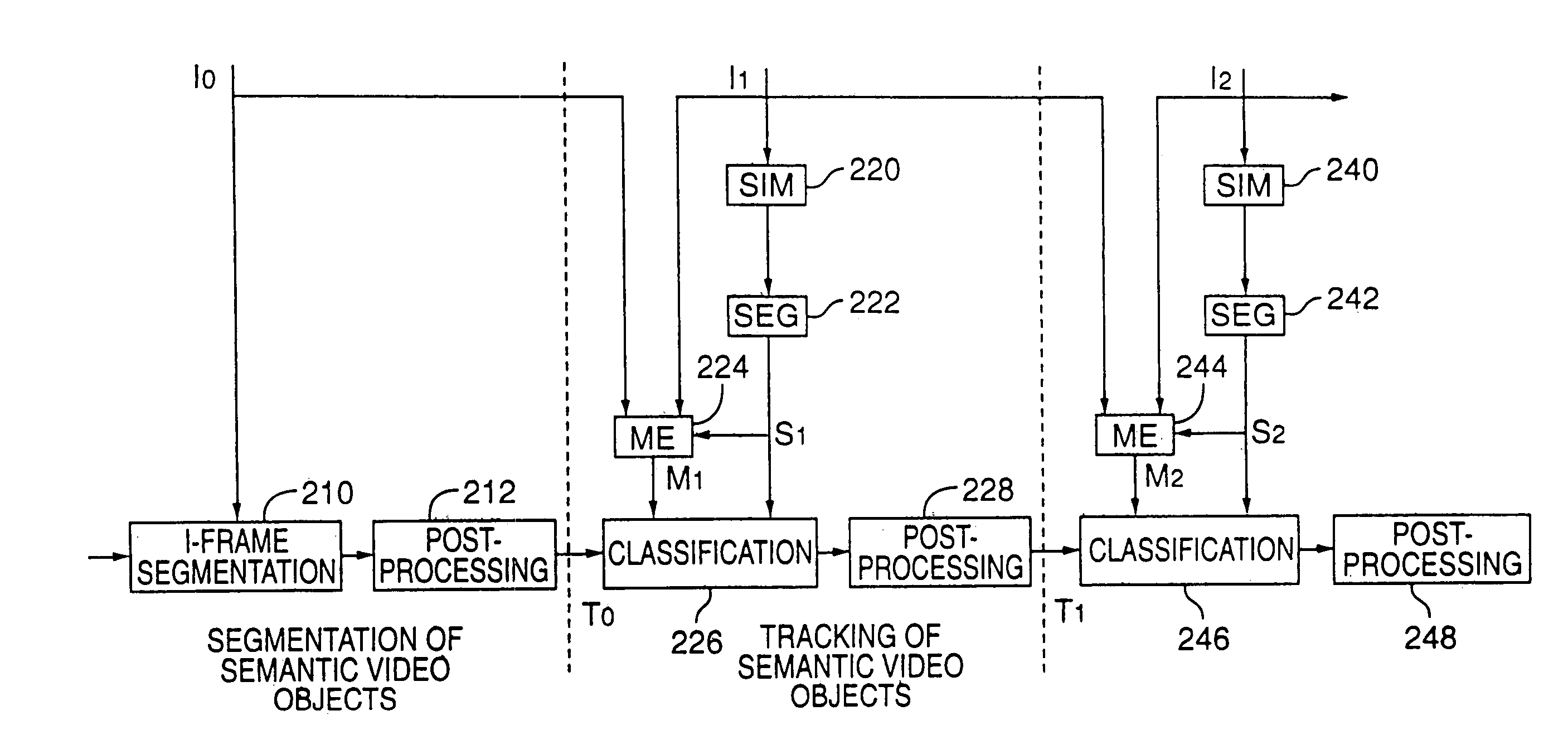
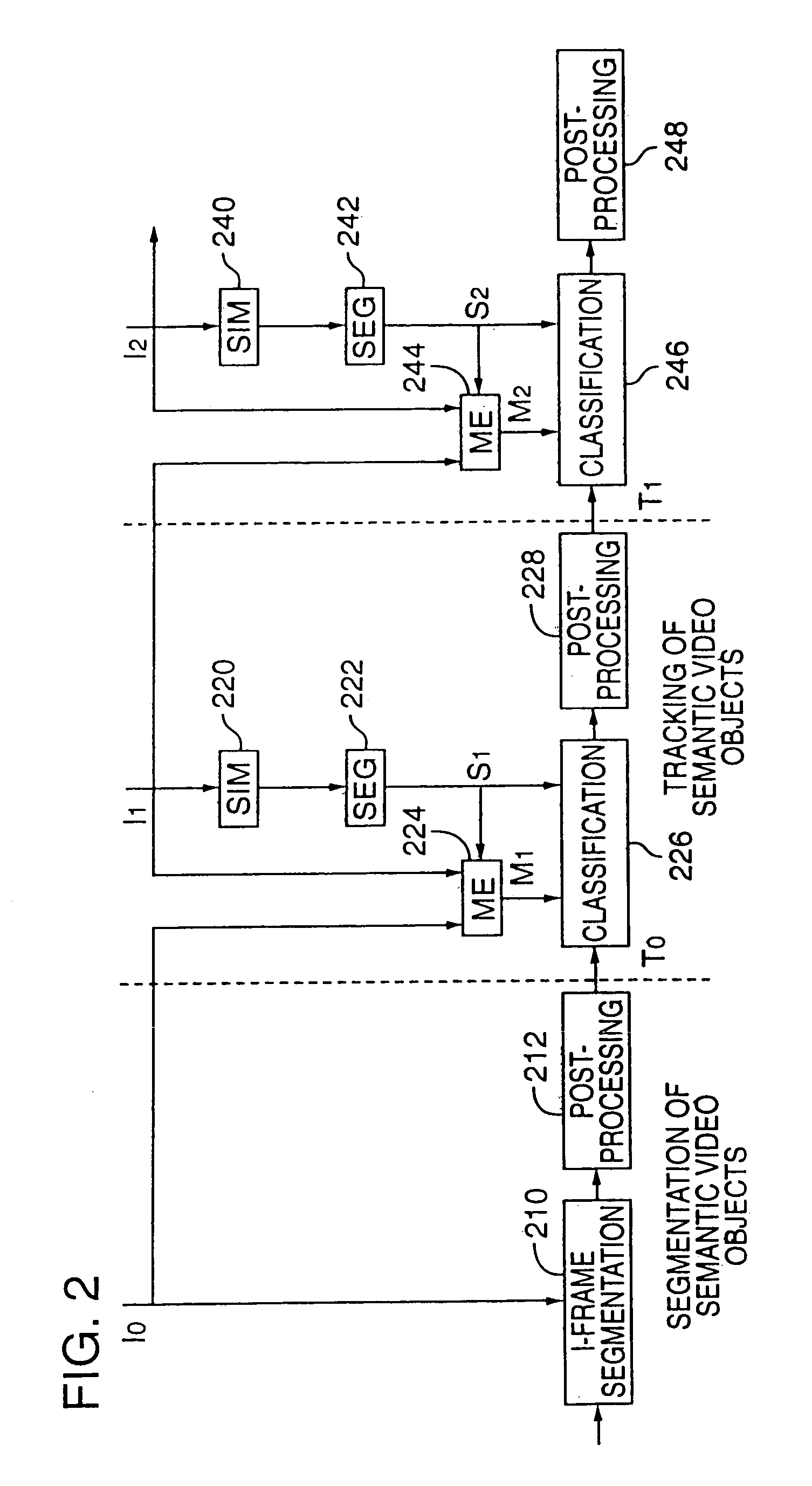
Tracking semantic objects in vector image sequences
InactiveUS20050240629A1Improve accuracyImage analysisDigital data processing detailsObject basedRigid motion
A semantic object tracking method tracks general semantic objects with multiple non-rigid motion, disconnected components and multiple colors throughout a vector image sequence. The method accurately tracks these general semantic objects by spatially segmenting image regions from a current frame and then classifying these regions as to which semantic object they originated from in the previous frame. To classify each region, the method perform a region based motion estimation between each spatially segmented region and the previous frame to computed the position of a predicted region in the previous frame. The method then classifies each region in the current frame as being part of a semantic object based on which semantic object in the previous frame contains the most overlapping points of the predicted region. Using this method, each region in the current image is tracked to one semantic object from the previous frame, with no gaps or overlaps. The method propagates few or no errors because it projects regions into a frame where the semantic object boundaries are previously computed rather than trying to project and adjust a boundary in a frame where the object's boundary is unknown.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Region extraction in vector images
InactiveUS7088845B2Improve accuracyImage analysisDigital data processing detailsComputer graphics (images)Radiology
A semantic object tracking method tracks general semantic objects with multiple non-rigid motion, disconnected components and multiple colors throughout a vector image sequence. The method accurately tracks these general semantic objects by spatially segmenting image regions from a current frame and then classifying these regions as to which semantic object they originated from in the previous frame. To classify each region, the method perform a region based motion estimation between each spatially segmented region and the previous frame to computed the position of a predicted region in the previous frame. The method then classifies each region in the current frame as being part of a semantic object based on which semantic object in the previous frame contains the most overlapping points of the predicted region. Using this method, each region in the current image is tracked to one semantic object from the previous frame, with no gaps or overlaps. The method propagates few or no errors because it projects regions into a frame where the semantic object boundaries are previously computed rather than trying to project and adjust a boundary in a frame where the object's boundary is unknown.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Tracking semantic objects in vector image sequences
InactiveUS7162055B2Improve accuracyTelevision system detailsImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A semantic object tracking method tracks general semantic objects with multiple non-rigid motion, disconnected components and multiple colors throughout a vector image sequence. The method accurately tracks these general semantic objects by spatially segmenting image regions from a current frame and then classifying these regions as to which semantic object they originated from in the previous frame. To classify each region, the method performs a region based motion estimation between each spatially segmented region and the previous frame to compute the position of a predicted region in the previous frame. The method then classifies each region in the current frame as being part of a semantic object based on which semantic object in the previous frame contains the most overlapping points of the predicted region. Using this method, each region in the current image is tracked to one semantic object from the previous frame, with no gaps or overlaps. The method propagates few or no errors because it projects regions into a frame where the semantic object boundaries are previously computed rather than trying to project and adjust a boundary in a frame where the object's boundary is unknown.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
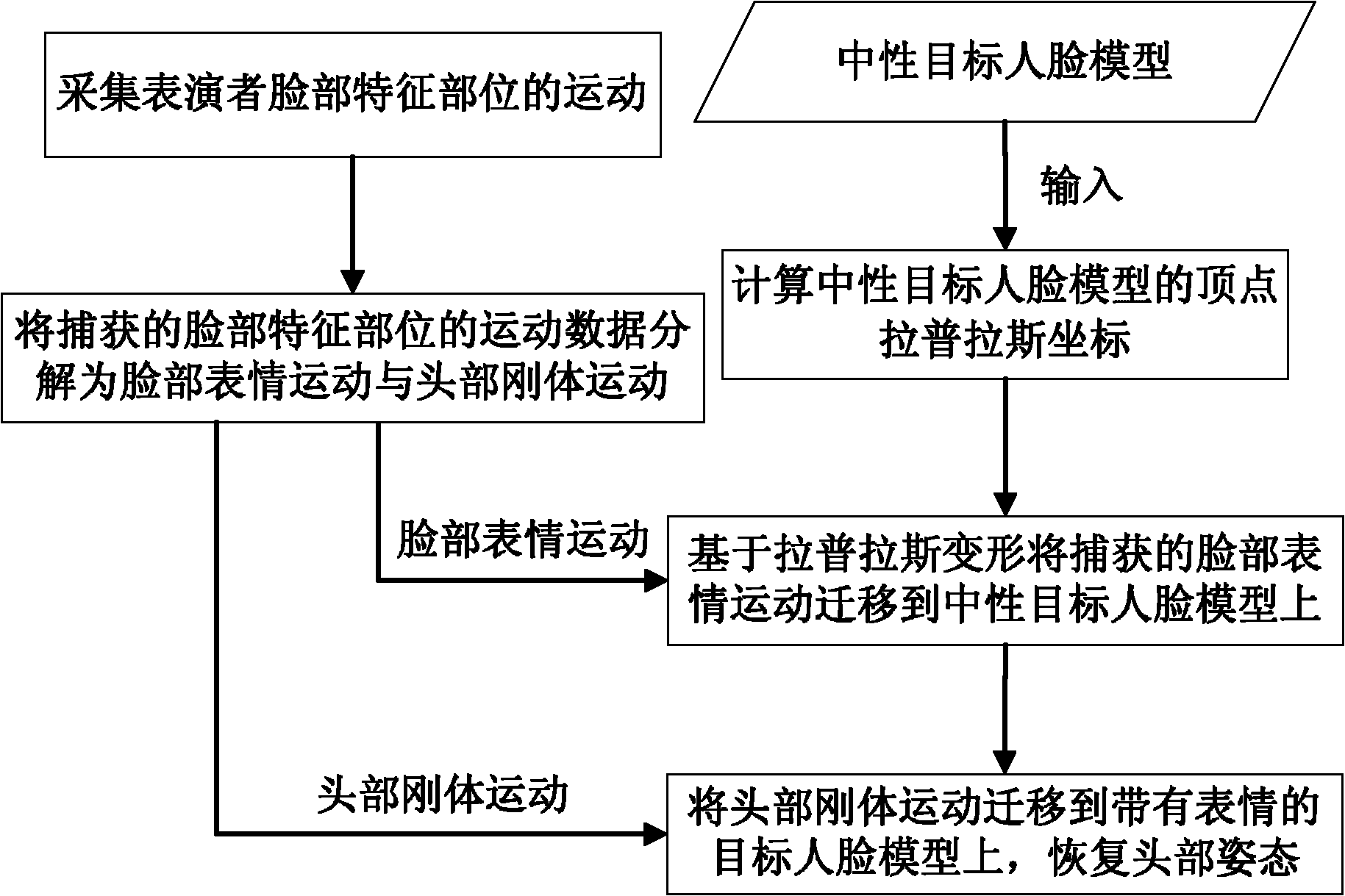
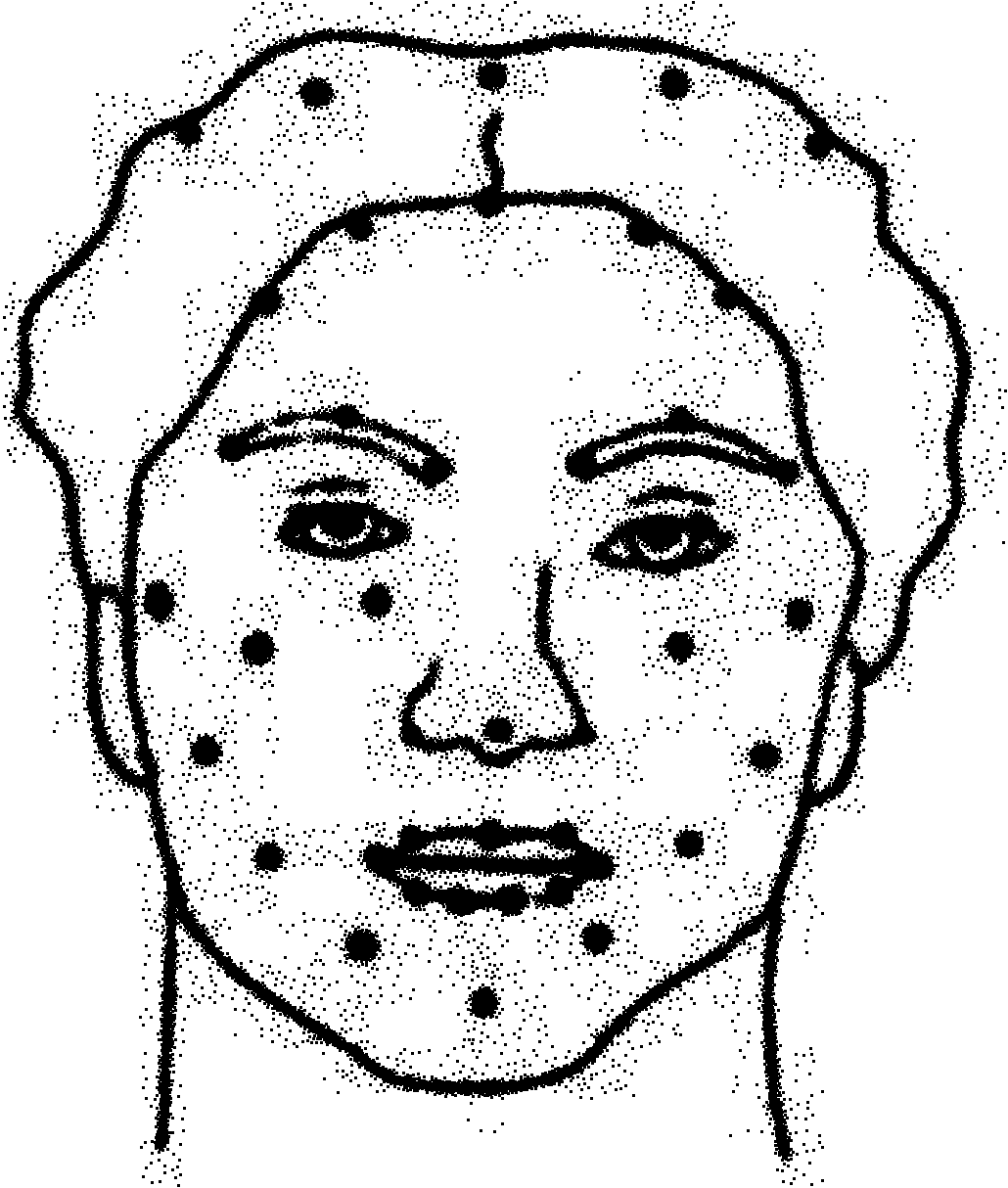
Data driving face expression synthesis method based on Laplace transformation
InactiveCN101944238AAchieve migrationClear algorithmAnimationLaplacian coordinatesPattern recognition
The invention discloses a data driving face expression synthesis method based on Laplace transformation, comprising the following steps of: resolving face motion data captured after the face motion of a performer is acquired into a face expression motion and a head rigid motion; calculating the Laplace coordinates of each peak in a loaded neutral target face model; moving the face expression motion to the neutral target face model to make the neutral target face model have consistent expressions with the performer; and moving the head rigid motion to the target face model having the consistent expressions with the performer to make the final target face model have consistent face expressions and head postures with the performer. Based on a Laplace transformation technology being capable of keeping the original detail features of the model, the invention keeps the existing detail features on the target face model while realizing the moving of the face expressions, has the advantages of definite arithmetic, friendly interface and robust result and can be conveniently applied to the computer game field, the online chat field and other man-machine interaction fields.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
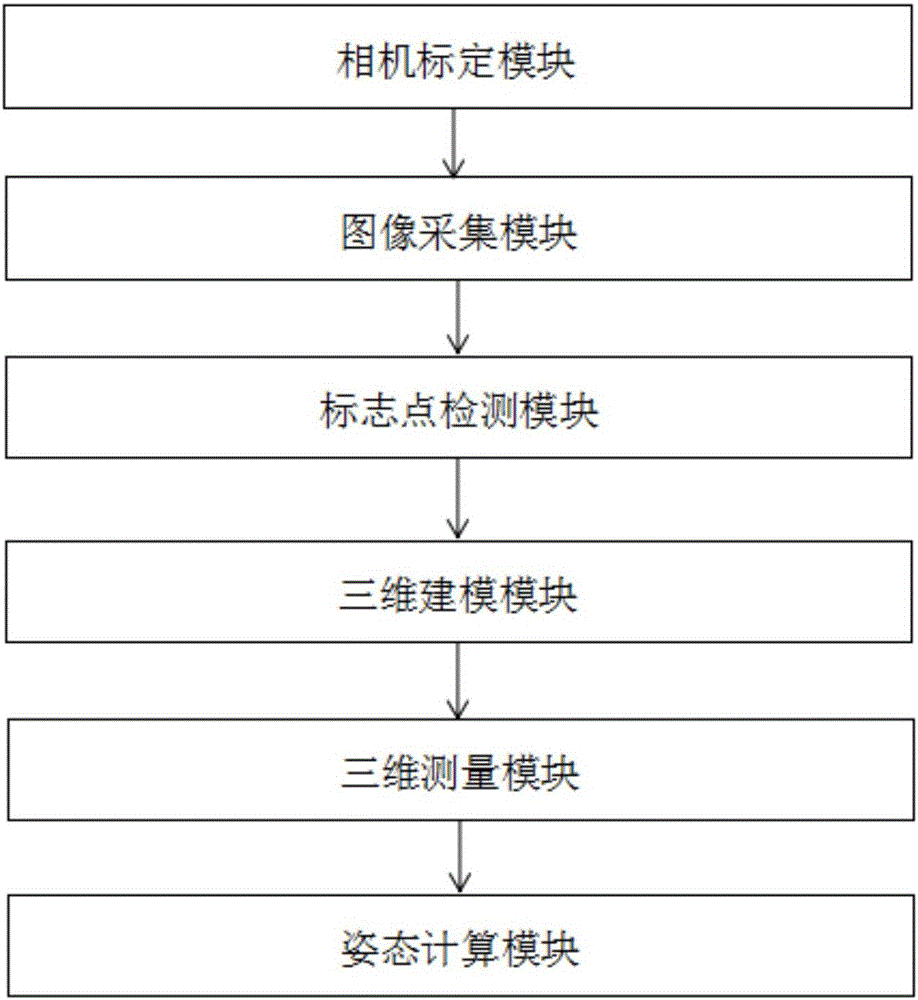
Rigid body motion capturing method and system based on mark point
InactiveCN106600627AHigh precisionSolve the problems of low accuracy of motion capture and lack of calculation of motion degrees of freedomImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional measurementRigid motion
The invention discloses a rigid body motion capturing method based on a mark point, and the method is used for calculating the position and posture of a rigid body in a measurement scene, controlling the motion of the rigid body, and obtaining the track of the rigid body. The method comprises the steps: firstly carrying out the collection of a two-dimensional image sequence of the rigid body and the detection of the mark point, and secondly achieving the three-dimensional measurement and posture resolving of the mark point. The method solves problems that a conventional rigid body motion capturing method is not high in instantaneity, is usually low in motion capturing precision when there is no mark motion, and causes the motion freedom calculation loss. The method improves the motion capturing precision. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses a rigid motion capturing system based on the mark point.
