File metadata incremental scanning method and system for electron microscope data storage system
A data storage system and file metadata technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as missed remedial time, unacceptable scanning time for system administrators, and a rather long time-consuming problem, so as to improve computing efficiency and reduce metadata acquisition operations , the effect of saving the required time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
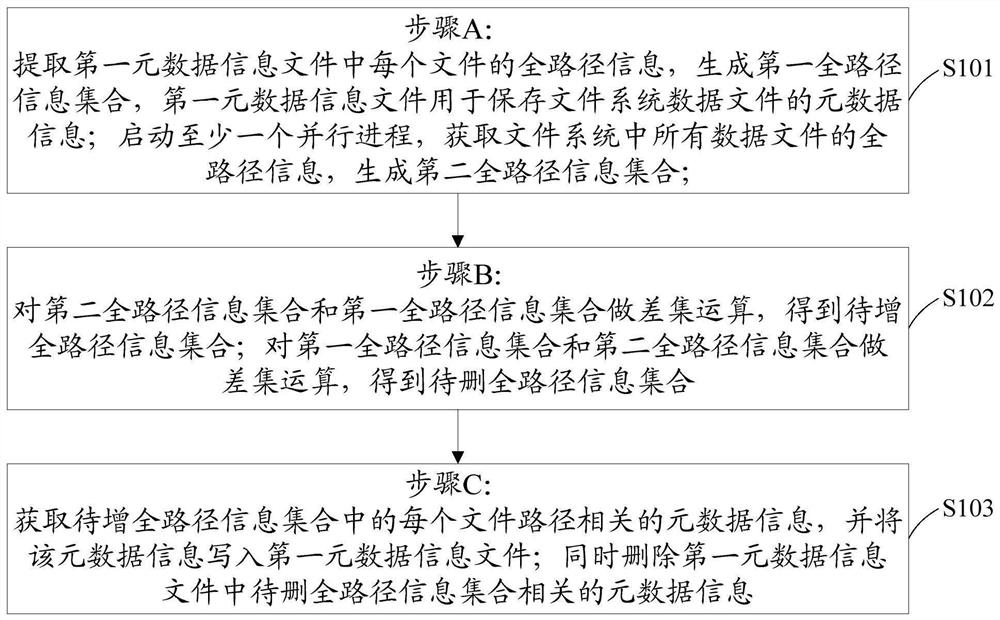
[0025] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0026] It should be noted that the terms "first" and "second" in the description and claims of the present invention and the above drawings are used to distinguish similar objects, but not necessarily used to describe a specific sequence or sequence. It is to be understood that the data so used are interchangeable under appropriate circumstances such that the embodiments of the invention described herein can be practiced in sequences other than those illustrated or described herein.
[0027] The file system is system software, and the hardware devices of the storage system are managed through the file system. It should be pointed out that the file systems in this application include parallel file systems and non-parallel file systems.
[0028] Su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com