Desalting well for cultural relics
A technology for salt wells and cultural relics, applied in the selection of auxiliary conditions for crystallization, separation methods, and cleaning methods using liquids, etc., and can solve problems such as cultural relic damage and cultural relic damage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and the following embodiments. It should be understood that the following embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
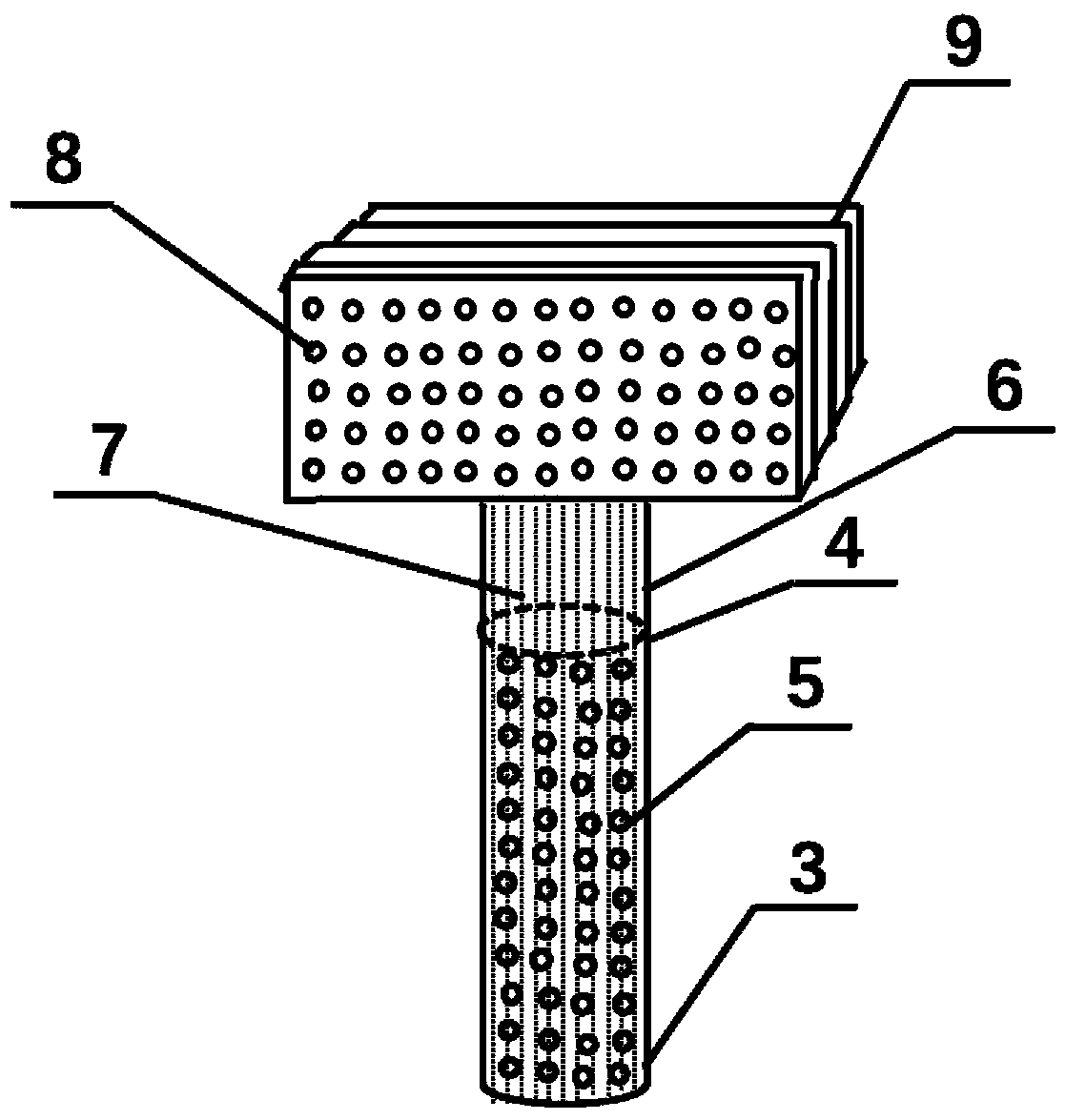
[0028] Aiming at the various deficiencies in the process of desalting cultural relics, especially large and immovable cultural relics in the prior art, the present invention provides a cultural relic that reduces the source of soluble salt solution of cultural relics, mainly the content of soluble salt in the water quality of buried ruins The desalination well mainly includes an internal unit and an external unit; the internal unit includes a casing and a salt solution migration channel located in the casing; the external unit includes a crystallization box connected to the salt solution migration channel; the salt solution Both the solution migration channel and the interior of the crystallization bo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com