Owner:CHENGDU TOPPLUSVISION TECH CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for automated part positioning based on geometrical comparisons
ActiveUS20070279414A1Simple definitionImage analysisCathode-ray tube indicatorsAlgorithmRigid motion
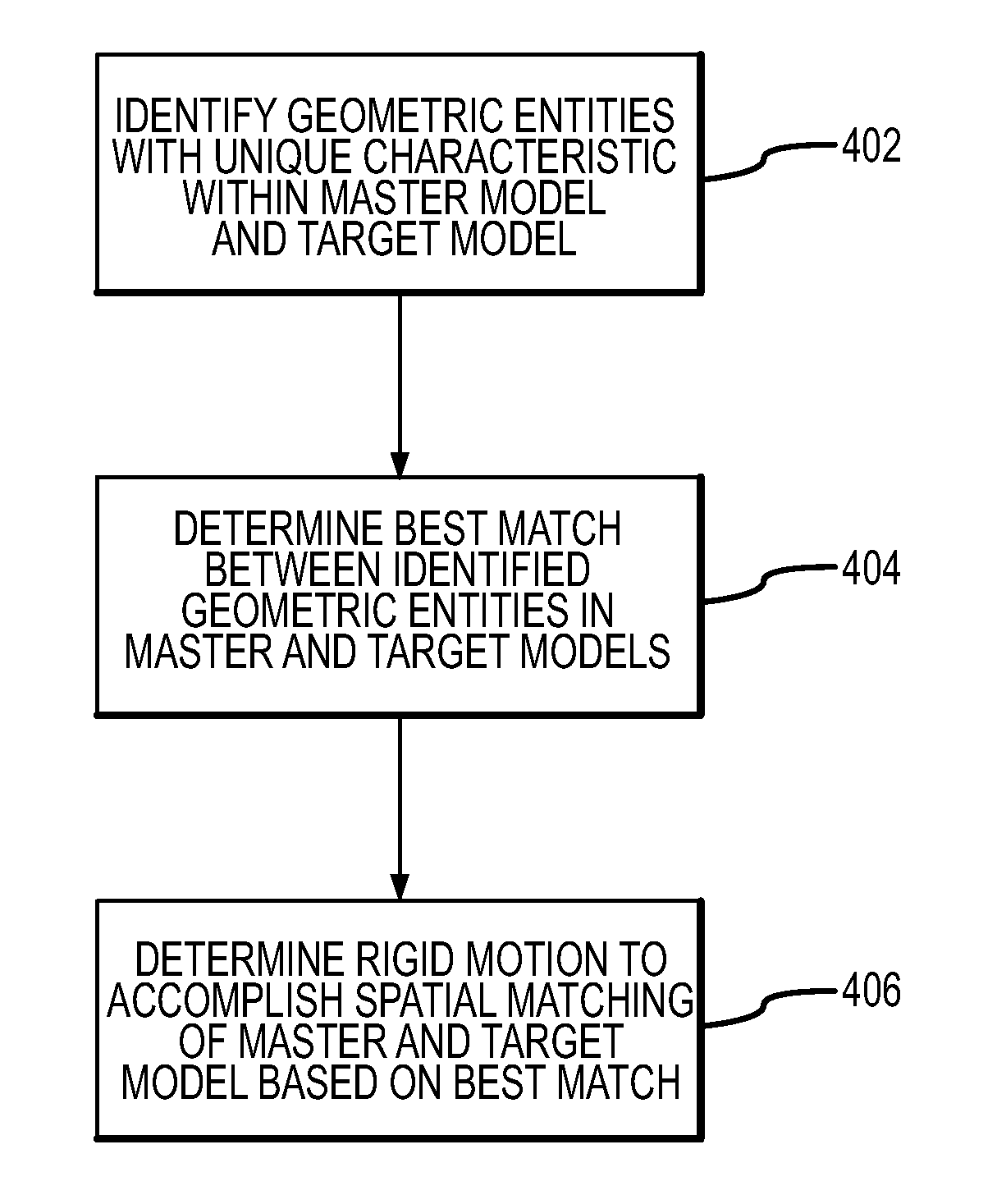
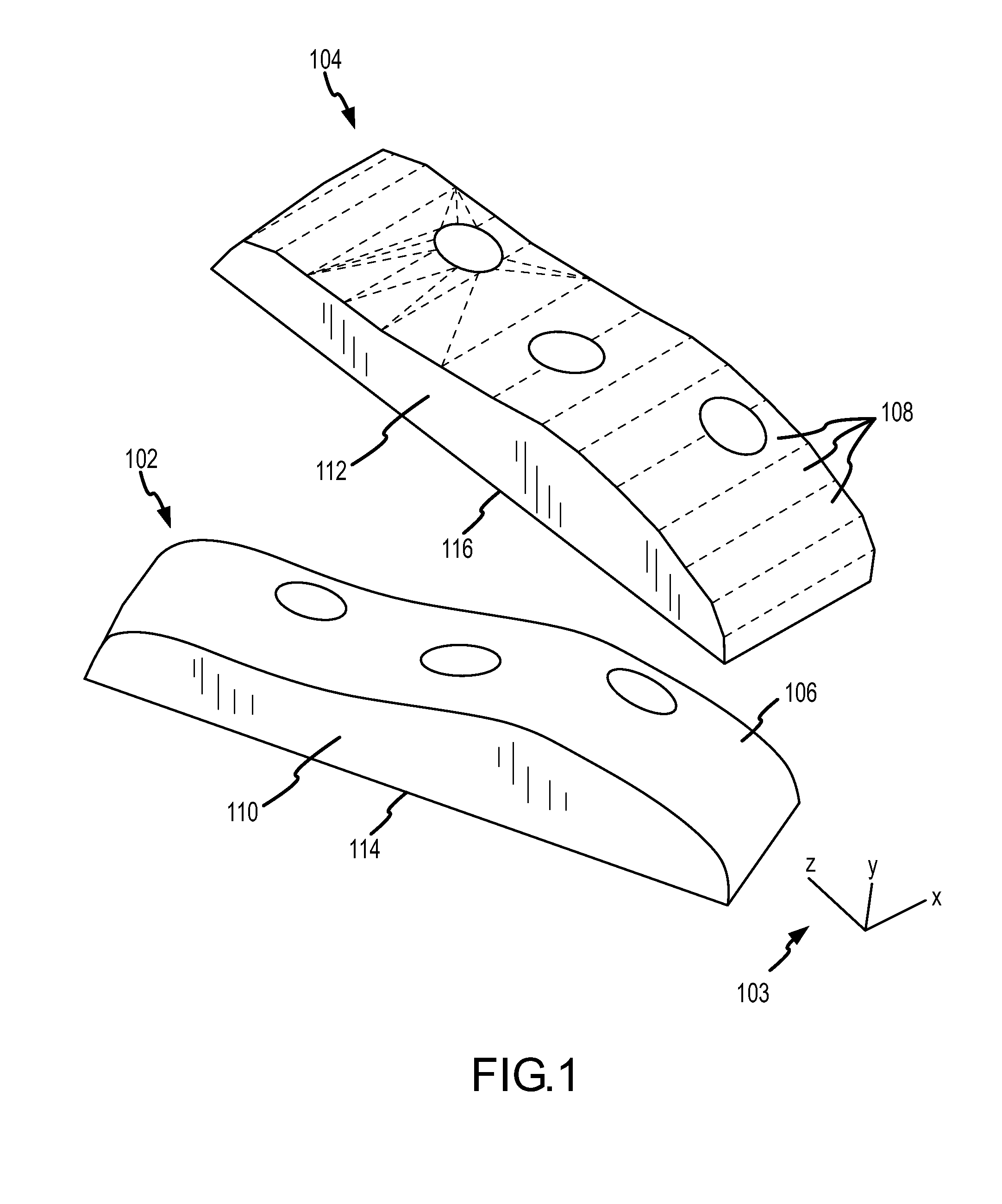
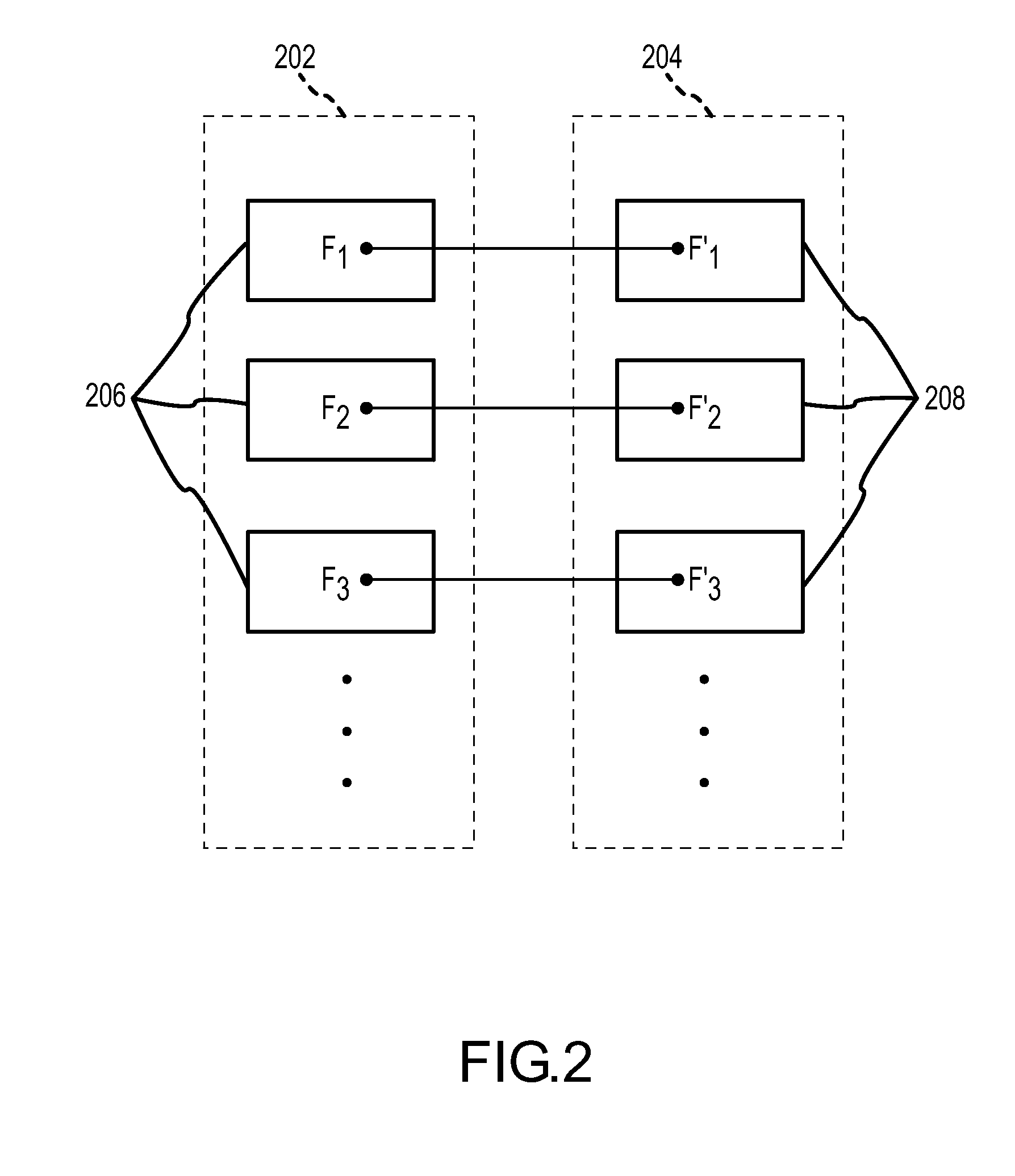
A method of determining a rigid motion between a master solid model and an approximated target model (or, more generally, between any two models having different types) includes identifying, within each model, geometrical entities having a unique characteristic, and then determining the best match between the identified geometric entities. The system provides, in machine-readable form, a master model comprising a precise definition of a three-dimensional solid and a target model comprising a simplified definition of the three-dimensional solid. Then it identifies a first set of geometric entities (e.g., planar faces) within the master model that have a unique characteristic (e.g., planar area), and identifies a second set of geometric entities in the target model that have the unique characteristic. The system then determines a best match between a member of the first set of geometric entities and a member of the second set of geometric entities using, for example, a Hungarian matching algorithm. Linear edges of matched faces are compared to determine the appropriate rigid motion.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Self-calibrating projection geometry for volumetric image reconstruction
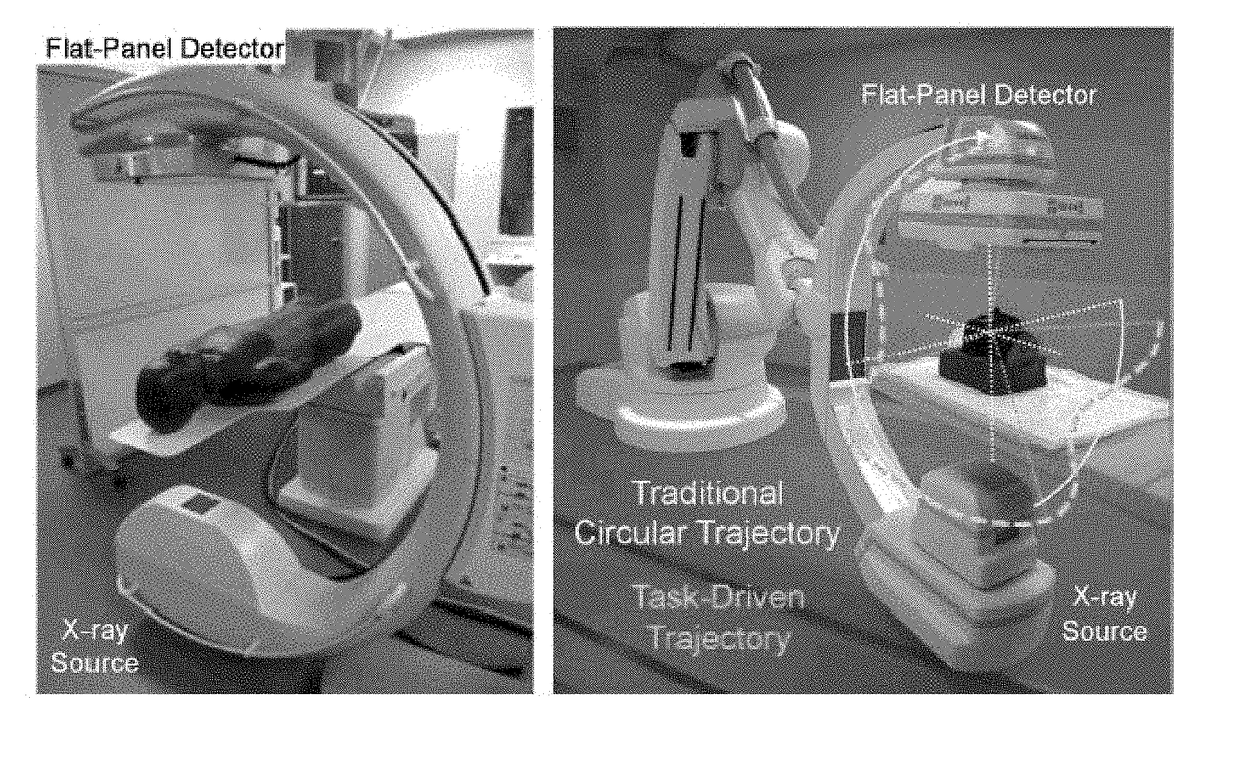
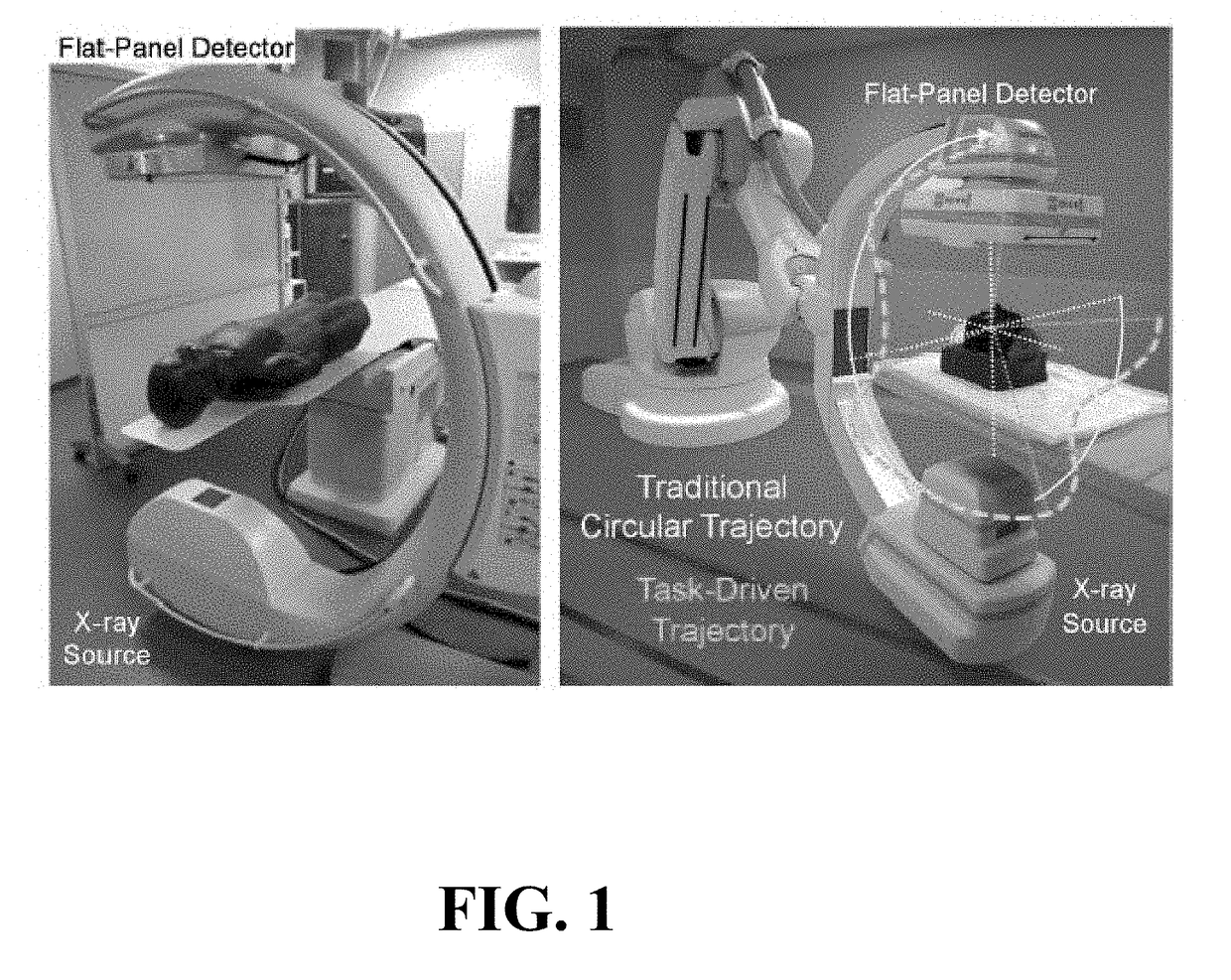
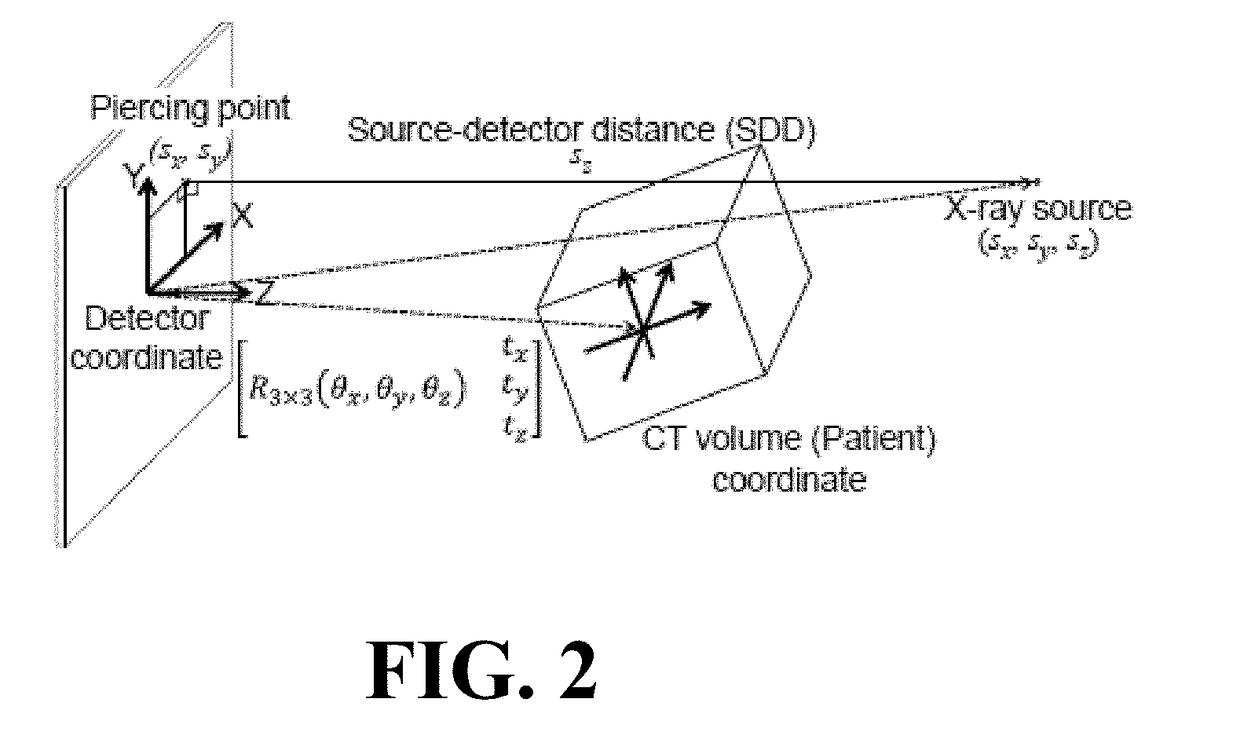
The present invention is directed to a method for enabling volumetric image reconstruction from unknown projection geometry of tomographic imaging systems, including CT, cone-beam CT (CBCT), and tomosynthesis systems. The invention enables image reconstruction in cases where it was not previously possible (e.g., custom-designed trajectories on robotic C-arms, or systems using uncalibrated geometries), and more broadly offers improved image quality (e.g., improved spatial resolution and reduced streak artifact) and robustness to patient motion (e.g., inherent compensation for rigid motion) in a manner that does not alter the patient setup or imaging workflow. The method provides a means for accurately estimating the complete geometric description of each projection acquired during a scan by simulating various poses of the x-ray source and detector to determine their unique, scan-specific positions relative to the patient, which is often unknown or inexactly known (e.g., a custom-designed trajectory, or scan-to-scan variability in source and detector position).
