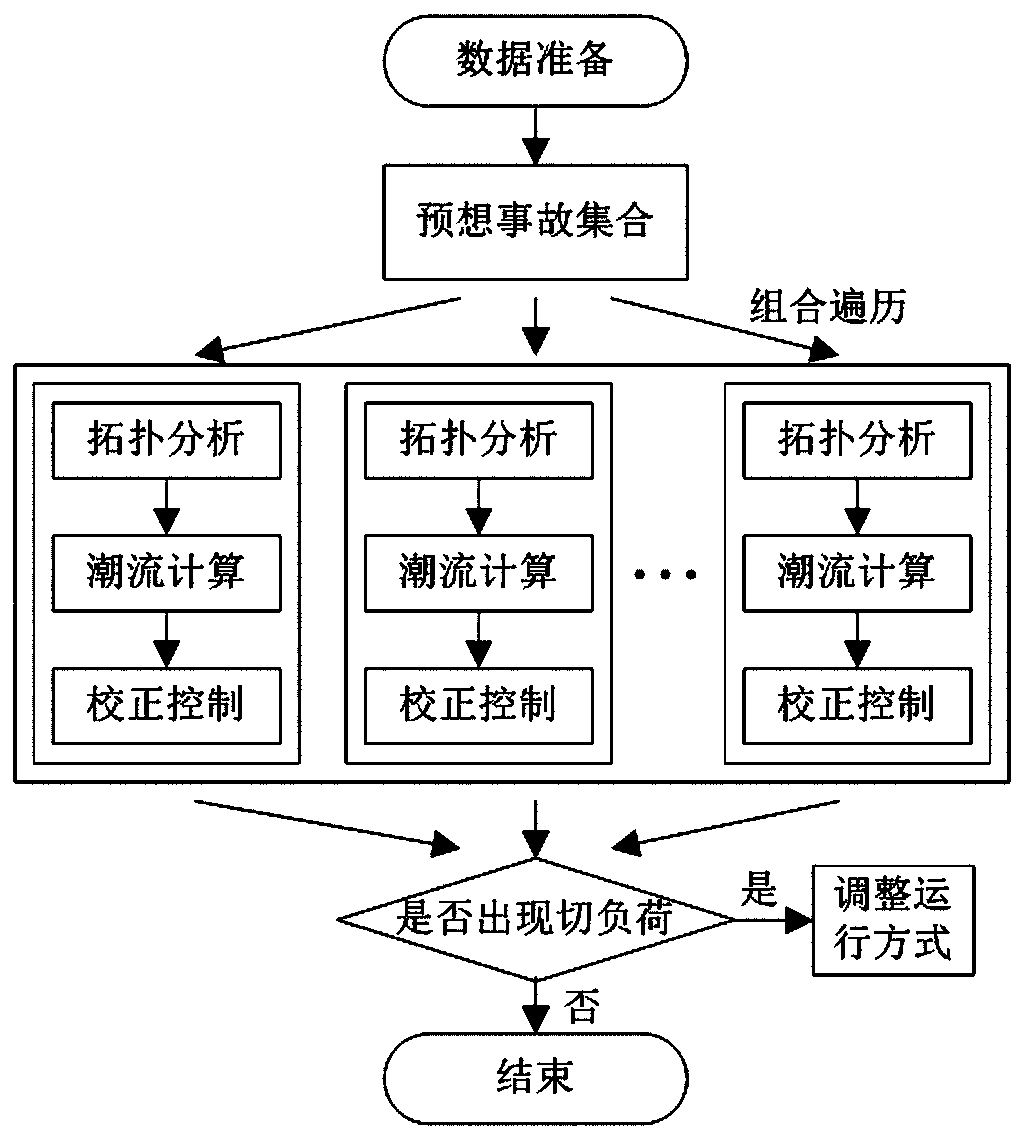
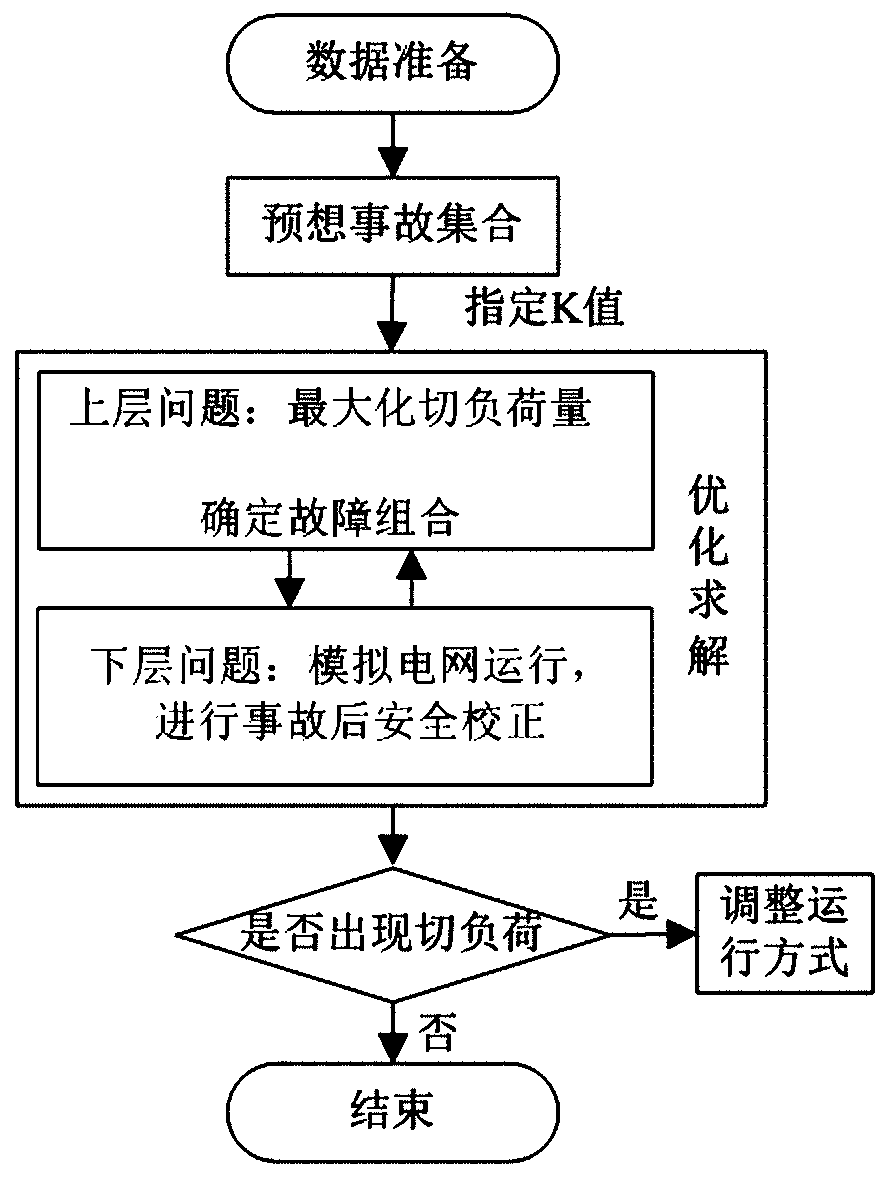
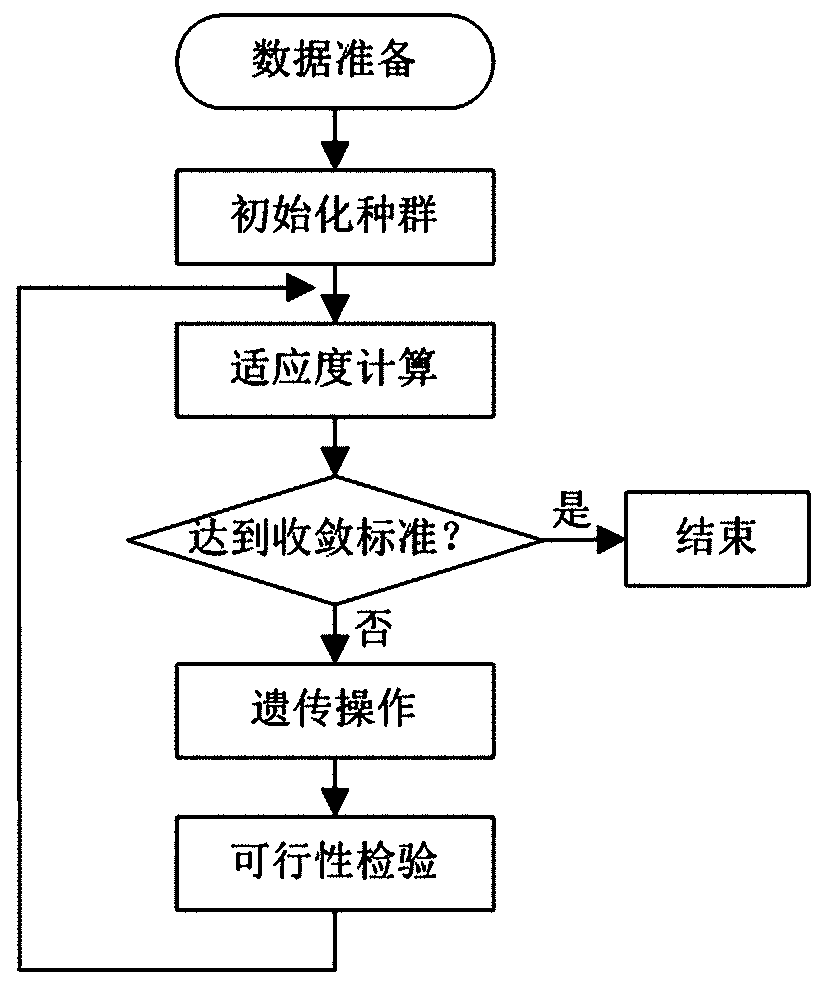
An n-k fault analysis method for power systems based on two-level programming
A fault analysis method and power system technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, circuit devices, AC network circuits, etc., can solve problems such as not getting rid of the framework of combination traversal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0100] Example 1: IEEE-14 node calculation system
[0101] Firstly, the IEEE-14 node system is taken as an example for description. See Table 1 for IEEE-14 node system network parameters, Table 2 for generator data, and Table 3 for load data. Set the population size to 100, the crossover probability to 1.0, and the mutation probability to 0.001.
