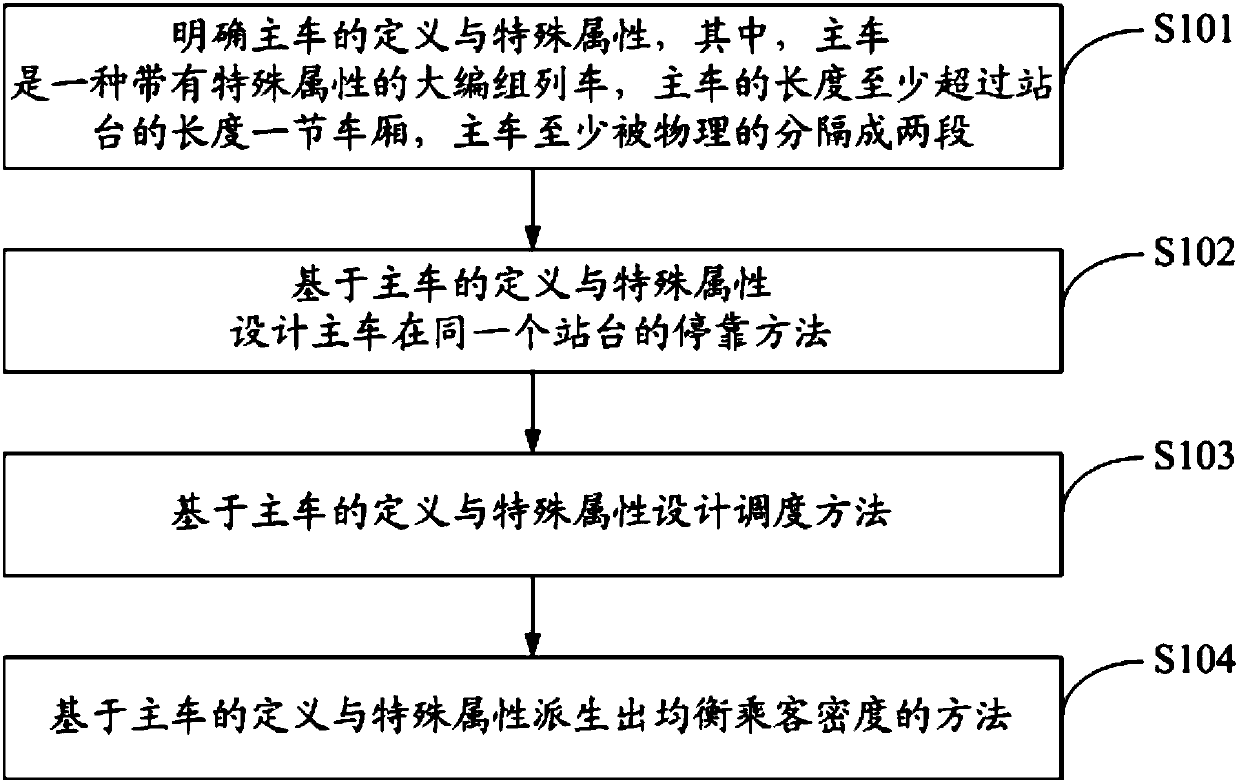
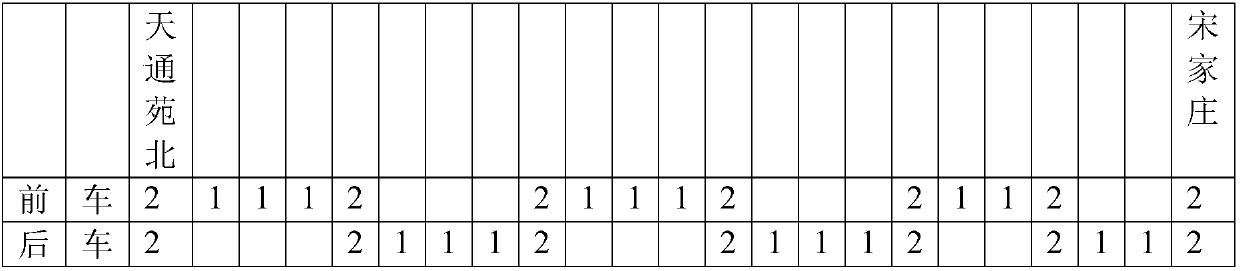
Scheduling method for multiplying transport capacity of rail transit trains based on concepts of main and auxiliary trains
A technology for rail transit trains and scheduling methods, which can be applied to tracks, railway traffic management, stations, etc., and can solve problems such as poor passenger experience and hidden safety hazards in rail transit.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0167] Example 1 is an example of the application of the two-stage method in the tidal method.
[0168] Beijing Metro Line 6, during the morning rush hour, the passenger flow from Tongzhou to the city is very large, while the passenger flow from the city direction is small. This situation is well suited for the application of the tidal method.
[0169] In the direction from east to west, large marshalling trains with twice the platform length can be used. From west to east, only ordinary marshalling trains are used. In order to prevent the excessive backlog of trains in the west, ordinary trains can be towed with empty cars on the return journey. Empty vehicles that are being towed cannot be loaded.
[0170] The characteristic of the morning rush hour of Line 6 is that, with Shilipu Station as the boundary, the east and west sections are roughly equal in length.
[0171] In the east of Shilibao, there are almost only superiors and no inferiors. To the west of Ten Mile For...
example 2
[0183] Example 2: An example of the application of the three-segment method in the tidal method
[0184] According to the plan, Line 6 will extend westward to Pingguoyuan Station in the future. With such a long subway line, the scheduling should be more precise.
[0185] 1. Divide Line 6 into east, middle and west sections according to needs.
[0186] 2. Alternately send the marshalling trains of the two stopping methods.
[0187] 3. The marshalling train of the first parking method is divided into the first half section and the second half section. The first half is called 6sss and the second half is called 6ddd.
[0188] Regardless of that section, 6sss only stops at odd stations. 6ddd only stops at even-numbered stations.
[0189] 4. The marshalling train of the second parking method is also divided into the first half section and the second half section. The first half is called 6sds, and the second half is called 6dsd.
[0190] In the eastern section, 6sds only stop...
example 3
[0197] Example 3: An example of the application of the three-segment method in the tidal method
[0198] 1. Divide Line 6 into east, middle and west sections according to needs.
[0199] 2. Alternately send the marshalling trains of the two stopping methods.
[0200] 3. The marshalling train of the first parking method is divided into the first half section and the second half section. The first half is called 6ssd, and the second half is called 6dds.
[0201] In the eastern section, 6ssd only stops at odd stations. In the middle section, 6ssd only stops at odd stations. In the west section, 6ssd only stops at even-numbered stations.
[0202] In the eastern section, 6dds only stops at even-numbered stations. In the middle section, 6dds only stops at even-numbered stations. In the western section, 6dds only stops at odd-numbered stations.
[0203] 4. The marshalling train of the second parking method is also divided into the first half section and the second half section...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com