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
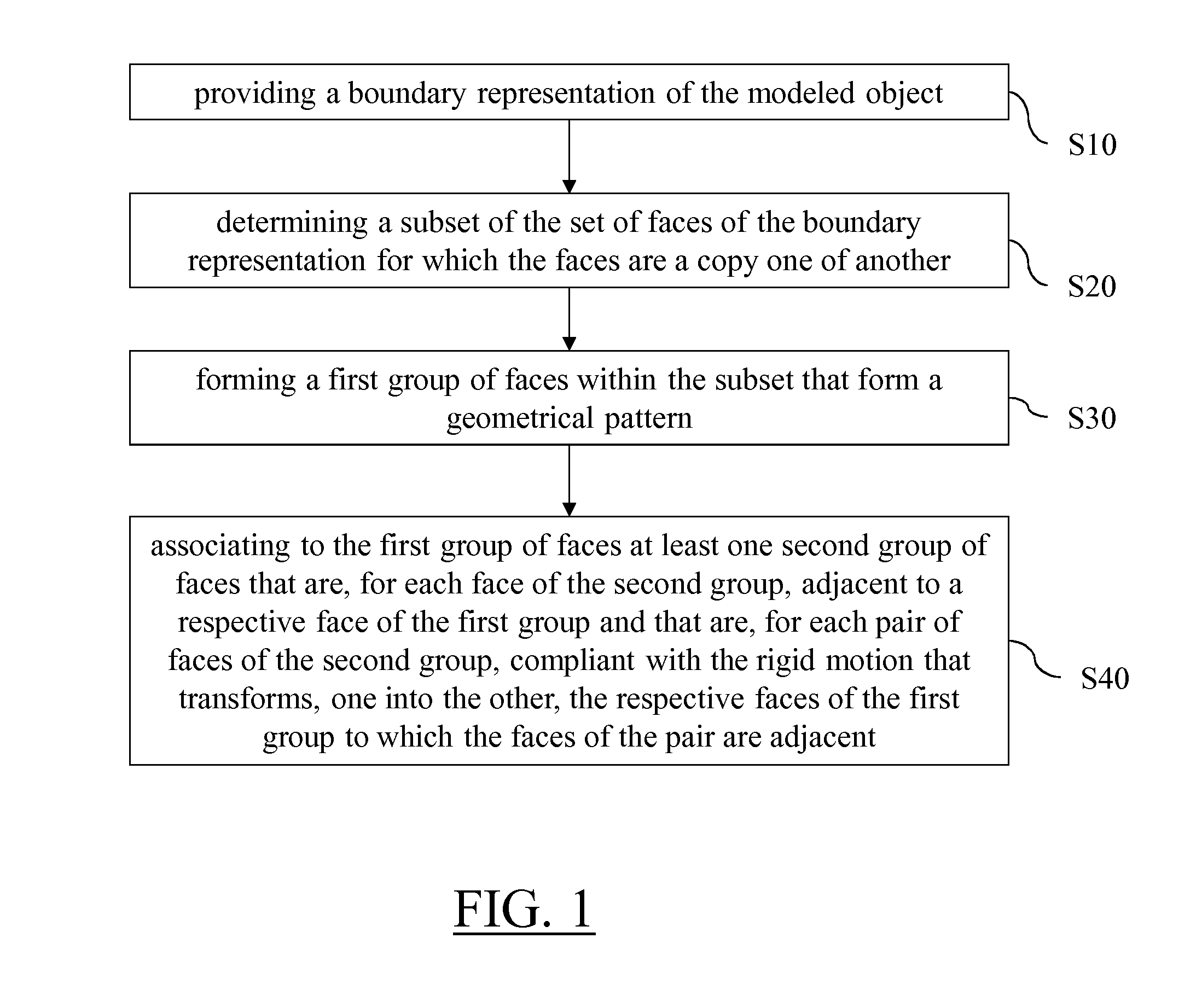
Groups Of Faces That Form A Geometrical Pattern
It is provided a computer-implemented method for designing a three-dimensional modeled object. The method comprises providing a boundary representation of the modeled object; determining a subset of the set of faces for which the faces are a copy one of another; forming a first group of faces within the subset that form a geometrical pattern; and associating to the first group of faces at least one second group of faces that are, for each face of the second group, adjacent to a respective face of the first group and that are, for each pair of faces of the second group, compliant with the rigid motion that transforms, one into the other, the respective faces of the first group to which the faces of the pair are adjacent. Such a method improves the design of a 3D modeled object.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES
Dynamic tracking of moving targets
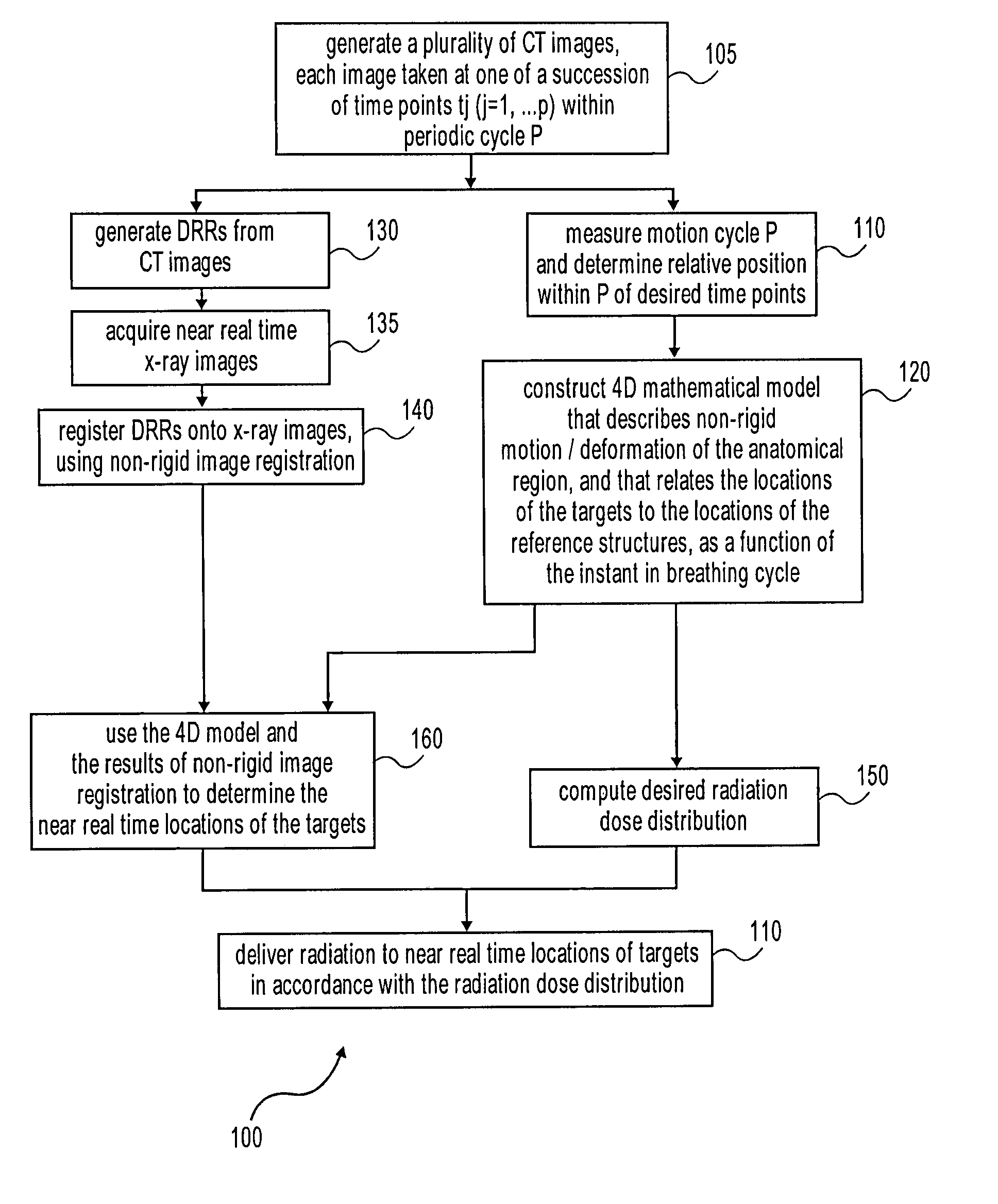
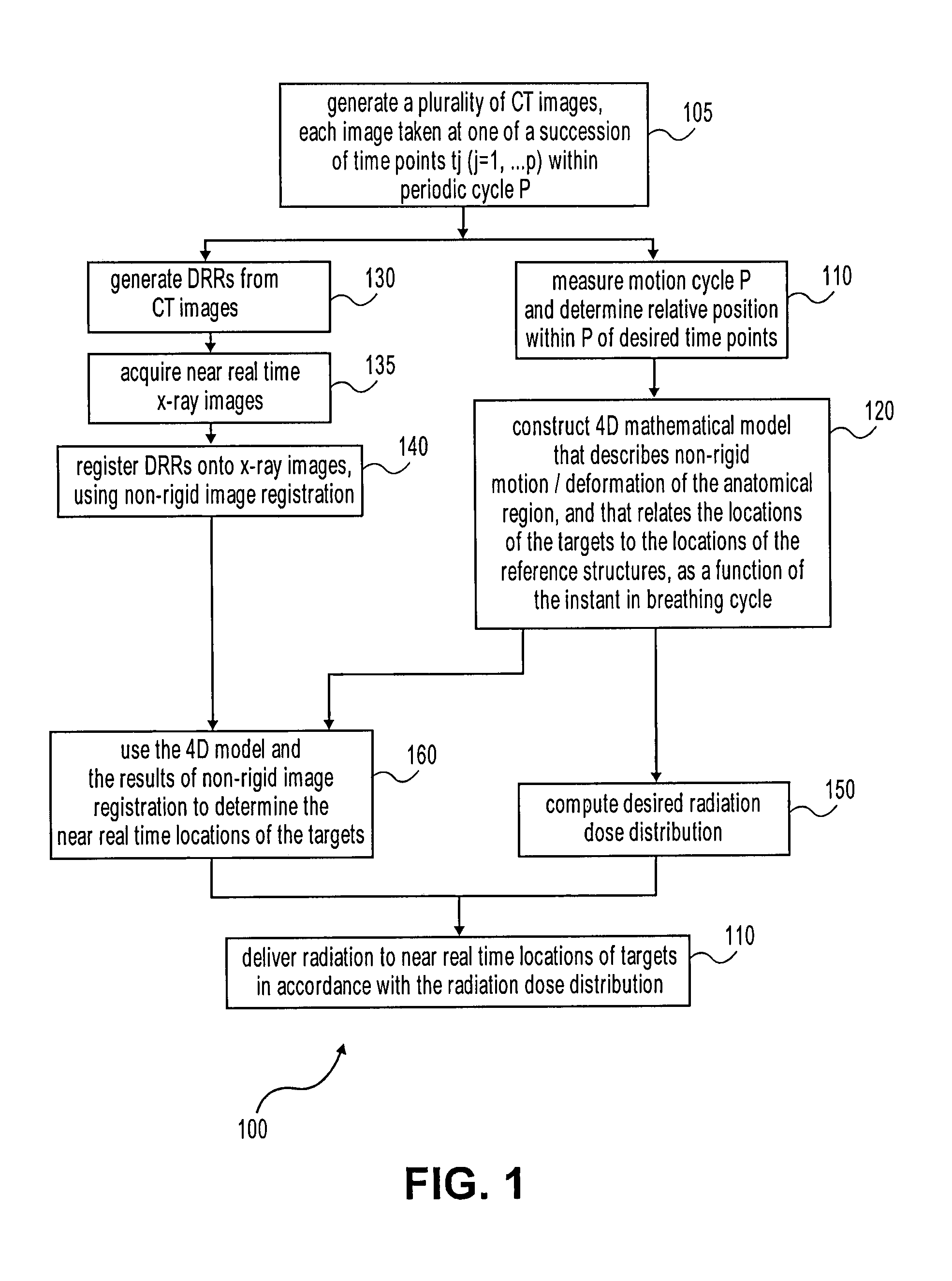
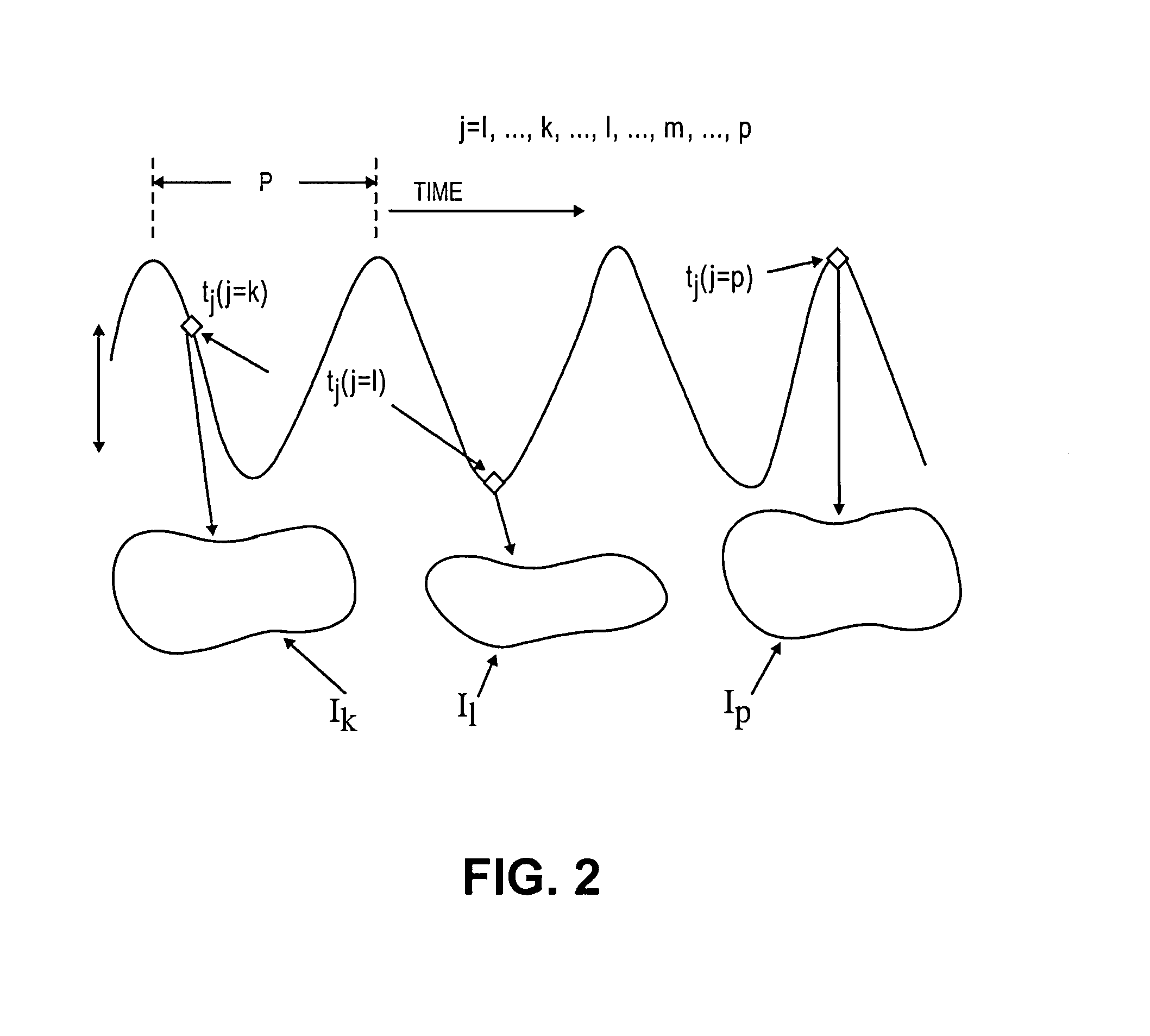
Treatment targets such as tumors or lesions, located within an anatomical region that undergoes motion (which may be periodic with cycle P), are dynamically tracked. A 4D mathematical model is established for the non-rigid motion and deformation of the anatomical region, from a set of CT or other 3D images. The 4D mathematical model relates the 3D locations of part(s) of the anatomical region with the targets being tracked, as a function of the position in time within P. Using fiducial-less non-rigid image registration between pre-operative DRRs and intra-operative x-ray images, the absolute position of the target and / or other part(s) of the anatomical region is determined. The cycle P is determined using motion sensors such as surface markers. The radiation beams are delivered using: 1) the results of non-rigid image registration; 2) the 4D model; and 3) the position in time within P.