[0102] Table 1: IEEE-14 node system network parameters
[0103]
[0104] Table 2: Generator Set Data
[0105]
[0106] Table 3: Load Data
[0107]
[0108] In order to illustrate the effectiveness of the method of the present invention, the calculation results of the present invention are compared with the calculation results of the traditional combined traversal method. When K takes different values, the calculation results are shown in the table below.
[0109] Table 4: Comparison of Results
[0110]
[0111] It can be seen that the calculation results of this method are consistent with the calculation results of ...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Example 2: 4.2 IEEE-118 node calculation system
[0113]In order to illustrate the advantages of this method in the security analysis of large-scale power grids, the IEEE-118 node calculation system is further illustrated as an example. The system contains 186 lines, 54 units, and 91 load nodes. If the pre-screening of the expected accident set is not included, when K=3, the number of faults traversed by the combination will exceed 1 million, and when K=4, the number of faults traversed by the combination will be close to 50 million. The traditional method is obviously difficult to apply directly, and it is necessary to take heuristic simplification measures such as reducing the expected accident set and fault ranking. The method in this paper can effectively reduce the calculation time through intelligent search.
[0114] Taking K=3 as an example, the computer configuration is an AMD A8-6410 processor, the main frequency is 2.0GHz, and the memory is 4G. The tradition...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com