Secondary k-anonymity privacy protection algorithm for differentiating quasi-identifier attributes
A quasi-identifier and privacy protection technology, applied in the fields of digital data protection, computing, computer security devices, etc., can solve the problems of information loss, loss, and poor availability of published data sheets, and achieve the effect of reducing information loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
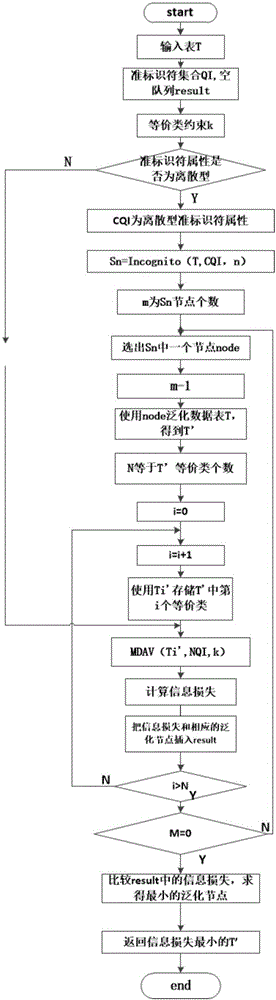
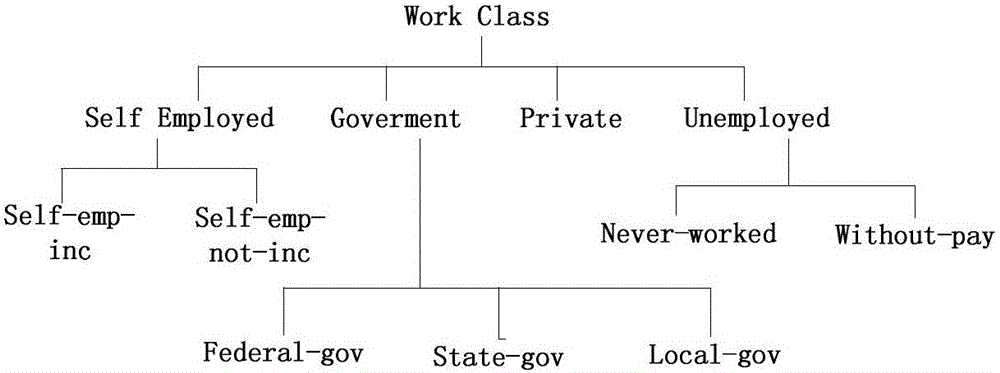
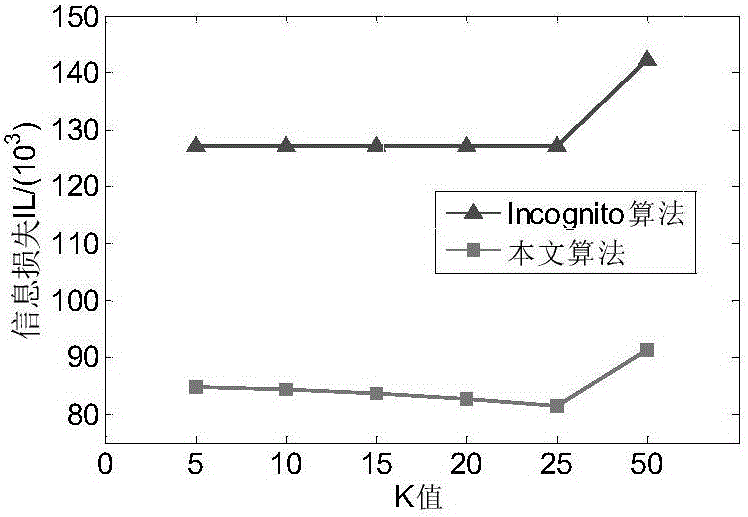
[0049] When realizing k-anonymity, take Table 1 as an example to define the NQLG algorithm. Suppose the data table held by the data publisher is T(A 1 ,A 2 ,...,A n ), each tuple in the table indicates the relevant information of a specific entity, such as Age, Workclass, Race, Sex, Hours-per-week, Salary, etc., see Table 1.
[0050] Table 1
[0051]
[0052] Definition 1 Quasi-identifier: Suppose a data set U, a specific data table T(A 1 ,A 2 ,...,A n ), fc:U→T and fg:T→U′, where A quasi-identifier QI of T T , is a set of attributes Then f(f c (p i )[Q T ]) = p i established. The attributes in Table 1 can all be used as quasi-identifiers, and the selection of quasi-identifiers is based on actual needs.
[0053] Definition 2 Generalization rule: Given an attribute Q, f: Q→Q', f is the set of generalization functions acting on the attribute Q, then represents the process of generalization of quasi-identifiers in sequence, and {f 1 , f 2 ,..., f m} repr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com