Owner:ACCURAY
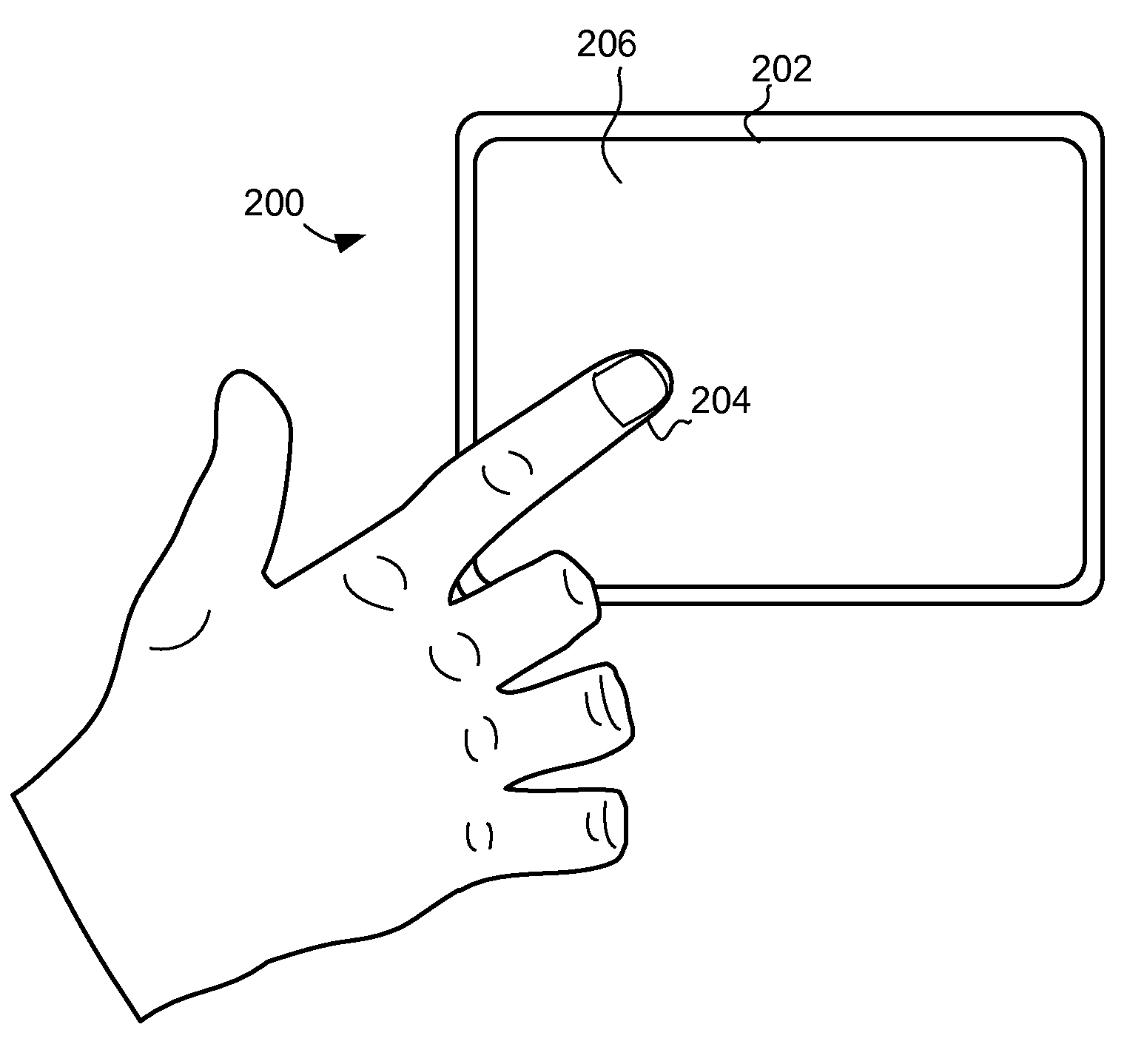
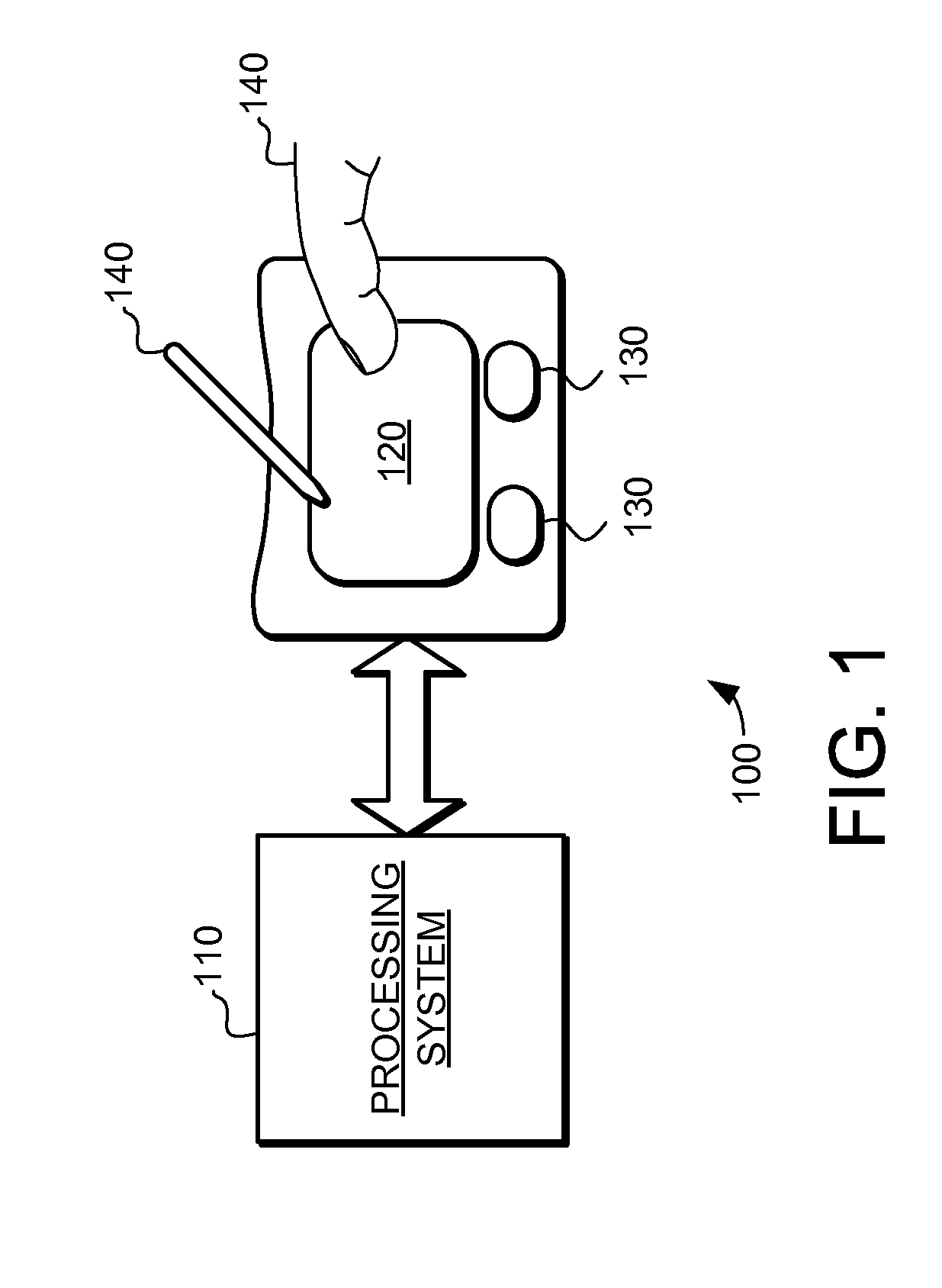
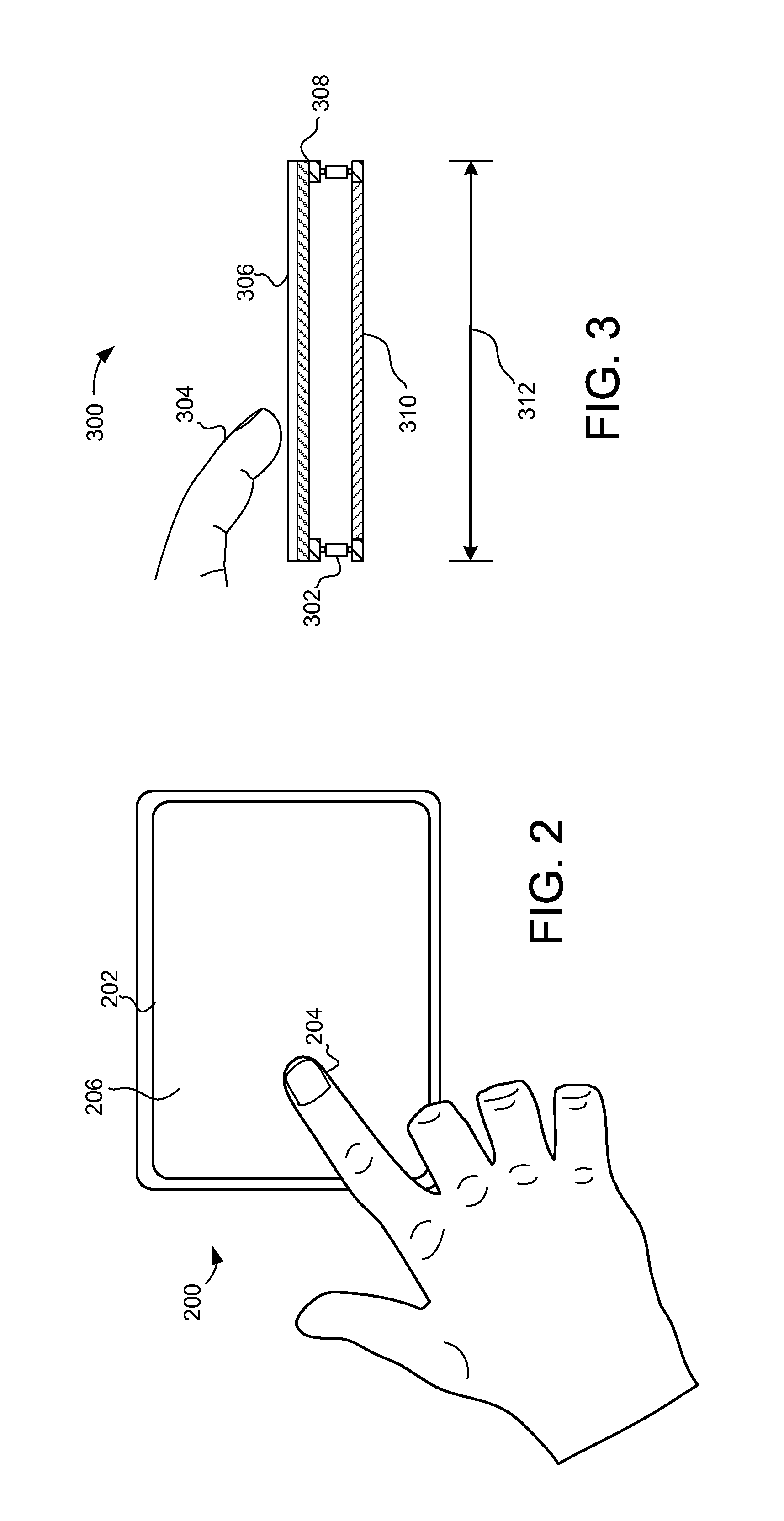
System and method for determining object information using an estimated rigid motion response
ActiveUS20120146935A1Facilitate improved sensor devicesTransmission systemsInput/output processes for data processingElectronic systemsCapacitive coupling
The embodiments described herein provide devices and methods that facilitate improved performance. Specifically, the devices and methods provide the ability to determine object information for objects causing rigid motion on a capacitive sensor device. In one embodiment, the device and method is configured to determine an estimated rigid motion response associated with a substantially rigid motion of the at least one sensing electrode using a set of sensor values, where the substantially rigid motion was caused by one or more objects in contact with the input surface. The estimated rigid motion response at least partially accounts for effects of capacitive coupling with the object(s) in contact with the input surface. The device and method may determine object information using the estimated rigid motion response. Where the input device is used to direct an electronic system, the object information may be used to facilitate a variety of interface actions.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Methods and apparatus for robust rigid and non-rigid motion tracking
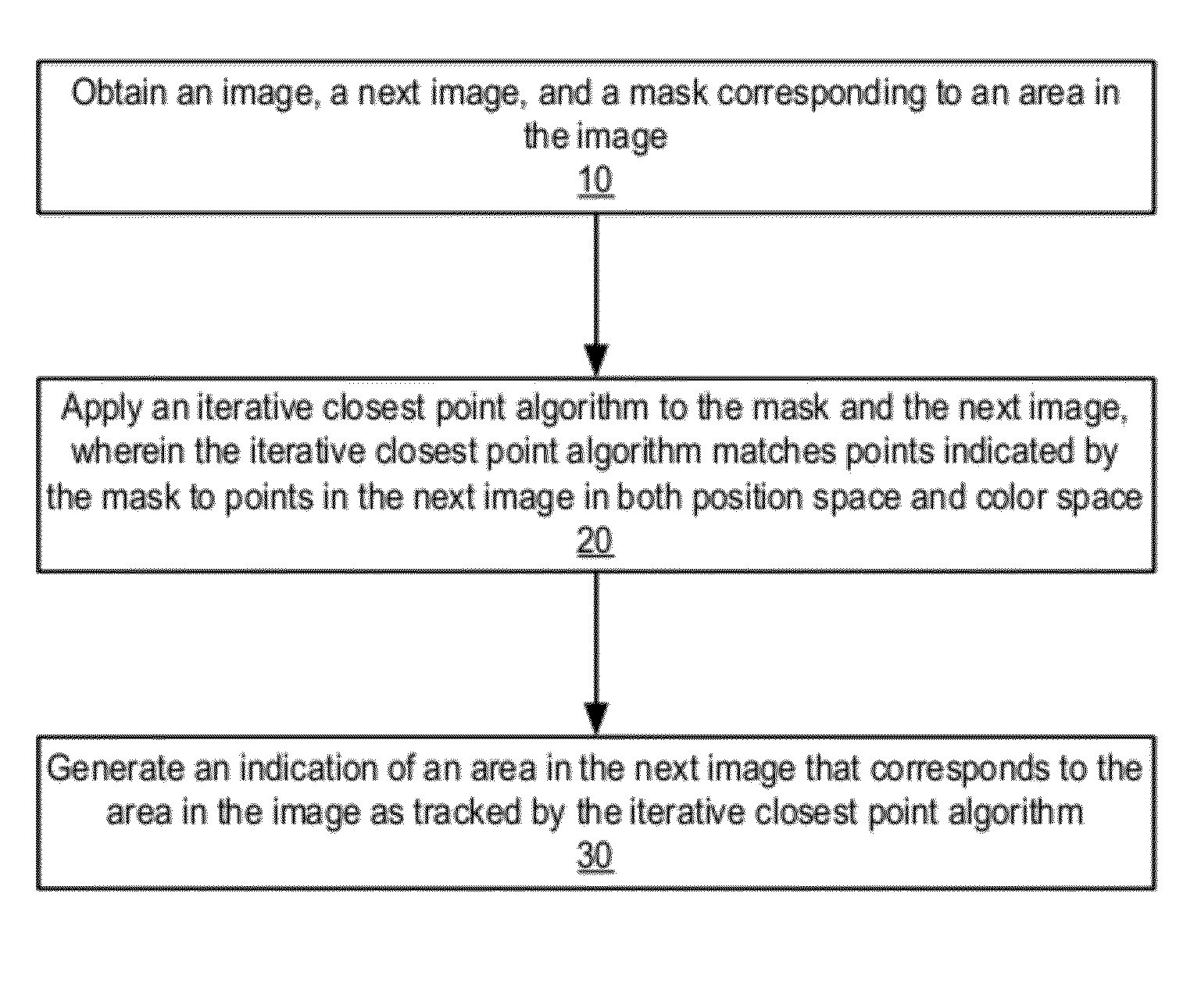
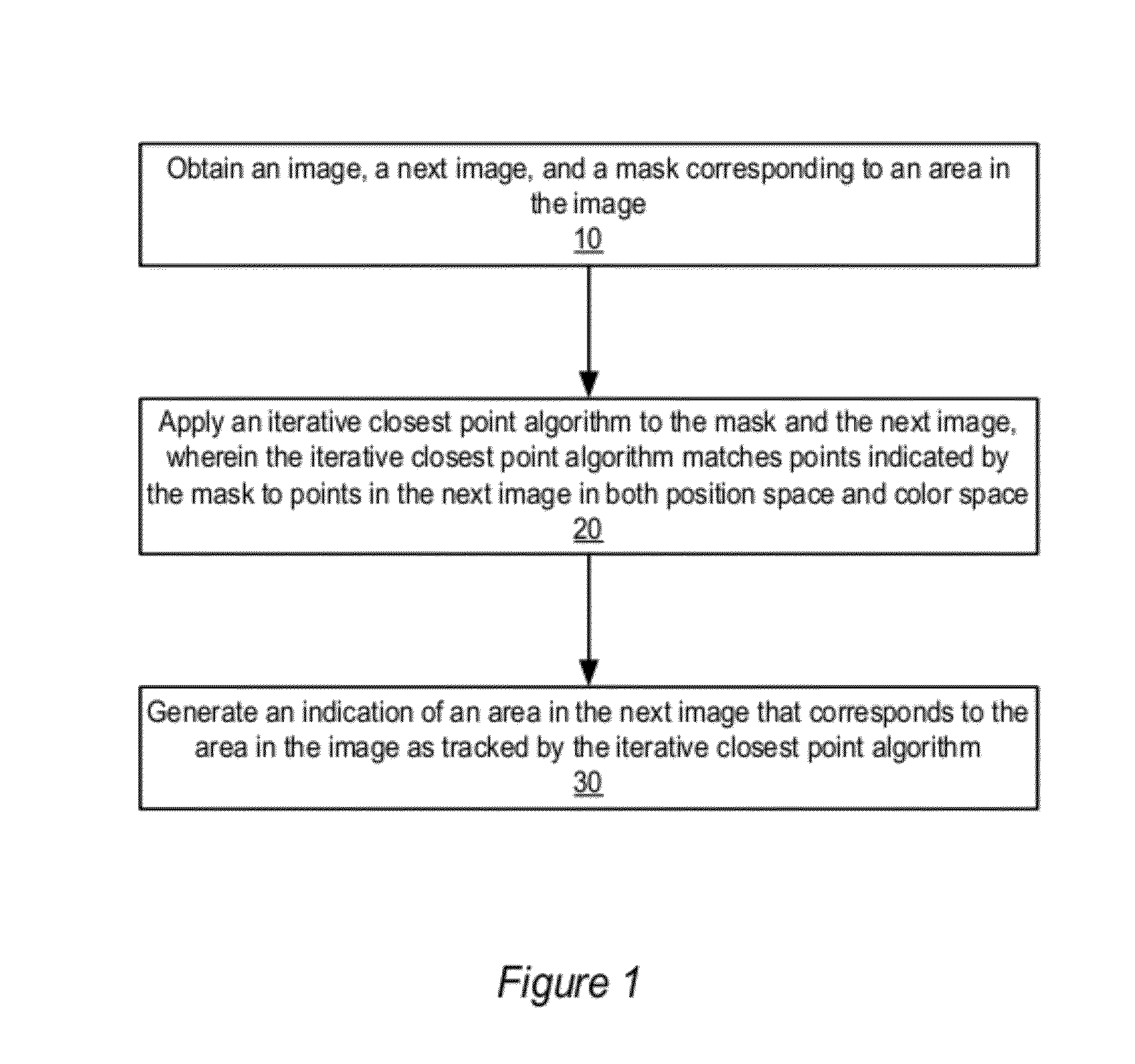
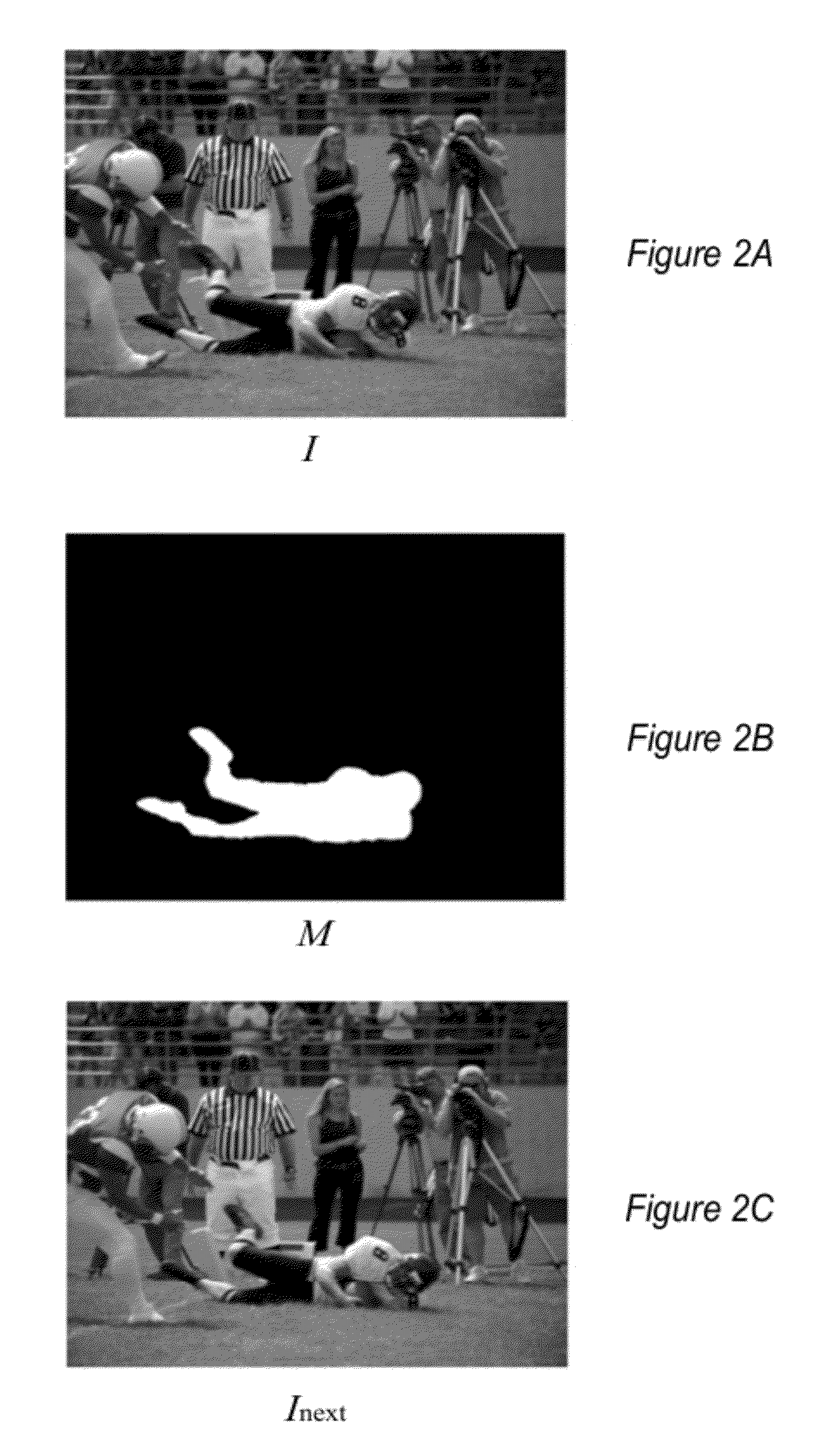
Methods and apparatus for robust rigid and non-rigid motion tracking. An image, a next image, and a mask corresponding to an area in the image may be obtained. The area includes a plurality of points; each point indicates a location of the point in a position space and a color of the point in a color space. An iterative closest point algorithm may be applied that iteratively computes correspondences from a transformation and computes a new transformation from the correspondences. The algorithm tracks motion of the area in the image between the image and the next image. The algorithm matches points indicated by the mask to points in the next image in both position space and color space. An indication of an area in the next image that corresponds to the area in the image as tracked by the algorithm is generated.
