Inter-cluster multi-hop routing algorithm of energy consumption balance in wireless sensor networks
A wireless sensor and multi-hop routing technology, applied in wireless communication, network topology, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as prolonging the network life cycle, and achieve the effect of prolonging the network life cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
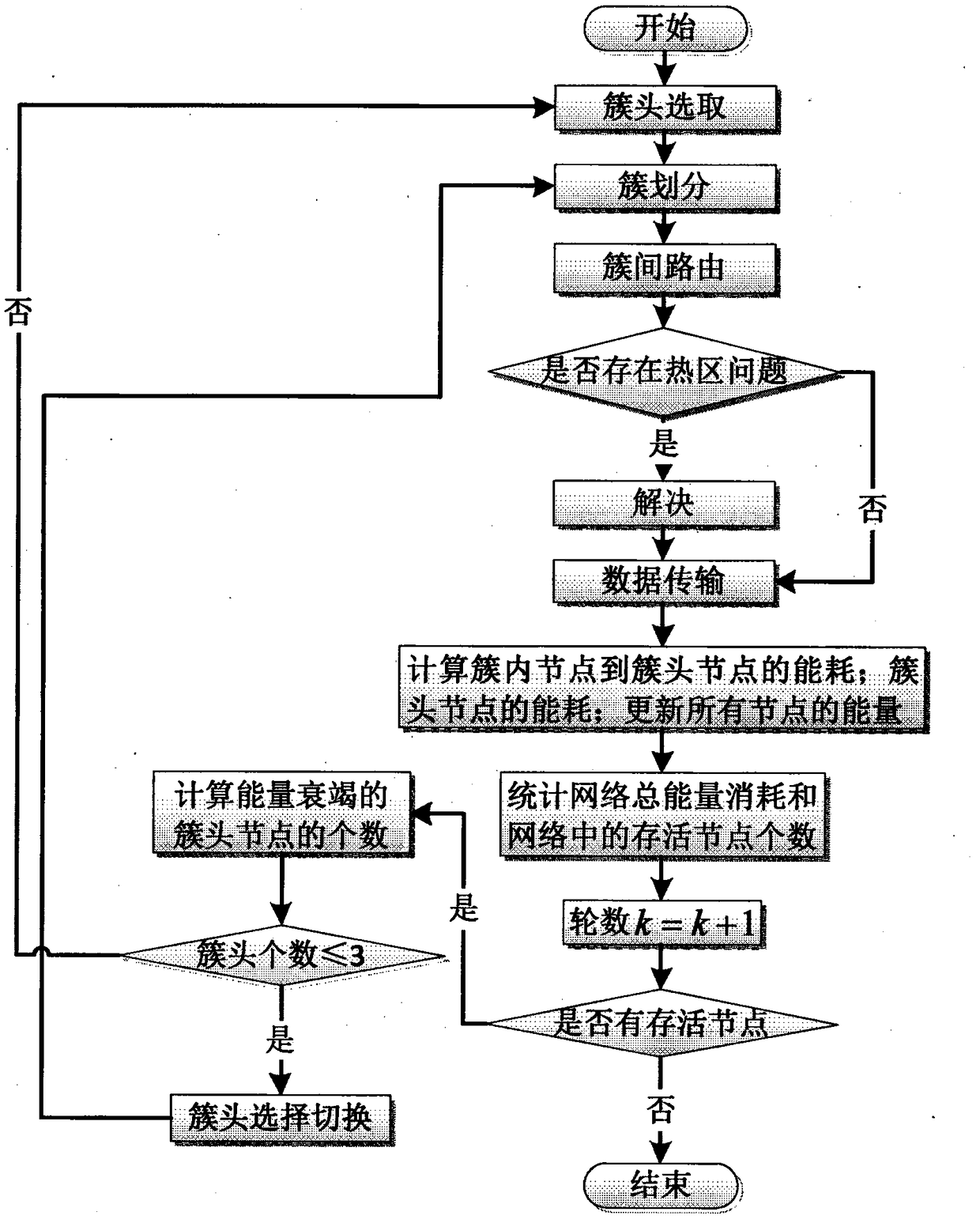
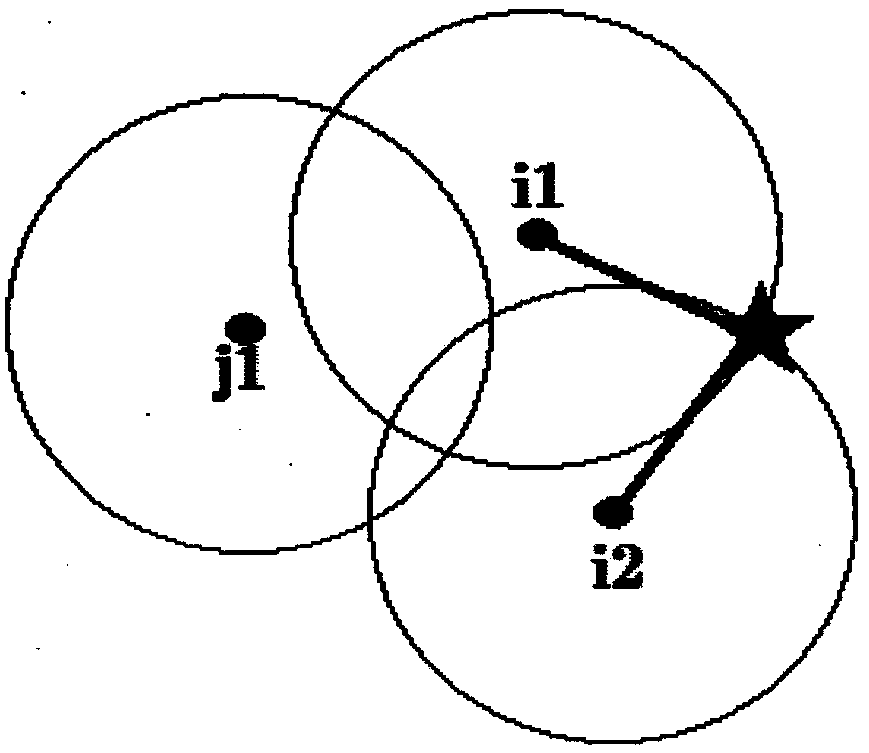
[0038] 1: The cluster head selection method is: when the network is initialized, the aggregation node collects and saves the ID information, location information, and remaining energy information of the nodes in the entire network, and then only updates the remaining energy of the nodes. The converging node sorts all nodes and energy, takes the top 5% points as the cluster head, and takes the radius r ch Search for nearby nodes to form a cluster. If the entire area cannot achieve full coverage, for the remaining unclustered nodes, take the node with the energy of the top 5% as the cluster head, and use the radius r ch Search for nearby nodes to form a cluster. This cycle is repeated until the entire area is fully covered by communication. After the node sleeps for a fixed time, it receives the network clustering table broadcast by the sink node.
[0039] Because the search radius r ch It is related to the remaining energy of the node and the distance from the sink k node. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com