Devices and methods of source-encoding and decoding of data
A data and encoding technology, applied in the field of data source encoding and decoding equipment and methods, to achieve the effect of improving encoding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
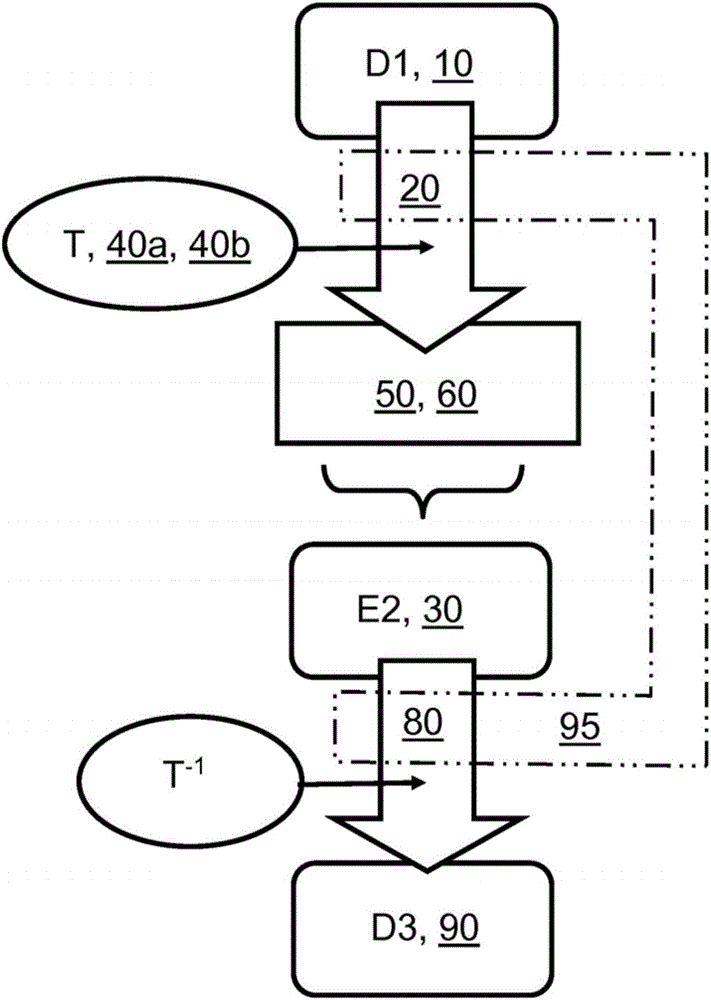
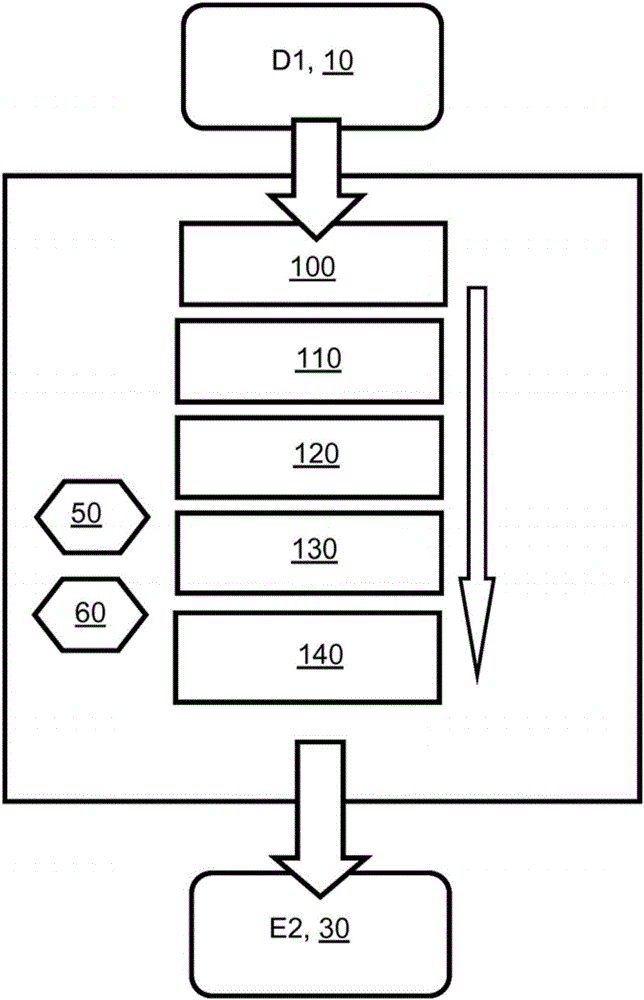
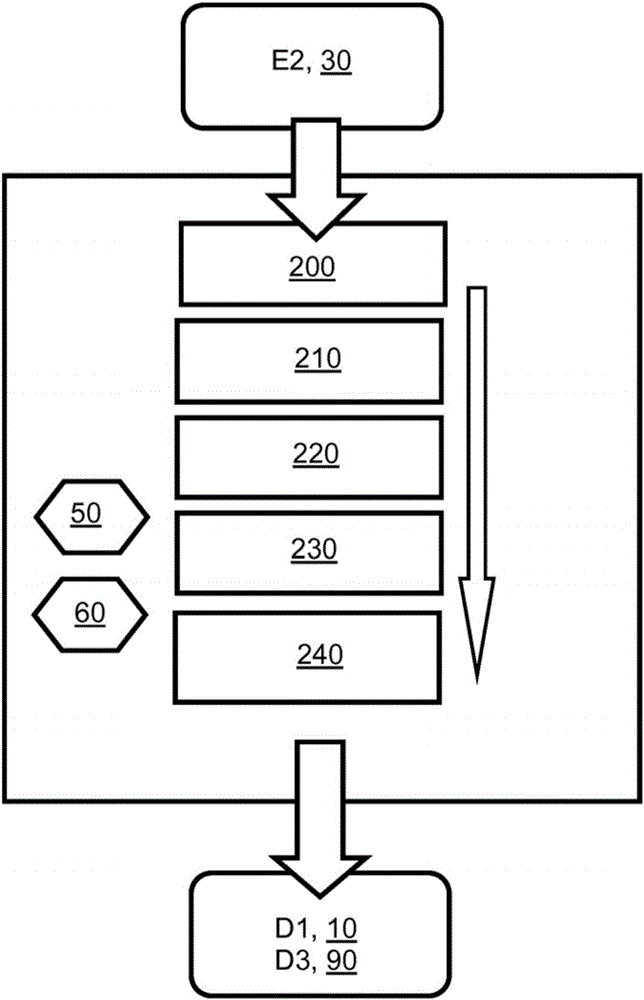
[0066] In general, when range coding is used to code data (D1), the probability of symbols in the data (D1) to be coded must be known, otherwise the achievable compression efficiency of this range coding is greatly affected accordingly. damage. The probability of each symbol defines an "interval" during encoding, where the greater the probability, the larger the interval. When encoding a symbol, the corresponding interval is updated according to the probability of the encoded symbol. If the range gets small enough, the range encoder transmits (for example) bytes and increases the range. Thus, for more common symbols, its interval slowly decreases, and more symbols can be encoded before the bytes are transmitted.
[0067] When performing interval coding in the encoder, the frequency table index, probability table index or interval table index or the frequency, probability or interval value of the symbol is transmitted in the encoded data (E2) generated by the encoder with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com