Owner:ADOBE INC
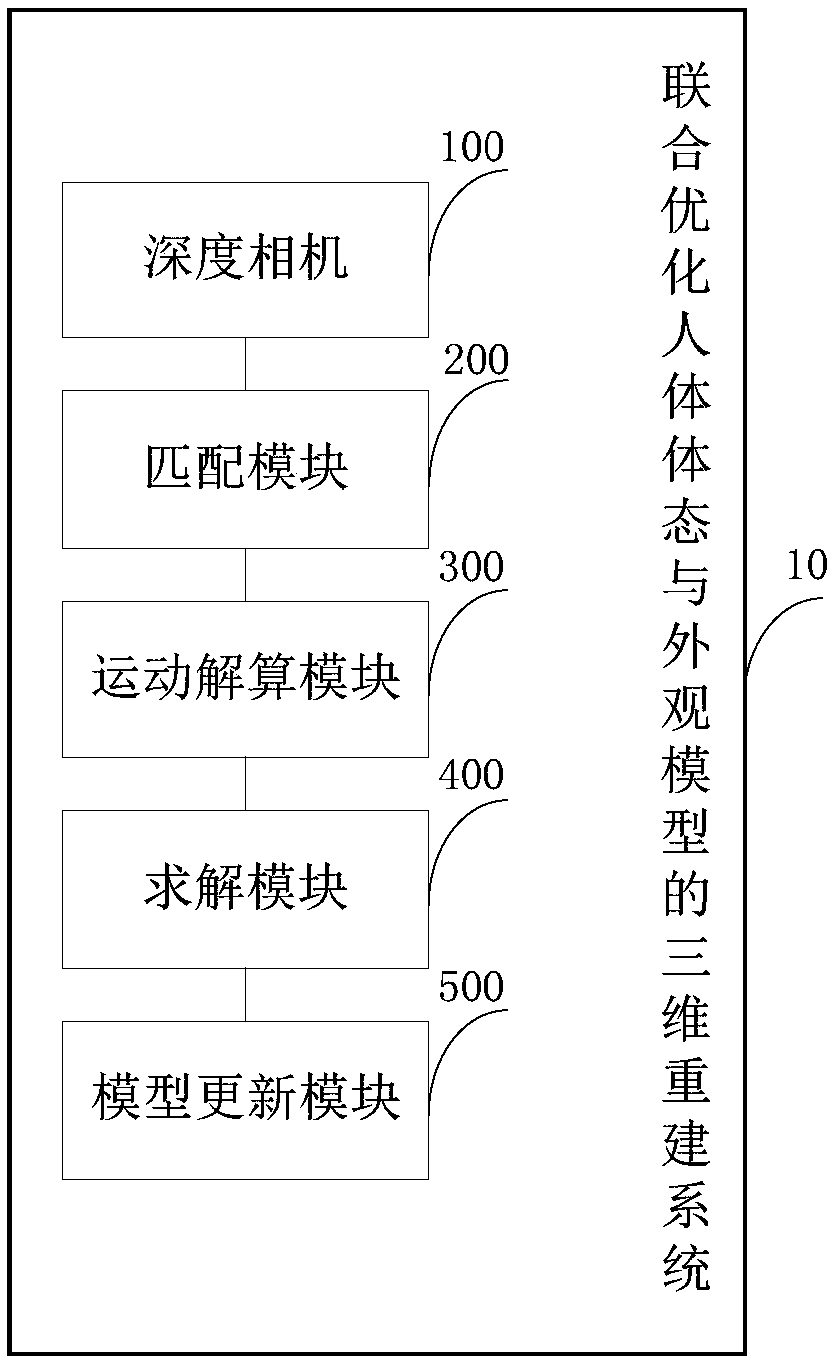
Three-dimensional reconstruction method and system for combined optimization of the human body posture and appearance model
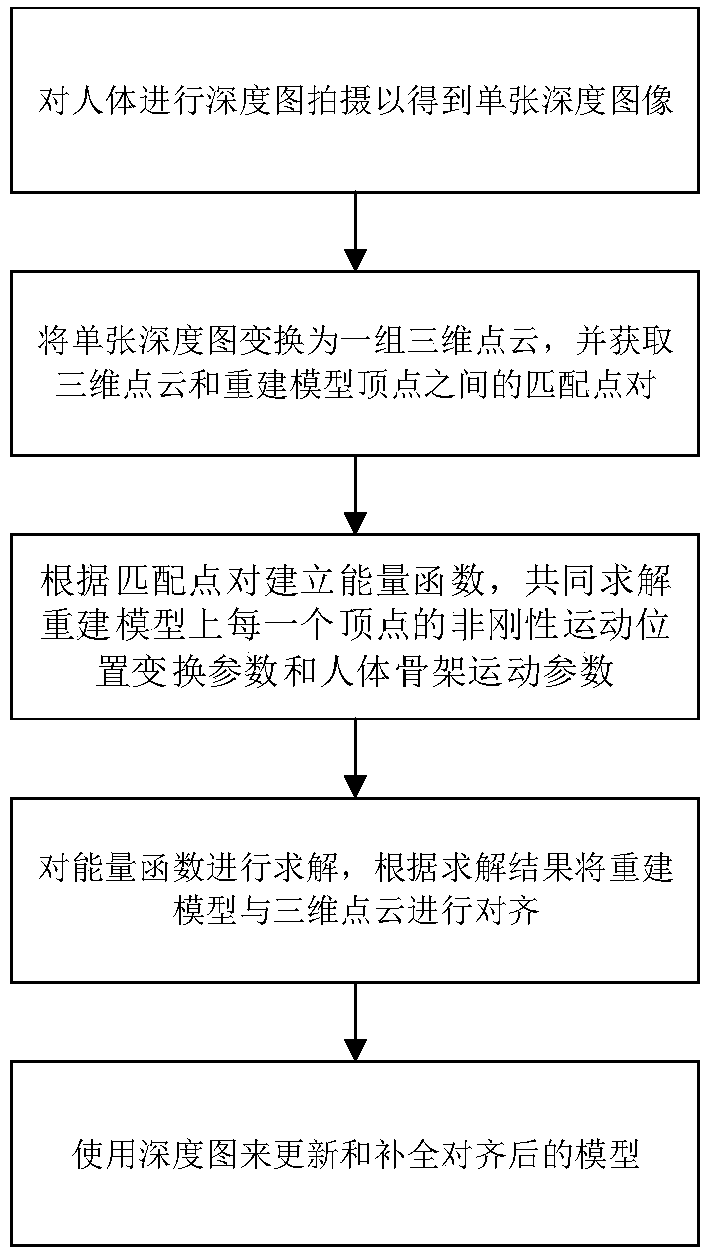
ActiveCN108665537AImprove real-time performanceImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyReconstruction method
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method and system for combined optimization of the human body posture and the appearance model. The method comprises the following steps of performing depth map photographing on a human body to obtain a single depth image; converting the single depth image into a three-dimensional point cloud, and obtaining the three-dimensional point cloud, rebuilding model vertexes, and parameterizing matching point pairs among the human body model vertexes; according to the matching point pairs, building an energy function, and jointly solving non-rigid motion position transformation parameters and parameterization human body posture model parameters of each vertex on the rebuilt model; solving the energy function, and performing alignment on the rebuilt model and the three-dimensional point cloud according to the obtained result; updating and complementing the aligned model through the depth map to perform real-time human body dynamic three-dimensional rebuilding. The method can effectively improve the rebuilding real-time performance, robustness and accuracy and is high in expandability and simple and easy to implement.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Flight flutter model
InactiveCN105954000AAccurately reflect the motion characteristics of rigid bodiesImprove securityAerodynamic testingGround installationsJet aeroplaneStructural dynamics
The invention relates to a flight flutter model, and the model comprises an elastic model, a power system, a flight control system, a taking-off and landing system, and a data collection system. The elastic model, the power system, the flight control system, the taking-off and landing system and the data collection system form a flutter model which can fly in the air. The model simulates the structural dynamic characteristics of an airplane, can accurately reflect the rigid motion characteristics of the airplane, can verify the conventional flutter characteristics, rigid and elastic coupling flutter characteristics and aeroservoelastic stability. The model is high in safety, is wide in application range, and is low in cost.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
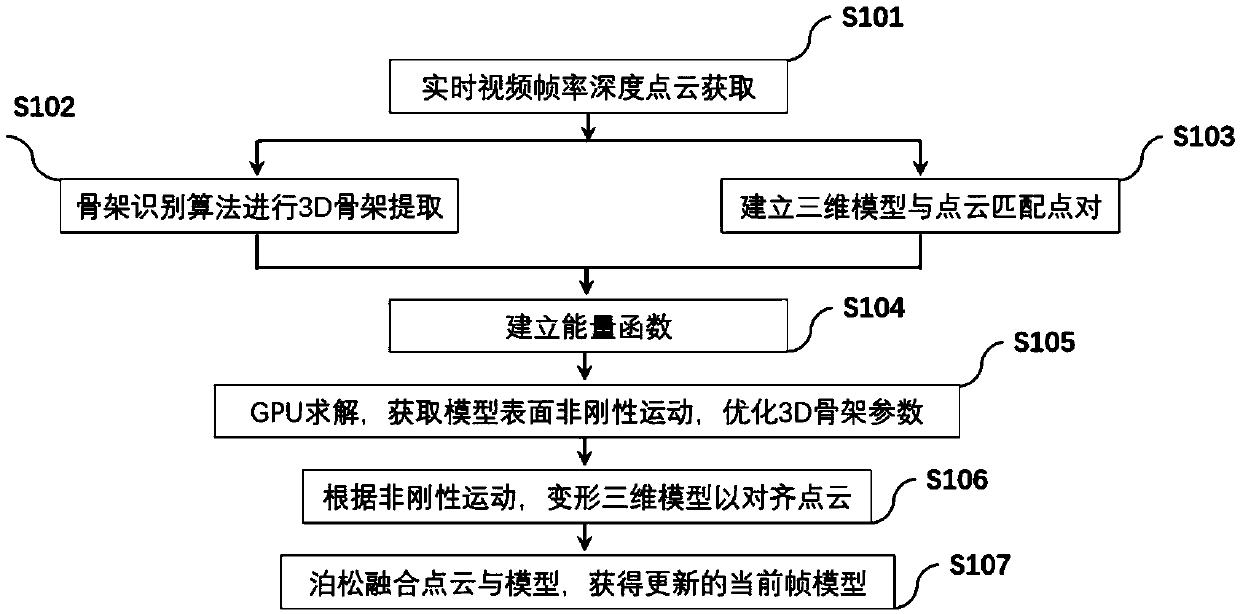
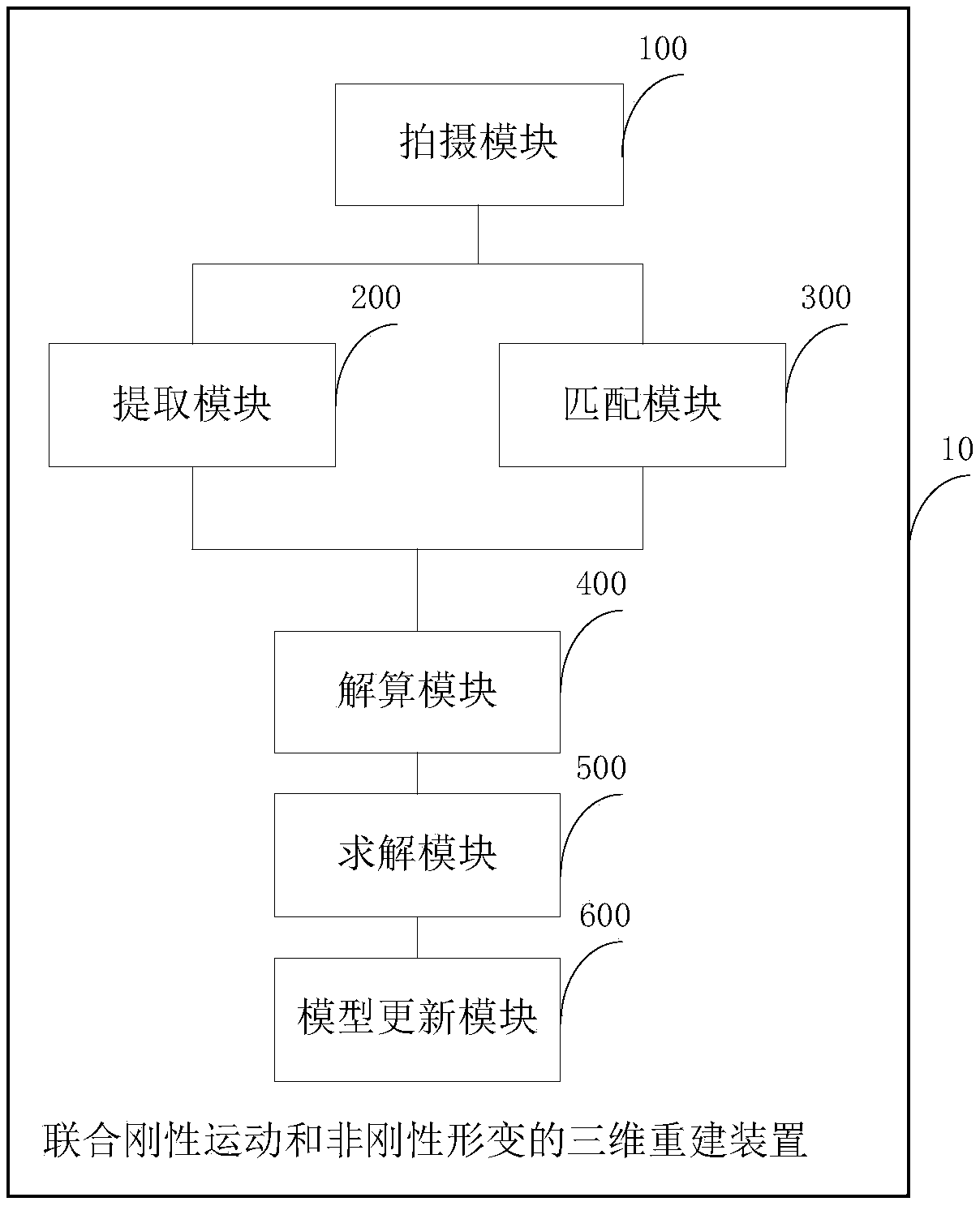
Three-dimensional reconstruction method and device uniting rigid motion and non-rigid deformation
ActiveCN108711185AImprove real-time performanceImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisExtensibilityPoint cloud
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method and device uniting rigid motion and non-rigid deformation. The method comprises the steps that photographing based on a depth camera is performed on a target object to obtain a single depth image; three-dimensional framework extraction is performed on a depth point cloud through a three-dimensional framework extraction algorithm; amatching point pair between a three-dimensional point cloud and each reconstruction model vertex is acquired; an energy function is established according to the matching point pairs and three-dimensional framework information, non-rigid motion position transformation parameters of each vertex on a reconstruction model are solved, and object framework parameters are optimized; GPU optimal solving is performed on the energy function to obtain non-rigid deformation of each surface vertex, and the reconstruction three-dimensional model in the previous frame is deformed according to the solving result, so that the deformed model is aligned to the three-dimensional point cloud in the current frame; and the updated model in the current frame is obtained to enter iteration of the next frame. Through the method, the instantaneity, robustness and accuracy of reconstruction can be effectively improved, extensibility is high, and the method is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
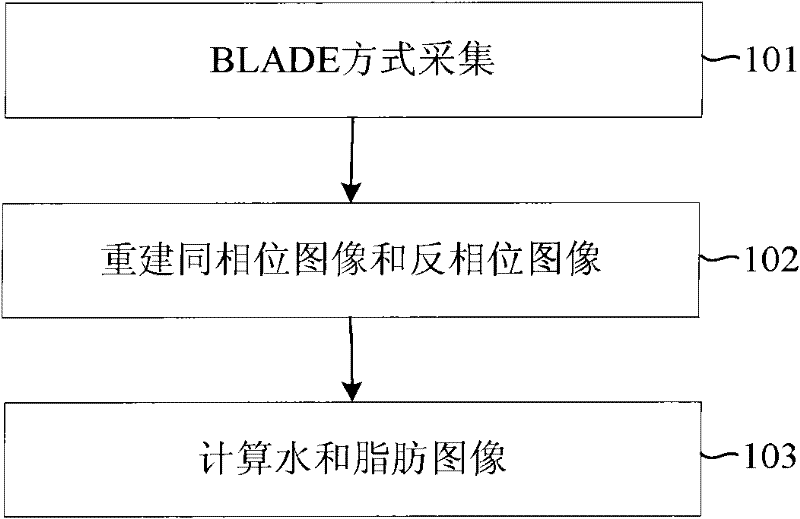
Magnetic resonance imaging method for realizing water-fat separation
ActiveCN102232831AReduce sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase correctionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging and discloses a magnetic resonance imaging method for realizing water-fat separation. The method comprises: acquiring the primary data on a frame of in-phase images and primary data on two frames of opposed-phase images by using blade tracking; reconstructing the in-phase images according to the primary data of the in-phase images, calibrating the phase of the primary data on the opposed-phase images according to the primary data on the in-phase images, and reconstructing the opposed-phase images; and calculating the images of water and fat according to the in-phase images and the opposed-phase images. In the invention the blade tracking is adopted to acquire the k spatial data, so the rigid motion and impulse insensitivity advantages of the blade tracking are inherited, the sensitivity to motion artifact is lowered, and the signal-to-noise ratios of the images are improved.
