A Discrete Element Method for Deformable 3D Convex Polyhedron Block Based on Distance Potential Function
A discrete element method, discrete element technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, CAD numerical modeling, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the influence of element stiffness and normal contact force calculation, without considering the deformation of discrete elements, Not quite in line with engineering practice and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving accuracy and reliability, reducing quantity, and satisfying energy conservation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0038] A deformable three-dimensional convex polyhedral block discrete element method based on distance potential function, comprising the following steps:
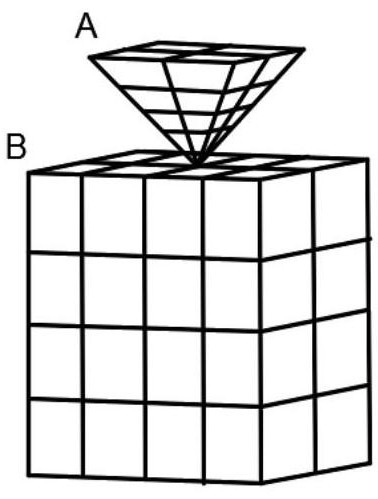
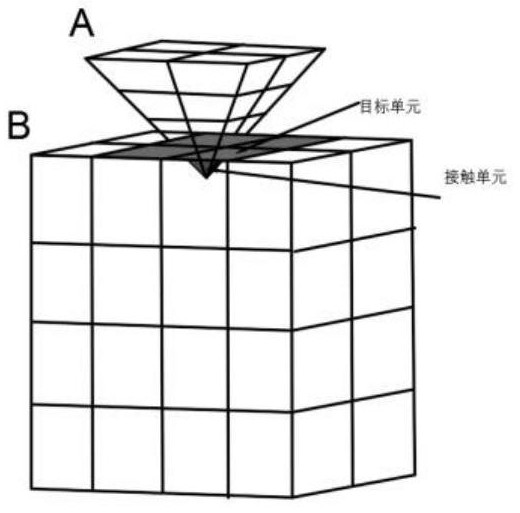
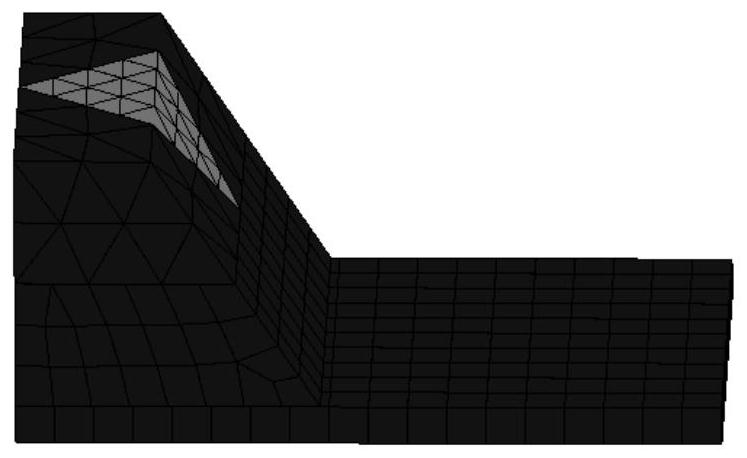
[0039] Step 1, select the research object, and establish a deformable discrete element system, the deformable discrete element system includes: a plurality of discrete elements, and a finite element formed by dividing the discrete elements into a grid; such as figure 1 As shown, each grid after the discrete unit meshes is defined as a grid unit, the node coordinates of the grid unit are consistent with the node coordinates of the finite element, and the parameters of the discrete unit include: the nodes of the discrete unit Coordinates, mass, damping ratio, stiffness, and the parameters of the finite element include: node coordinates, mass matrix, damping matrix, and stiffness matrix of the finite element.
[004...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com