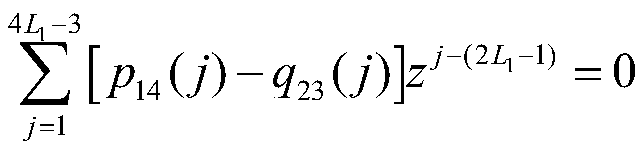Estimation Method of Direction of Arrival for Noncircular Signals Based on Polynomial Solution
A direction of arrival and non-circular signal technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve the problems of not being able to estimate enough signals, waste of reconnaissance and positioning resources, and no research on non-circular signals, so as to increase the number and improve the utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
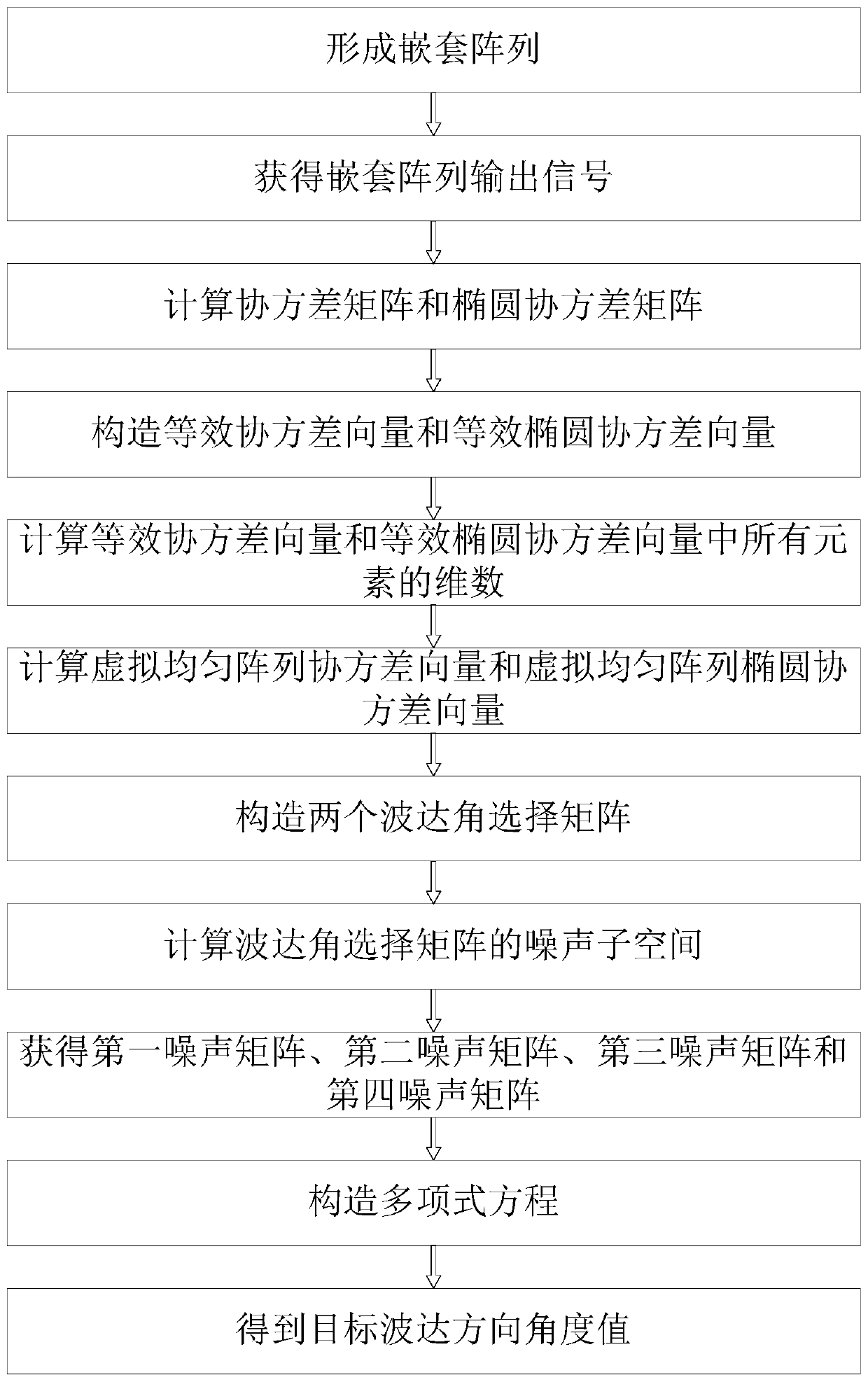
[0027] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of this example are as follows:
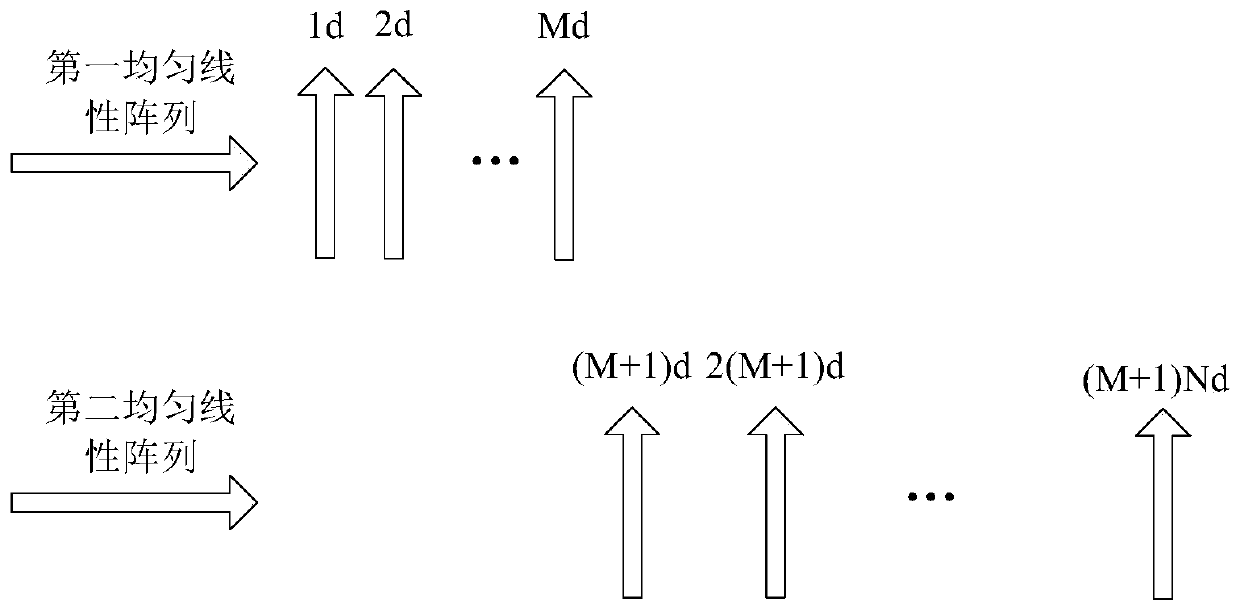
[0028] Step 1: Form a nested array with M+N antenna receivers.
[0029] (1a) Call each antenna receiver an array element, use M antenna receivers to form the first uniform linear array a, and its array element spacing is d, define the first array element of the first uniform linear array a as The initial array element defines the initial array element position D(1)=1, and the other array element positions of the first uniform linear array a are sequentially D(2)=2, D(3)=3, D(4)= 4,..., D(M)=M; wherein, the value range of M is M≥1, the value range of d is 0<d≤λ / 2, and λ is the narrowband signal wavelength incident to the array;
[0030](1b) Form a second uniform linear array b with N antenna receivers, the array element spacing is (M+1)d, and the array element positions of the second uniform linear array b are successively set to D(M+1)=M +1, D(M+2)=2(M+1), D(M+2)=3(M+1), ..., D(M+N)=N(M+1)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com