Owner:SIEMENS SHENZHEN MAGNETIC RESONANCE
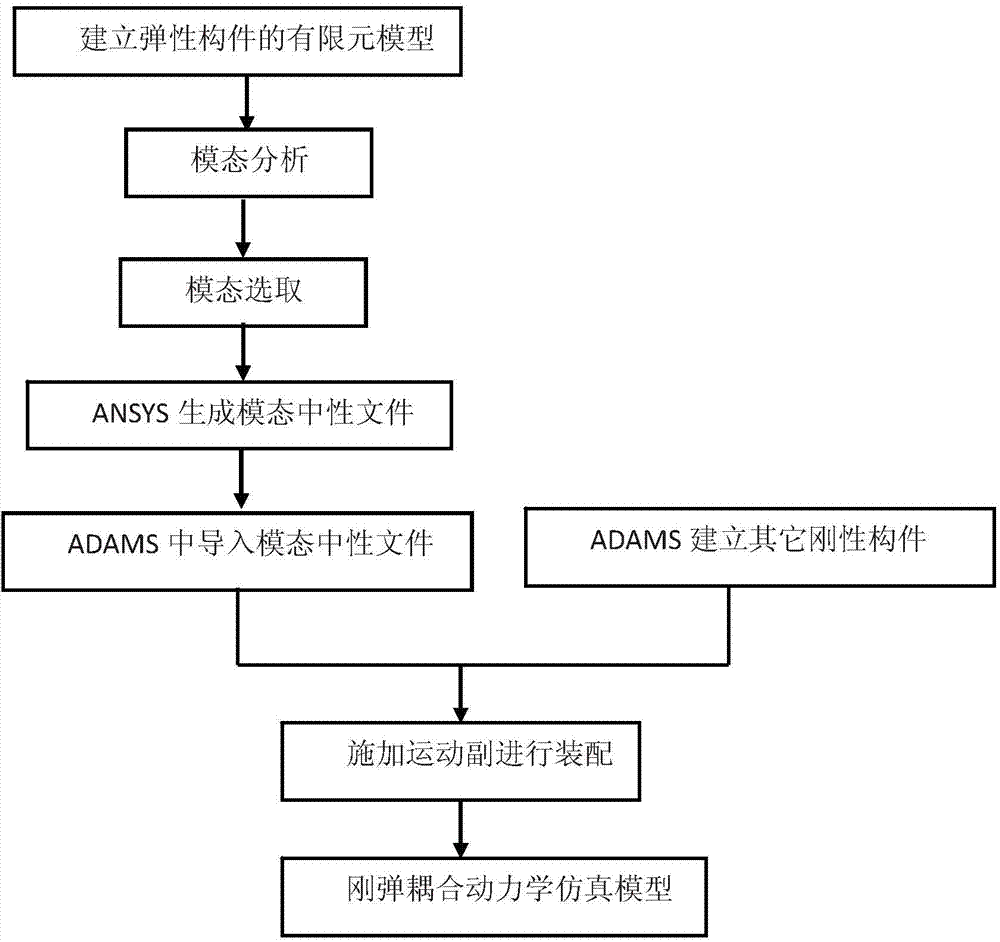
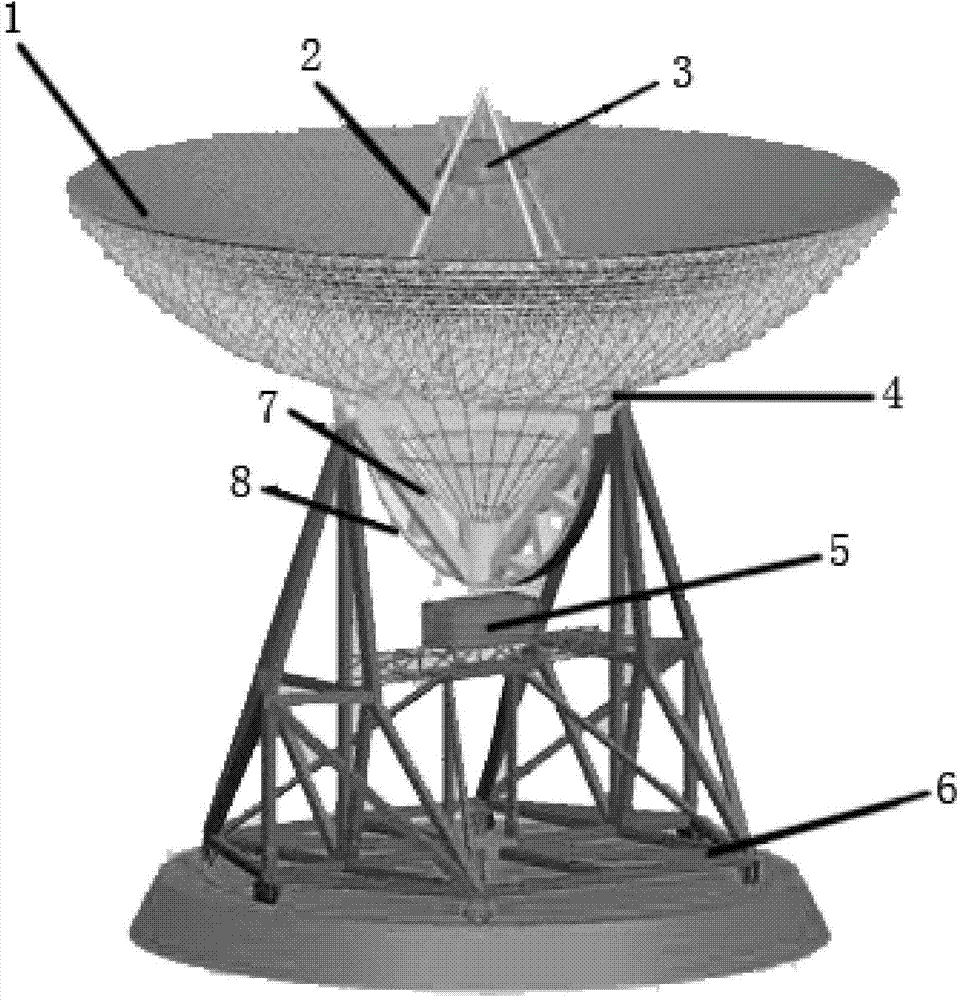
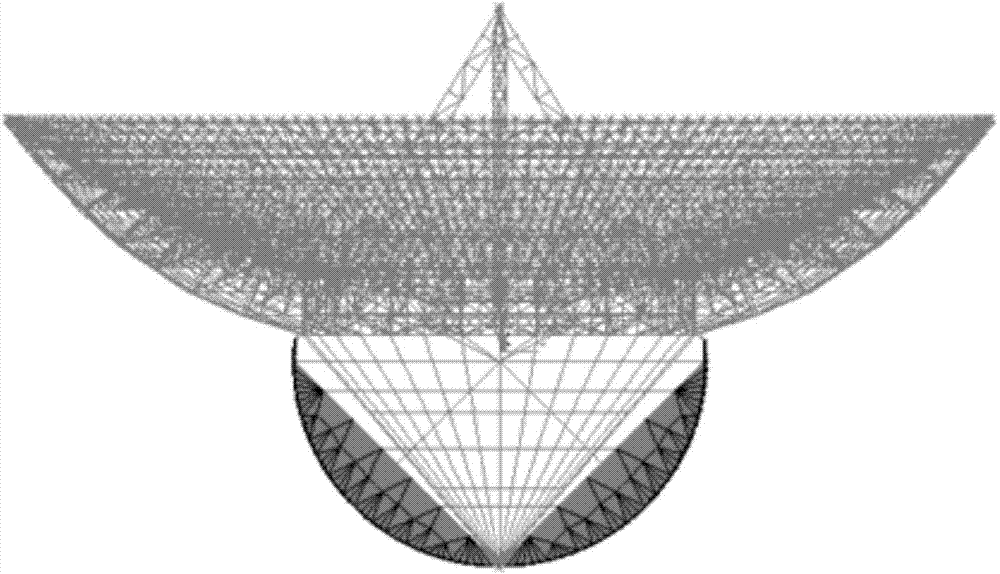
ANSYS and ADAMS-based large-scale antenna dynamical modeling method
InactiveCN104850697AShorten operation timeShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsElastomerElement model
The invention discloses an ANSYS and ADAMS-based large-scale antenna dynamical modeling method, and mainly solves the problem that the existing modeling method cannot be used for accurately describing rigid motion of an antenna and cannot consider the problem of rigid-elastic coupling in a movement process of the antenna. The modeling method comprises the steps: based on a finite element model of an elastic component of a large reflector antenna, according to a modal analysis result, selecting the modality with the maximal contribution to antenna output, replacing node coordinates with a small quantity of modal coordinates to condense the degree of freedom of elastic deformation, and then exporting a corresponding modal neutral file; by establishing the rigid component of the antenna in ADAMS, combining the modal neutral file describing an elastomer, and performing assembly to obtain the dynamical simulation model describing the integral movement of the antenna. The ANSYS and ADAMS-based large-scale antenna dynamical modeling method overcomes the defects of the traditional modeling method, and a development period can be obviously shortened.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Geometrical elements transformed by rigid motions
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES
Steering bias tool and steering bias method
InactiveCN101696628AHigh control precisionSimple and reliable monitoringDirectional drillingMechanical energy handlingNeedle roller bearingRolling-element bearing
The invention discloses a steering bias tool, which belongs to the technical field of automatic closed-loop steering drilling tools of petroleum, drilling, and exploration and development, and comprises a non-rotation jacket, a rotating mandrel and bias execution mechanisms, wherein the non-rotation jacket is sleeved outside the rotating mandrel, and at least two anti-rotation mechanisms are arranged on the outer surface of the non-rotation jacket; and a directional sleeve is arranged on the rotating mandrel through a needle bearing, the outside of the directional sleeve is circumferentially and evenly distributed with at least three sets of the bias execution mechanisms, each set of bias execution mechanism comprises a rolling bearing, a left sliding block, a reverse-flighted screw, a right sliding block, a left support and a right support, and the positions, which correspond to the left sliding block and the right sliding block, on the directional sleeve are provided with two symmetrical inclined planes. The steering bias tool realizes the bending of the rotating mandrel by using a machine, which is a rigid motion, so the control accuracy is higher; and the motion of a directional bending execution mechanism is static bias, so the power consumption is low, the spontaneous heating problem of the system is effectively solved, and the sealing requirement on the system is reduced and a sealing structure is simplified at the same time.
Owner:刘宝林 +1
Dynamic Tracking of Moving Targets
Dynamic tracking of moving targets. Treatment targets, such as tumors or lesions, located in an anatomical region that undergoes motion (which may be cyclic motion with cycles P) are dynamically tracked. Build a 4D mathematical model of non-rigid motion and deformation of an anatomical region from a set of CT or other 3D images. The 4D mathematical model relates the 3D position of the portion of the anatomical region to the target being tracked as a function of position in time in P. Determine the absolute position of targets and / or other parts of an anatomical region using fiducial-less, non-rigid image alignment between pre-operative DRR and intra-operative x-ray images. Cycle P is determined using a motion sensor such as a surface marker. Release the radiation beam using: 1) the result of non-rigid image alignment; 2) the 4D model; and 3) the position in time in P.
Owner:安科锐公司
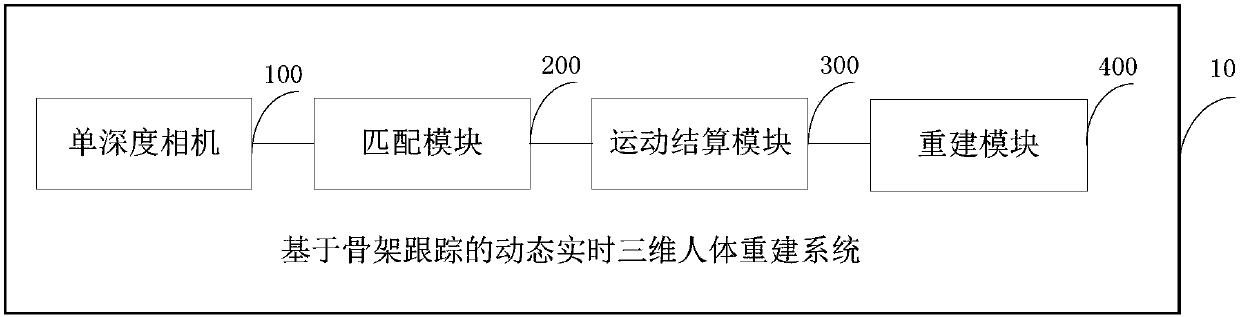
Skeleton tracking-based dynamic real-time three-dimensional reconstruction method and system
InactiveCN108122275AEasy to collectSolve accurate and robustImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyPoint cloud
The invention discloses a skeleton tracking-based dynamic real-time three-dimensional reconstruction method and a skeleton tracking-based dynamic real-time three-dimensional reconstruction system. Themethod comprises the following steps: performing depth image shooting on a human body to acquire a single depth image; converting the single depth image into three-dimensional point cloud and acquiring a matched point pair between the three-dimensional point cloud and a reconstruction model vertex; establishing an energy function according to the matched points and jointly solving a non-rigid motion position conversion parameter and a human body skeleton motion parameter on each vertex on the reconstruction model; and solving the energy function, aligning the reconstruction model with the three-dimensional point cloud according to the solving result, and updating and complementing the aligned model by using the depth image to realize three-dimensional human body reconstruction. By the method, the human body can be shot by a depth image, so that the depth image is acquired to serve as system input information; furthermore, the function of performing real-time three-dimensional reconstruction is completed based on the depth image, and the method and the system are accurate and robust in solution and are simple and easy to realize.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
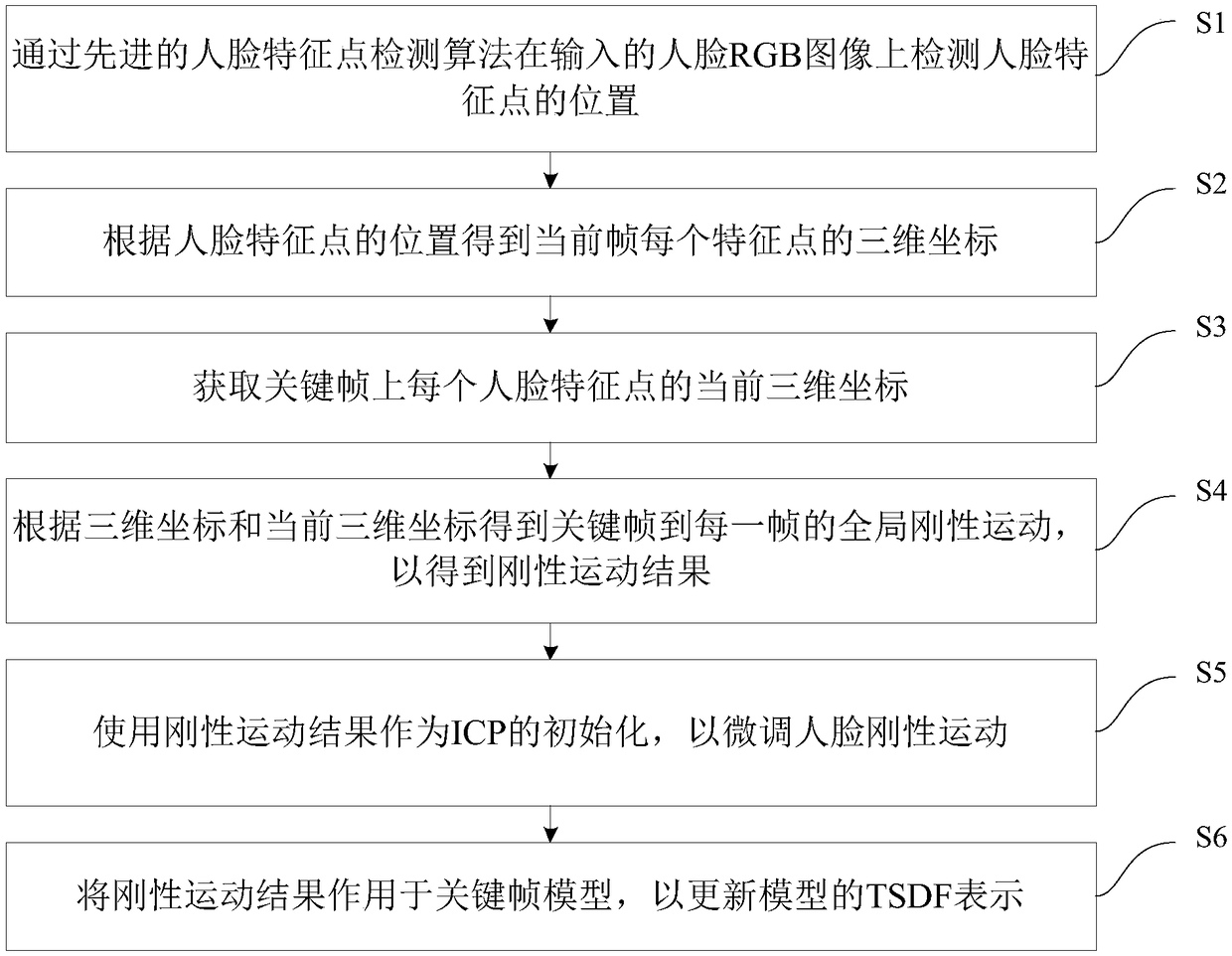
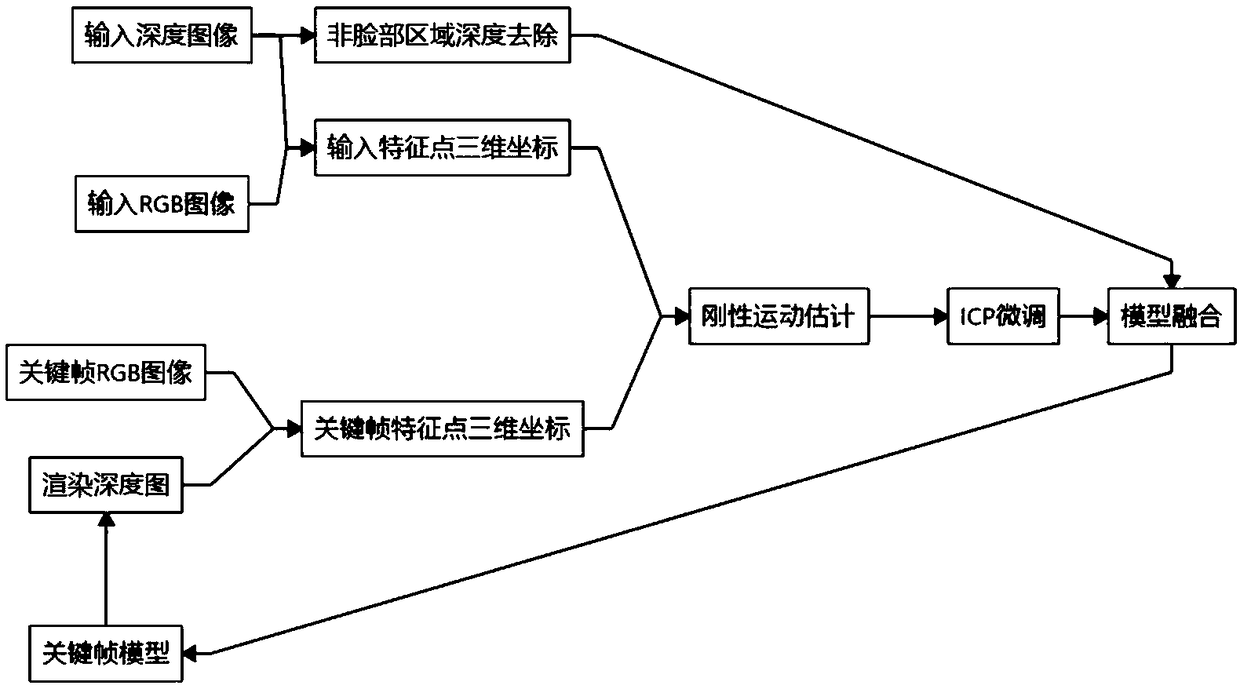
Monocular RGB-D camera real-time face reconstruction method and device
ActiveCN109472820AImprove accuracyRemoval depthImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionRgb image
The invention discloses a monocular RGB-D camera real-time face reconstruction method and device, wherein, that method comprise: detecting the position of the face feature point on the input face RGBimage through an advanced face feature point detection algorithm; Obtaining three-dimensional coordinates of each feature point of the current frame according to the position of the feature points ofthe face; Acquiring the current three-dimensional coordinates of each facial feature point on the key frame; The global rigid motion from the key frame to each frame is obtained according to the three-dimensional coordinates and the current three-dimensional coordinates, so as to obtain the rigid motion result; The result of rigid motion is used as the initialization of ICP to fine-tune the rigidmotion of human face. The rigid motion results are applied to the key frame model to update the TSDF representation of the model. This method effectively removes the depth of non-face region, eliminates the influence of rigid motion, and improves the accuracy of rigid motion estimation by using facial feature points.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
