System and method for determining a sufficient cause from multiple outcomes
A cause-observation technique applied in the field of systems to determine sufficient causes under circumstances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
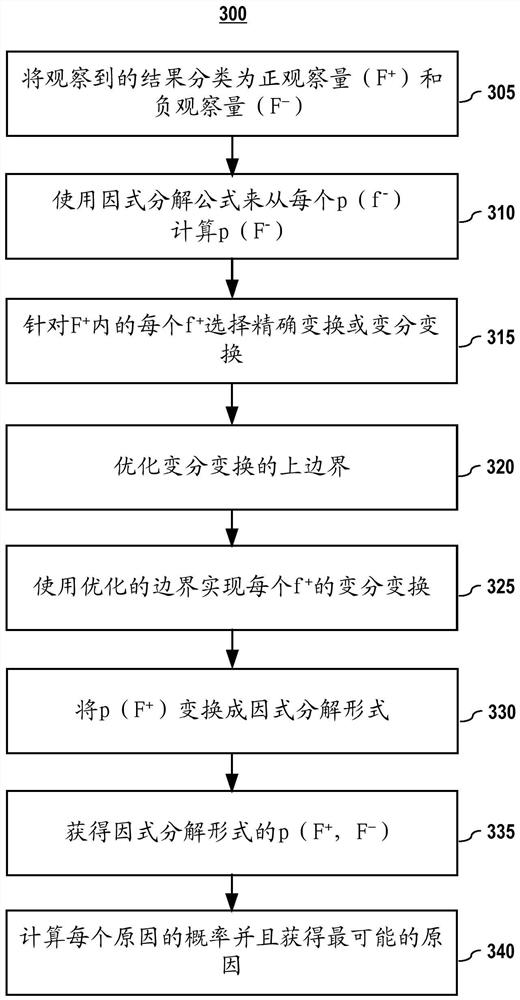
[0031] Example 1 - Variational Inference and then Exact Inference: In an embodiment, a variational inference process can be used to compute the posterior, which is used in the exact inference process. As an example, consider the following:
[0032]
[0033] where a variational inference method is used to find the first positive result set that has been identified via the above-assigned index In case of inferred disease d i (d i represents the probability of the i-th disease).
[0034] In an embodiment, the posterior of the variational inference process may be used as input for exact inference. As an example, consider the following:
[0035]
[0036] where the exact inference method is used for a given second positive result set that has been identified via the assigned index as described above Posterior and Negative Observation Sets F from Variational Inference - Inferred disease in case of d i The probability.
[0037] It should be noted that in an embodiment,...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 - Exact Inference and Then Variational Inference: In an embodiment, the exact inference process can be used to compute the posterior, which is used in the variational inference process. As an example, consider the following:
[0039]
[0040] where the exact inference method is used to find the second set of positive results and the set of negative results F – Inferred disease in case of d i The probability.
[0041] In an embodiment, the exact inferred posterior may be used as input for variational inference. As an example, consider the following:
[0042]
[0043] where a variational inference method is used to generate the first set of positive results that have been identified via the indices assigned as described above and infer the disease d in the case of the posterior from the exact inference i The probability.
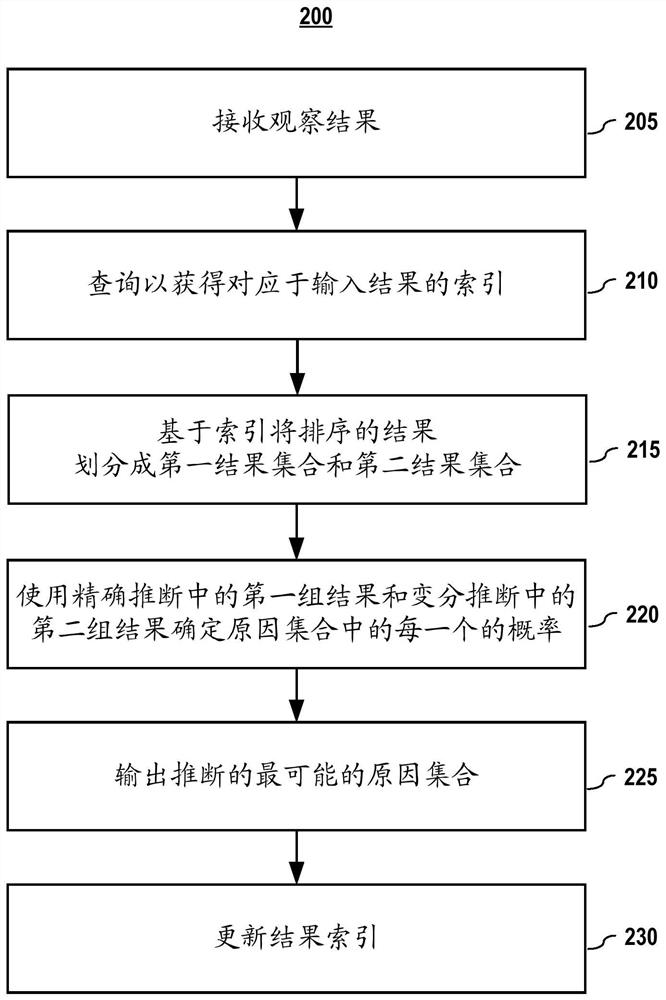
[0044] In an embodiment, in step 225, the results of the inference process are used to output the most likely cause. In the e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com