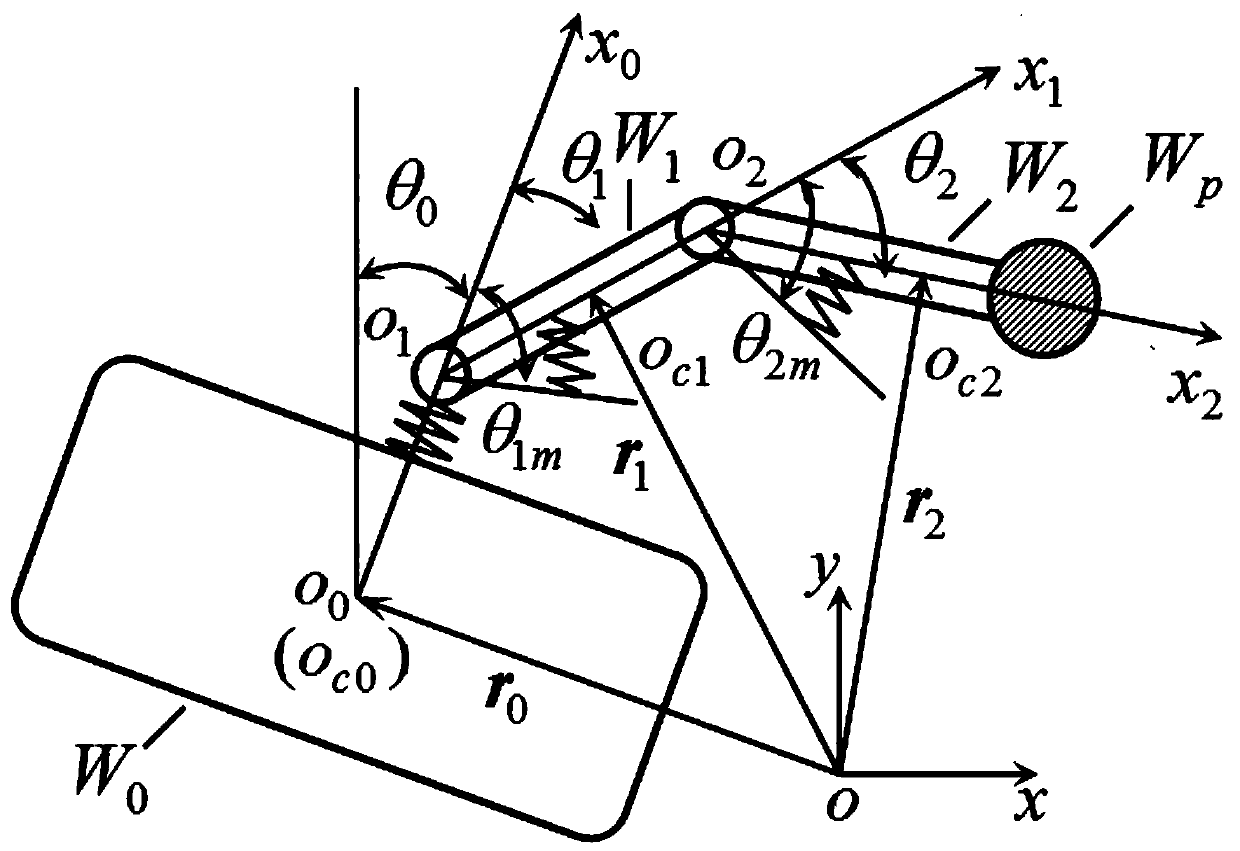
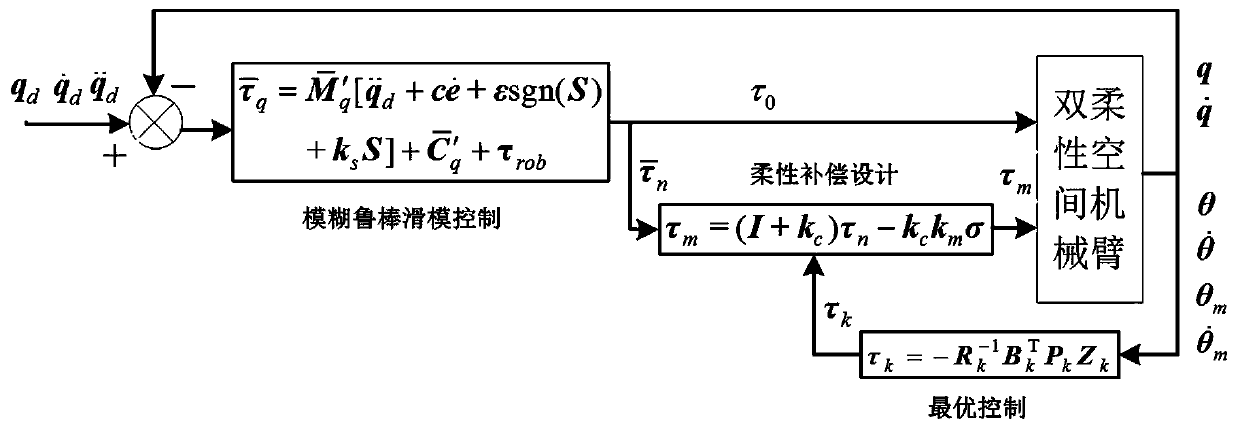
Fuzzy robust sliding mode buffeting reduction motion control method for double-flexibility space manipulator
ActiveCN107942670AReduce natural chatteringAvoid negative incentivesAdaptive controlOptimal controlRigid motion
The invention relates to a fuzzy robust sliding mode buffeting reduction motion control method for a double-flexibility space manipulator. The method is combined by a slowly changing sub-controller and a quickly changing sub-controller which can be independently designed based on a flexibility compensation singular perturbation model of the double-flexibility space manipulator. The slowly changingsub-controller comprises a type of exponential reaching sliding mode control laws and additionally designed fuzzy robust control items, and can realize effective reduction for inherent buffeting of the traditional sliding mode control and accurate tracking for a rigid motion trajectory of the system; and the quickly changing sub-controller is designed by adopting an optimal control theory so as to suppress flexible vibration generated by the system. The fuzzy robust sliding mode buffeting reduction motion control method provided by the invention for the double-flexibility space manipulator keeps very strong robustness for the parameter uncertainty of the system, and rigid and flexible motion control effect of the method also conform to expected control requirements.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
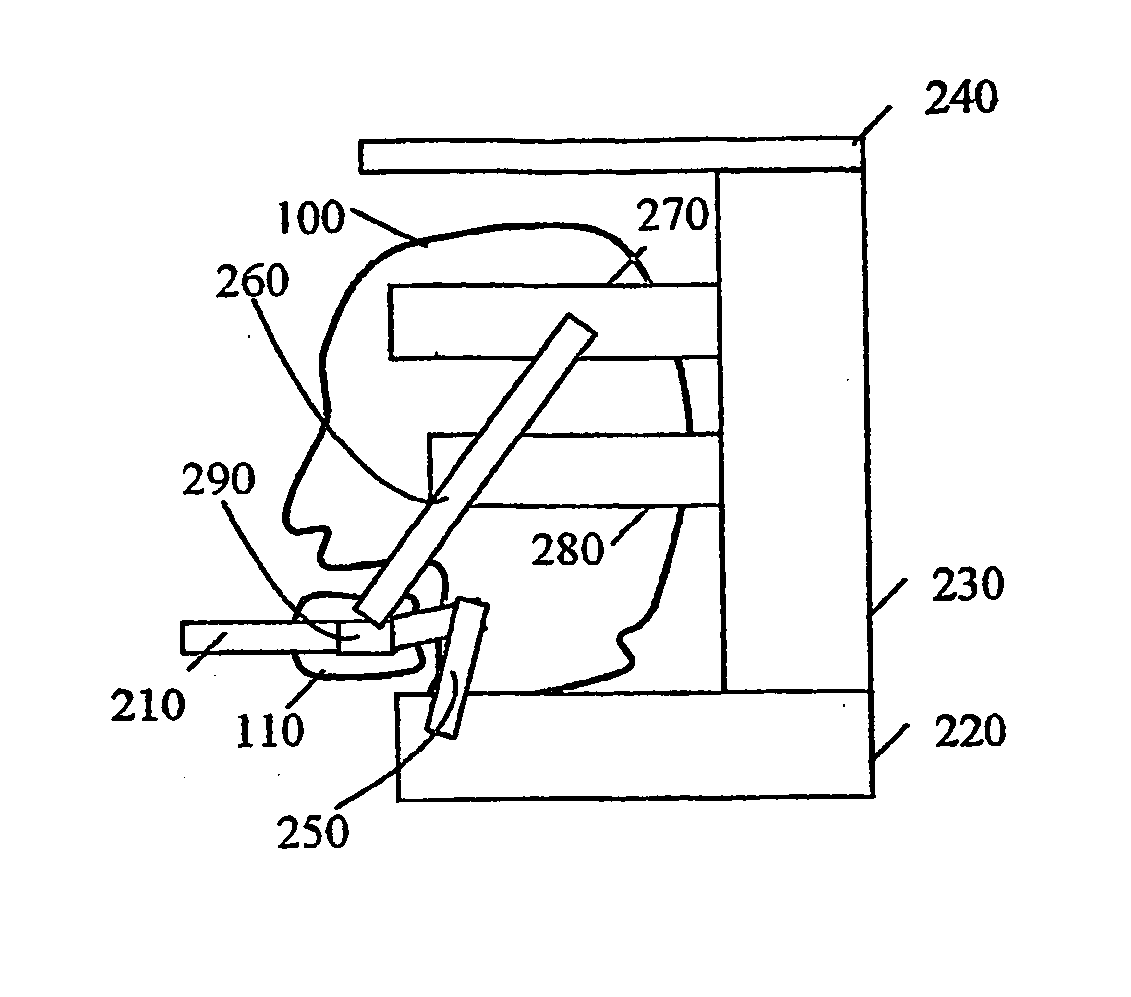
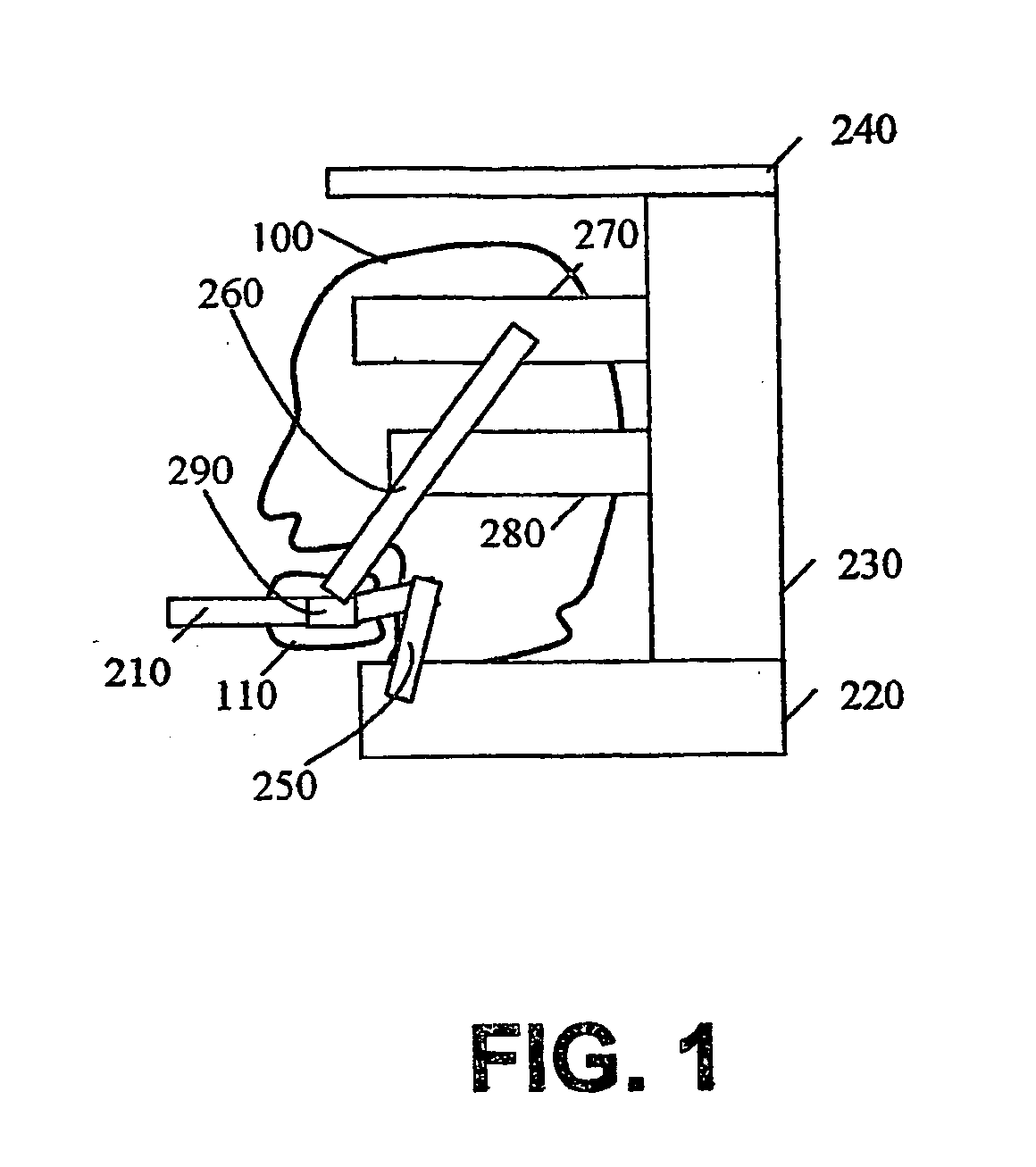
Cervical collar
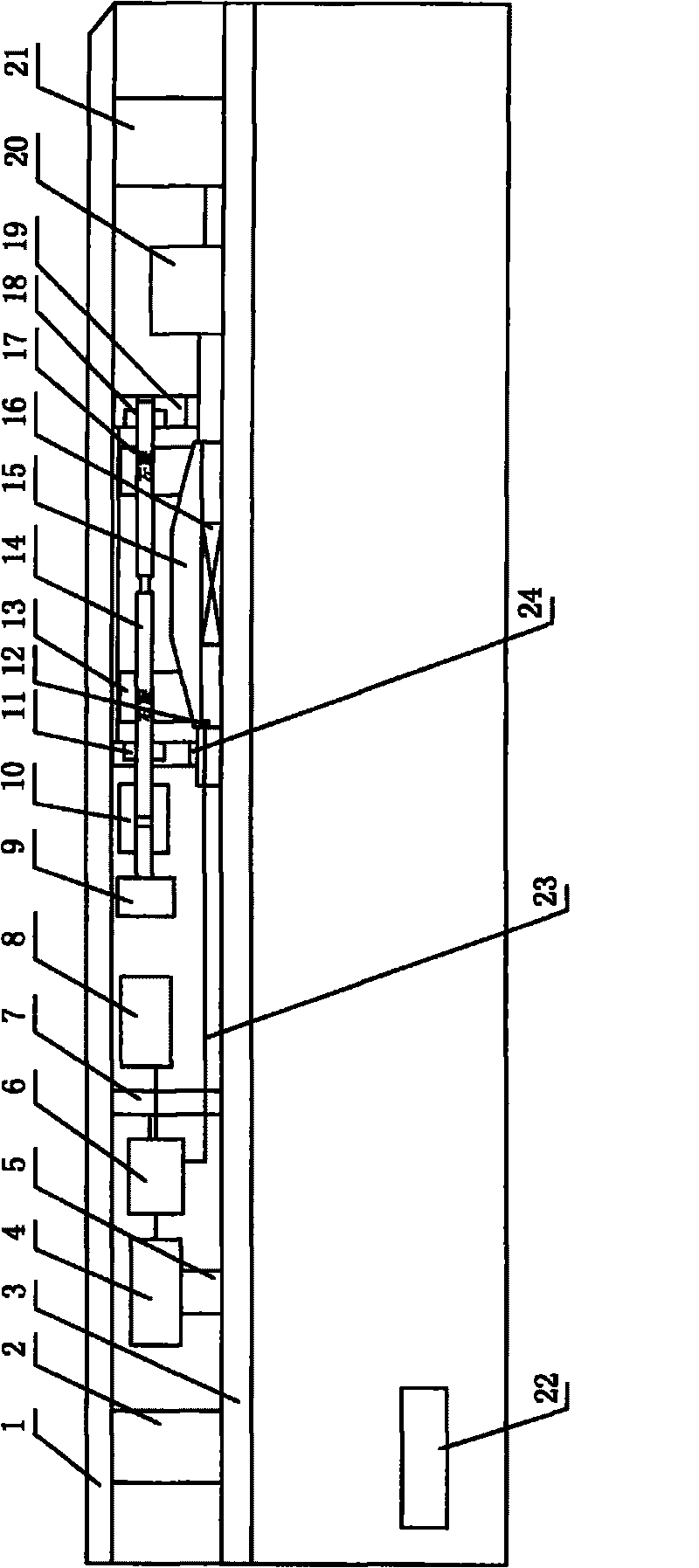
The present invention discloses a novel cervical collar for maintaining the airways in head and neck immobilized trauma patient open. This collar comprises a rigid motion-restricting frame (220, 230, 240, 270, 280) attached to the head (100); and, a jaw clasp (210, 290) attached to the jaw (110). The collar is simultaneously restricting the motion of the head (100) and neck while allowing motion of the jaw (110) to maintain open airways. A jaw clasp (290) useful for performing the jaw-thrust maneuver motion of the jaw (110) to maintain open airways is also presented. Said device comprising a plurality of movable fitting elements adapted to fit the jaw (110) tightly; and, a plurality of movable mover elements adapted to move the jaw (110).
Owner:INOVYTEC MEDICAL SOLUTIONS
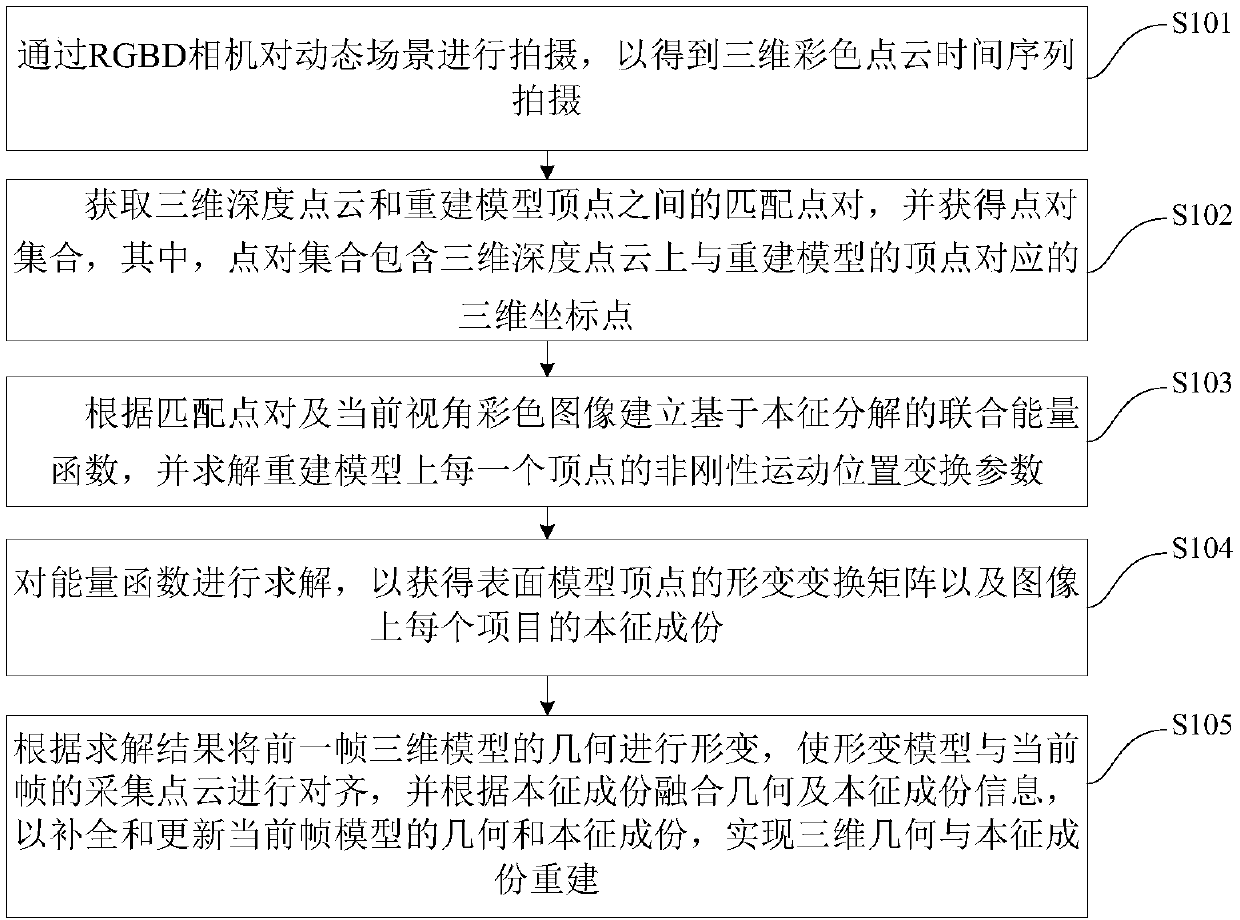
Three-dimensional geometry and eigencomponent reconstruction method and device based on light and shadow optimization
The invention discloses a three-dimensional geometry and eigencomponent reconstruction method and device based on light and shadow optimization. The method comprises the following steps of: obtainingthree-dimensional color point cloud time series shooting by an RGBD camera; obtaining matching point pairs between a three-dimensional depth point cloud and vertexes of a reconstructed model, and obtaining a point pair set; establishing a joint energy function based on eigendecomposition according to the matching point pairs and a current view angle color image, and solving non-rigid motion position transformation parameters of each vertex on the reconstruction model; solving the energy function to obtain a deformation transformation matrix of vertexes of a surface model and eigencomponents ofeach item on the image; deforming the geometry of the previous frame three-dimensional model according to the solution result, complementing and updating the geometry and eigencomponents of the current frame model, and realizing three-dimensional geometry and eigencomponent reconstruction. The method can improve the track deformation robustness of a dynamic object in a sparse and single viewpointcondition, can obtain accurate solution, is low in requirement for devices, and has broad application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Three-dimensional random convex polygon block discrete element method based on distance potential function
ActiveCN106529146AReduce in quantityImprove accuracyInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsResearch ObjectContact force
The invention discloses a three-dimensional random convex polygon block discrete element method based on a distance potential function. A research object is discretized into a block element system; carrying out contact detection on all block elements according to a nonuniform block discrete element contact detection method provided by the method; defining the distance potential function and carrying out normal contact force calculation on mutually contacting block elements, thereby obtaining normal contact force acting on each target block element and a torque caused by the normal contact force; on the basis of a tangential contact force direction vector calculation method provided by the method, carrying out calculation to obtain tangential contact force of each block element and the torque caused by the tangential contact force according to increment of tangential relative displacement; solving acceleration and angular acceleration of each block element through a rigid motion equation; and calculating velocity and displacement of each block element through a velocity verlet algorithm and describing deformation and motion state of a whole medium according to motion and relative position of each block element.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
3D synthesis fitting method and system
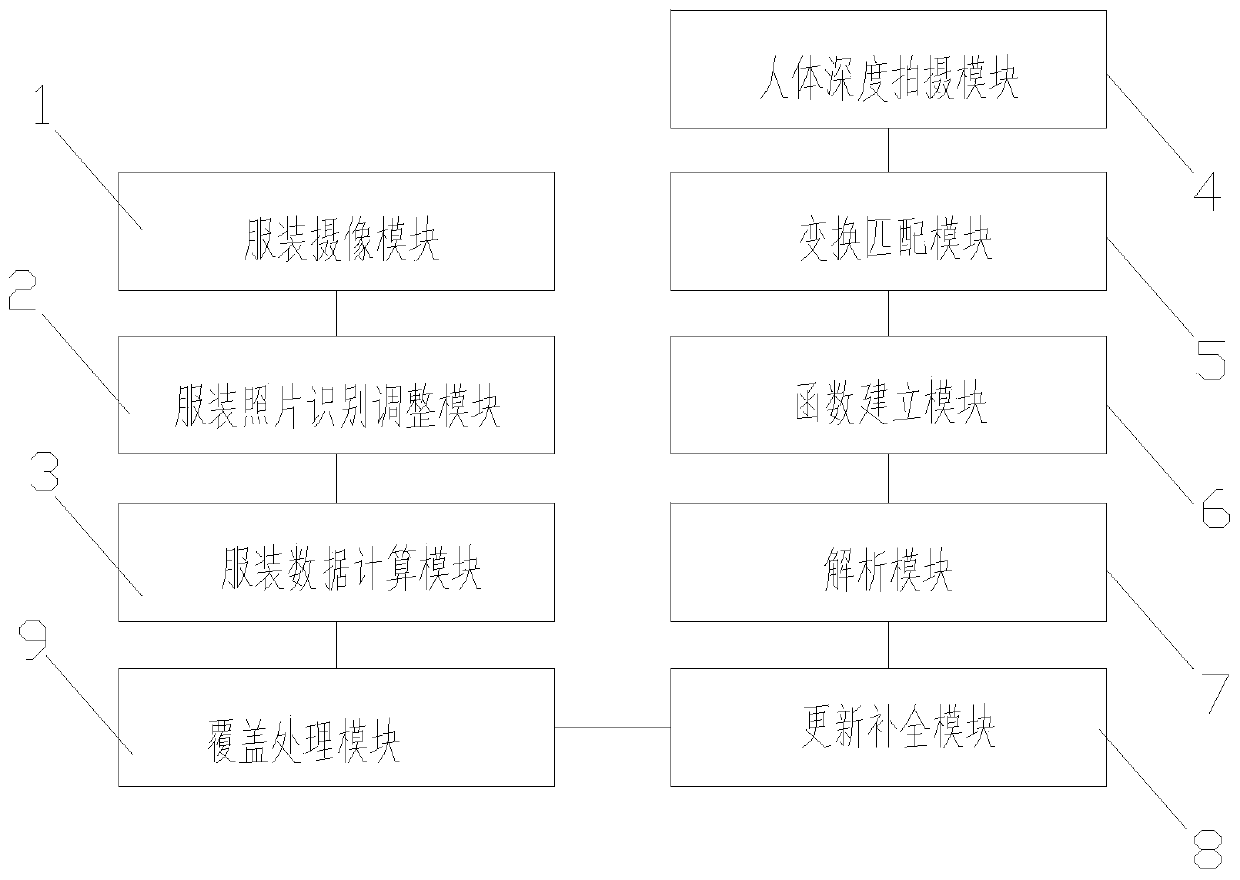
InactiveCN110175897ATo achieve the effect of trying onSynthesis speedBuying/selling/leasing transactions3D modellingEnergy functionalModel parameters
The invention discloses a 3D synthesis fitting method and system. The method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining two photos of a garment; 2) identifying a contour line and key nodes of the photos of the garment; 3) calculating the same fitting points of the two pictures for fitting, and generating a garment virtual three-dimensional model of the basic model; 4) carrying out depth image shooting on the human body to obtain a single depth image; 5) converting the single depth image into a three-dimensional point cloud, and obtaining matching point pairs between the three-dimensional point cloud and the vertex of the reconstruction model and between the three-dimensional point cloud and the vertex of the parameterized human body model; 6) establishing an energy function according to the matching point pair, and solving a non-rigid motion position transformation parameter and a parameterized human body posture model parameter of each vertex on the reconstruction model together, and7) solving the energy function, so that the 3D composite image generated based on the body data and the clothes data can be used for experiencing fitting conveniently and quickly.
Owner:YYC IND CO LTD CHINA
Cutter swept volume modeling method
ActiveCN104345687ASolve the blockageSmall amount of calculationNumerical controlNumerical controlSimulation
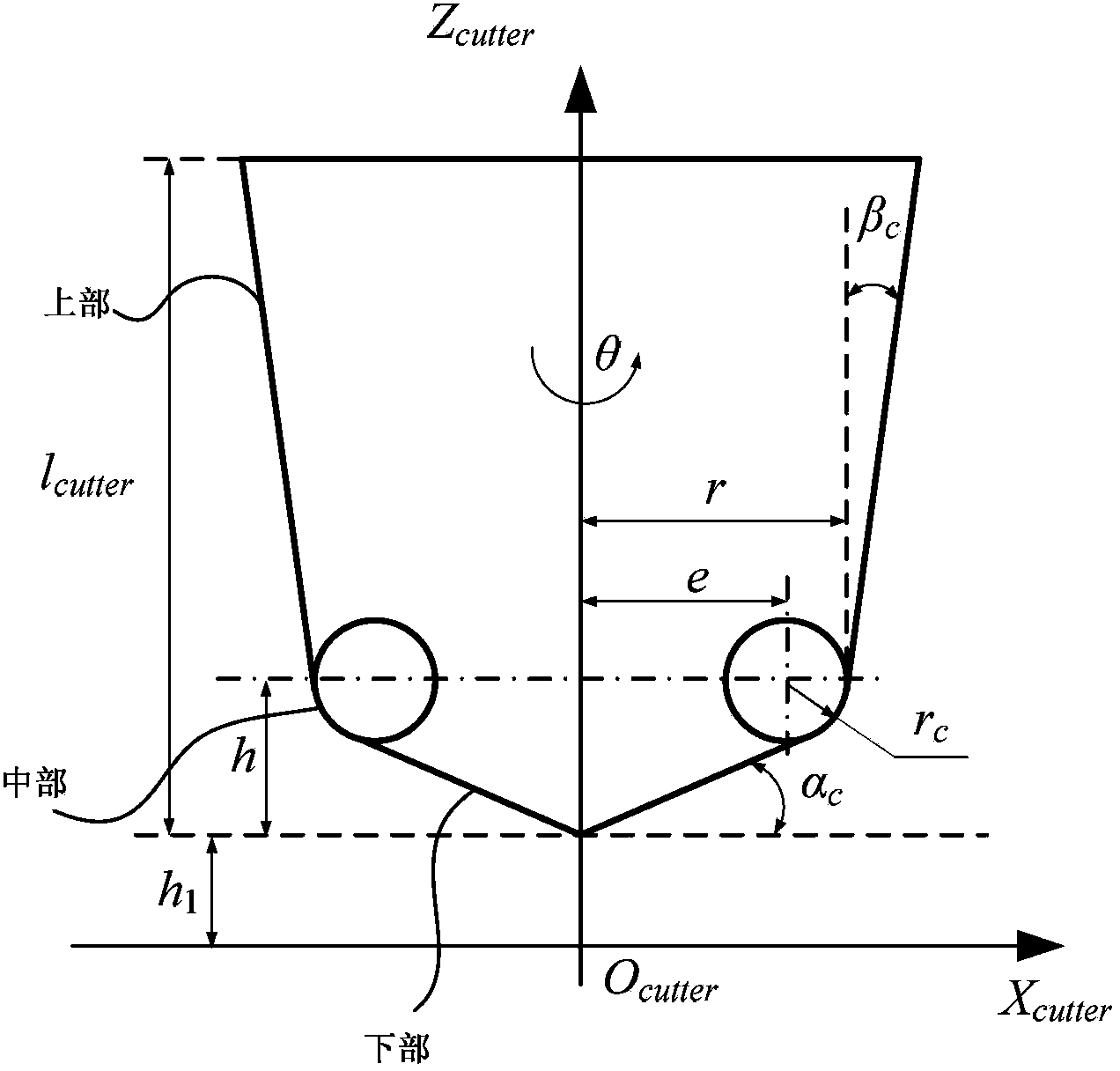
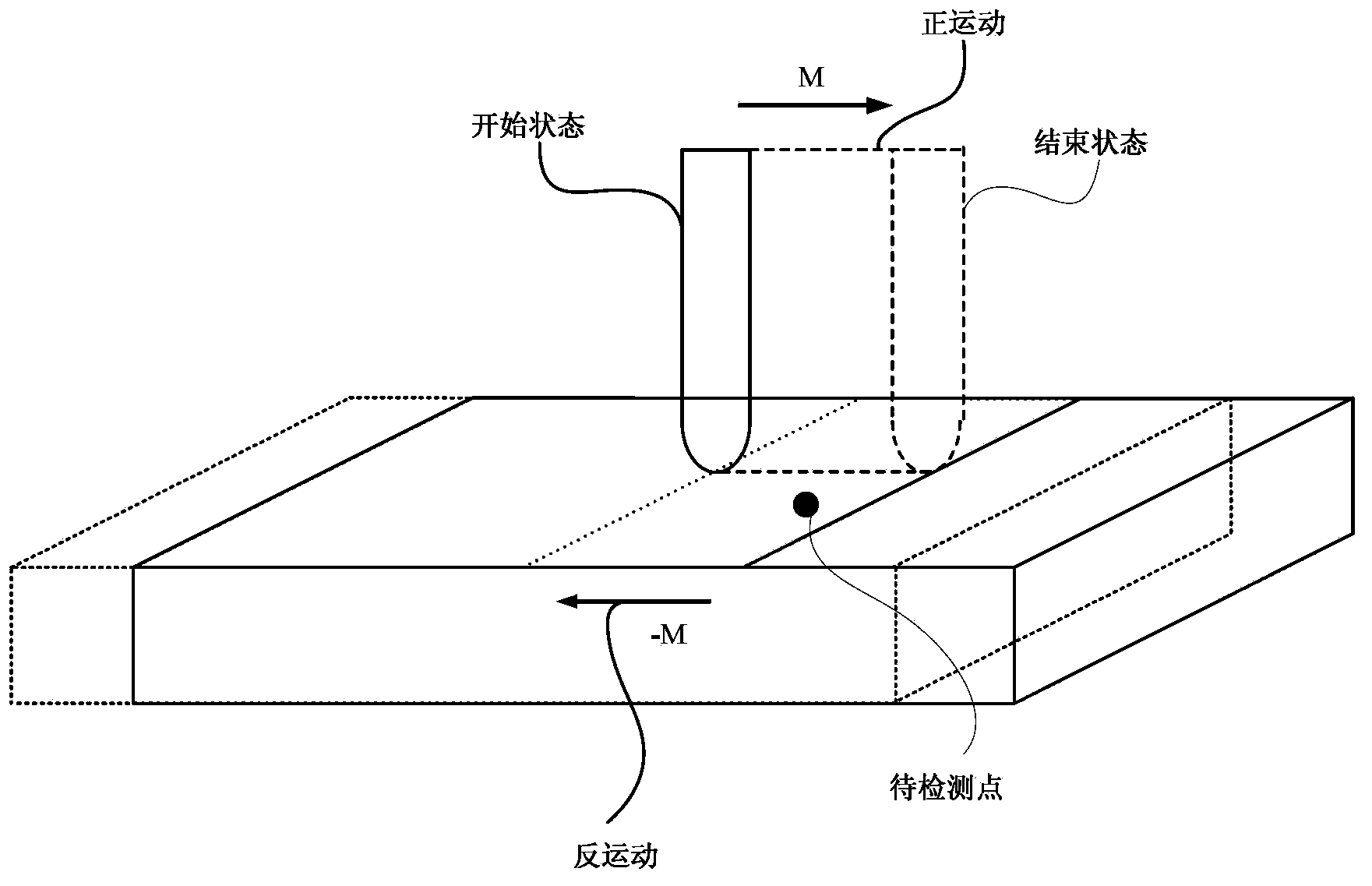
The invention relates to a cutter swept volume modeling method, in particular to a method for expressing a universal cutter model in a cutter frame system by implicit functions in the numerical control machining simulation application and expressing a universal cutter model swept volume by four-dimensional implicit functions comprising time parameters by a rigid motion frame theory and counter movement means. In the machining simulation, the position relationship between a point and the swept volume is rapidly judged so as to realize efficient material removing simulation and collision and interference detection.
Owner:中国科学院沈阳计算技术研究所有限公司
Computed tomography having motion compensation
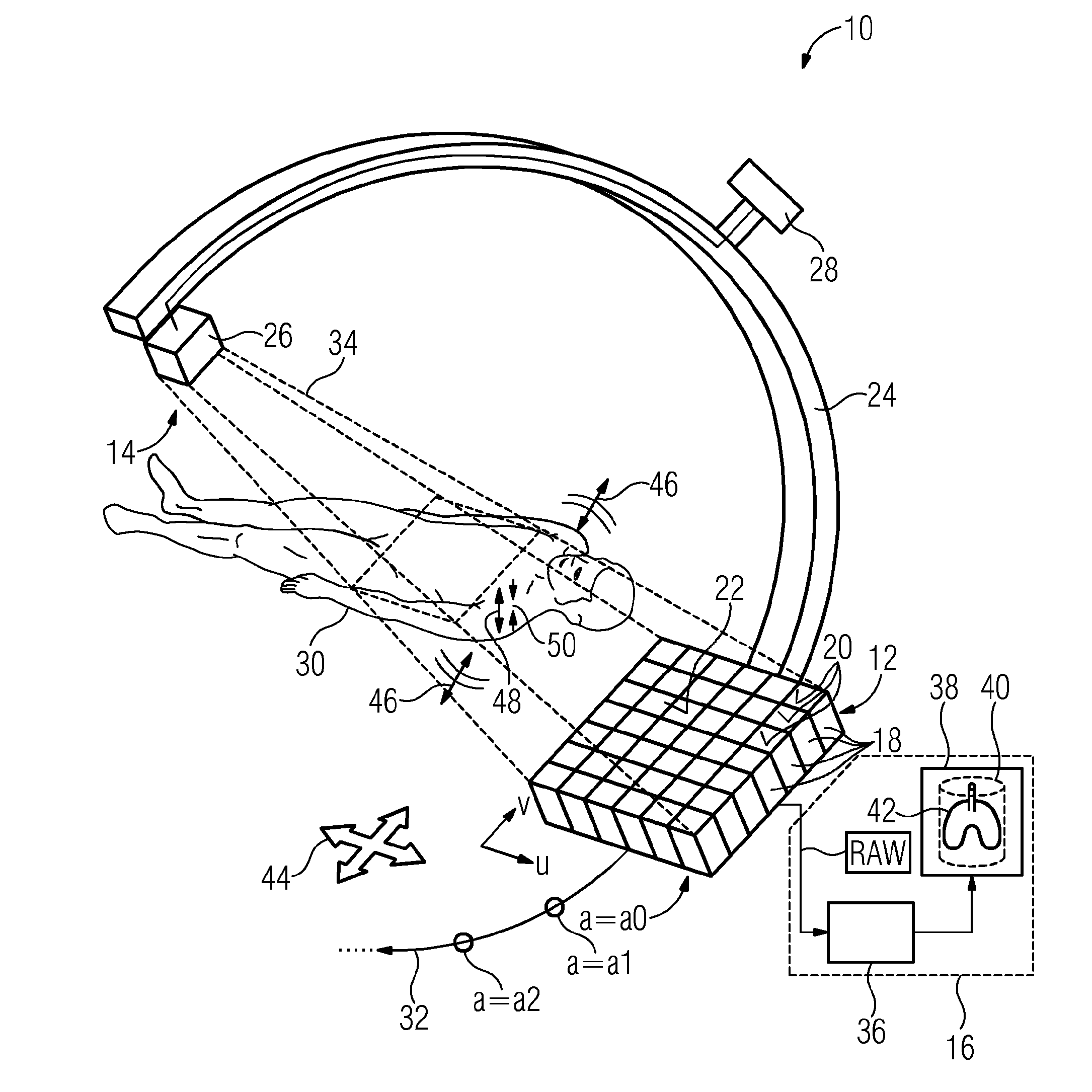
ActiveUS20160206272A1Improve imaging effectReduce image distortionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyRadiation sensor
The embodiments relate to a method for producing a digital volume model of a body volume by a sensor device, which sensor device includes a plurality of radiation sensors, of which each produces a pixel value in a projection. In order to produce the volume model, a plurality of projections from different projection angles (a) are produced and the volume model is computed from sensor positions of the radiation sensors and pixel values of the radiation sensors. For at least one projection angle (a), the sensor positions are corrected by a respective correction vector for rigid motion compensation. The problem addressed is that of also compensating the non-rigid motion of the body volume (i.e., the deformation) in the computation of the volume model. This problem is solved in that, in order to correct the sensor positions, the projection surface provided by the totality of the radiation sensors is divided into a plurality of sub-surfaces and a separate correction vector is determined for each of the sub-surfaces independently of each other.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
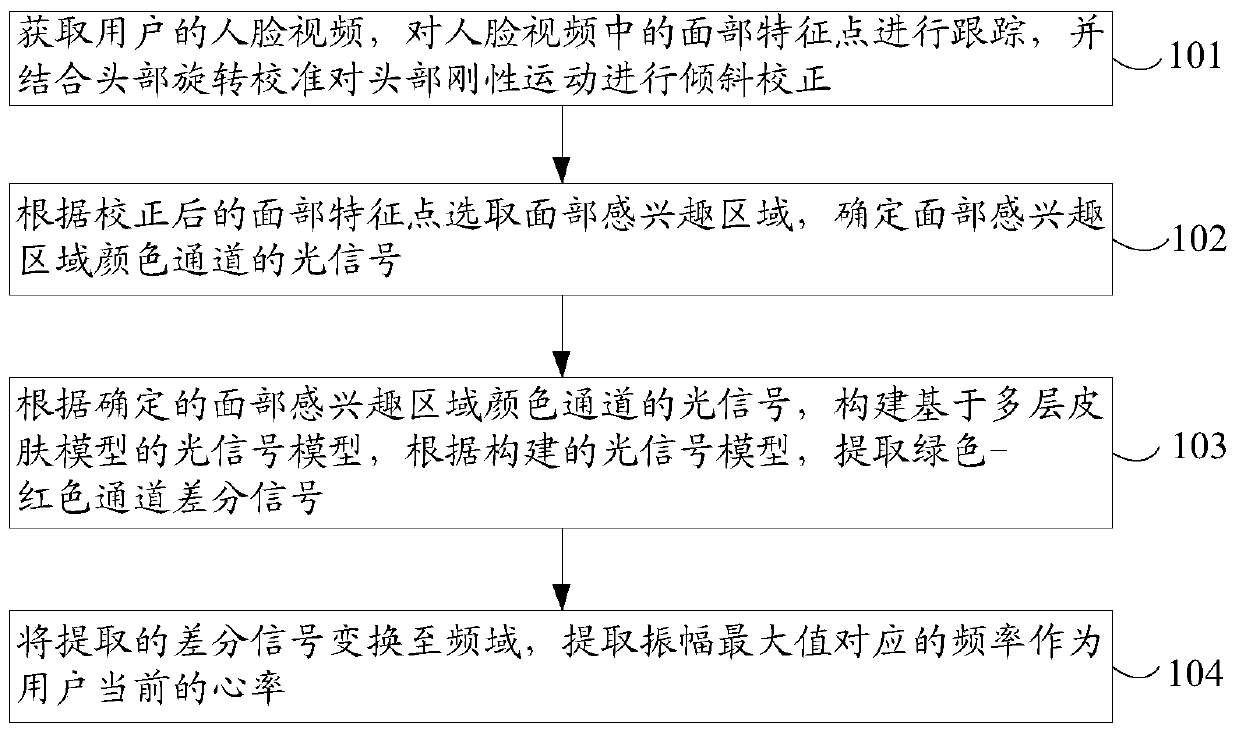
Heart rate detection method and device based on image analysis
ActiveCN109977858AReduce distractionsLow environmental requirementsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionHeart rate measurement
The invention provides a heart rate detection method and device based on image analysis, by which the accuracy of a heart rate measurement result is improved. The method comprises the following stepsof acquiring a face video of a user, tracking the facial feature points in the face video, and performing the tilt correction on head rigid motion by combining head rotation calibration; selecting a facial region of interest according to the corrected facial feature points, and determining an optical signal of a color channel of the facial region of interest; constructing an optical signal model based on a multilayer skin model according to the determined optical signal of the color channel of the region of interest of the face, and extracting a green-red channel differential signal accordingto the constructed optical signal model; and converting the extracted green-red channel differential signal into a frequency domain, and extracting the frequency corresponding to the maximum amplitudevalue as the current heart rate of the user. The invention relates to the field of biomedicine.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com